|
List Of Numerical-analysis Software
Listed here are notable end-user computer applications intended for use with numerical or data analysis: Numerical-software packages General-purpose computer algebra systems Interface-oriented Language-oriented Historically significant * Expensive Desk Calculator written for the TX-0 and PDP-1 in the late 1950s or early 1960s. * S is an (array-based) programming language with strong numerical support. R is an implementation of the S language. See also References {{DEFAULTSORT:Numerical Analysis Software Lists of software Mathematics-related lists *Software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods that attempt at finding approximate solutions of problems rather than the exact ones. Numerical analysis finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, and in the 21st century also the life and social sciences, medicine, business and even the arts. Current growth in computing power has enabled the use of more complex numerical analysis, providing detailed and realistic mathematical models in science and engineering. Examples of numerical analysis include: ordinary differential equations as found in celestial mechanics (predicting the motions of planets, stars and galaxies), numerical linear algebra in data analysis, and stochastic differential equations and Markov chains for simulating living cells in medicine a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weka (machine Learning)
Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis (Weka), developed at the University of Waikato, New Zealand, is free software licensed under the GNU General Public License, and the companion software to the book "Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques". Description Weka contains a collection of visualization tools and algorithms for data analysis and predictive modeling, together with graphical user interfaces for easy access to these functions. The original non-Java version of Weka was a Tcl/ Tk front-end to (mostly third-party) modeling algorithms implemented in other programming languages, plus data preprocessing utilities in C, and a makefile-based system for running machine learning experiments. This original version was primarily designed as a tool for analyzing data from agricultural domains, but the more recent fully Java-based version (Weka 3), for which development started in 1997, is now used in many different application areas, in particular for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAG Numerical Libraries
The NAG Numerical Library is a software product developed and sold by The Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd. It is a software library of numerical analysis routines, containing more than 1,900 mathematical and statistical algorithms. Areas covered by the library include linear algebra, optimization, quadrature, the solution of ordinary and partial differential equations, regression analysis, and time series analysis. Users of the NAG Library call its routines from within their applications in order to incorporate its mathematical or statistical functionality and to solve numerical problems - for example, finding the minimum or maximum of a function, fitting a curve or surface to data, or solving a differential equation. The Library is available in the many forms, but namely the NAG C Library, the NAG Fortran Library, and the NAG Library for .NET. Its contents are accessible from several computing environments, including standard languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Visual B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Sharp (programming Language)
C# (pronounced ) is a general-purpose, high-level multi-paradigm programming language. C# encompasses static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines. The C# programming language was designed by Anders Hejlsberg from Microsoft in 2000 and was later approved as an international standard by Ecma (ECMA-334) in 2002 and ISO/IEC (ISO/IEC 23270) in 2003. Microsoft introduced C# along with .NET Framework and Visual Studio, both of which were closed-source. At the time, Microsoft had no open-source products. Four years later, in 2004, a free and open-source project called Mono began, providing a cross-platform compiler and runtime environment for the C# programming language. A decade later, Microsoft released Visual Studio Code (code editor), Roslyn (compiler), and the unified .NET platform (software framework), all of which support C# and are free, op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (computing)
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often for software development. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subroutines, classes, values or type specifications. In IBM's OS/360 and its successors they are referred to as partitioned data sets. A library is also a collection of implementations of behavior, written in terms of a language, that has a well-defined interface by which the behavior is invoked. For instance, people who want to write a higher-level program can use a library to make system calls instead of implementing those system calls over and over again. In addition, the behavior is provided for reuse by multiple independent programs. A program invokes the library-provided behavior via a mechanism of the language. For example, in a simple imperative language such as C, the behavior in a library is invoked by using C's normal func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software or libre software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (gnu.org) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that source code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCSim
GNU MCSim is a suite of simulation software. It allows one to design one's own statistical or simulation models, perform Monte Carlo simulations, and Bayesian inference through (tempered) Markov chain Monte Carlo simulations. The latest version allows parallel computing of Monte Carlo or MCMC simulations. Description GNU MCSim is a simulation and statistical inference tool for algebraic or differential equation systems, optimized for performing Monte Carlo analysis. The software comprises a model generator and a simulation engine: * The model generator facilitates structural model definition and maintenance, while keeping execution time short. The model is coded using a simple grammar, and the generator translates it into C code. Starting with version 5.3.0, models coded in SBML can also be used. * The simulation engine is a set of routines that are linked to the model in order to produce executable code. The result is that one can run simulations of the structural model under a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science & Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ..., it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAPACK
LAPACK ("Linear Algebra Package") is a standard software library for numerical linear algebra. It provides routines for solving systems of linear equations and linear least squares, eigenvalue problems, and singular value decomposition. It also includes routines to implement the associated matrix factorizations such as LU, QR, Cholesky and Schur decomposition. LAPACK was originally written in FORTRAN 77, but moved to Fortran 90 in version 3.2 (2008). The routines handle both real and complex matrices in both single and double precision. LAPACK relies on an underlying BLAS implementation to provide efficient and portable computational building blocks for its routines. LAPACK was designed as the successor to the linear equations and linear least-squares routines of LINPACK and the eigenvalue routines of EISPACK. LINPACK, written in the 1970s and 1980s, was designed to run on the then-modern vector computers with shared memory. LAPACK, in contrast, was designed to eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages. Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numeric computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine allowing access to symbolic computing abilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and model-based design for dynamic and embedded systems. As of 2020, MATLAB has more than 4 million users worldwide. They come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics. History Origins MATLAB was invented by mathematician and computer programmer Cleve Moler. The idea for MATLAB was based on his 1960s PhD thesis. Moler became a math professor at the University of New Mexico a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
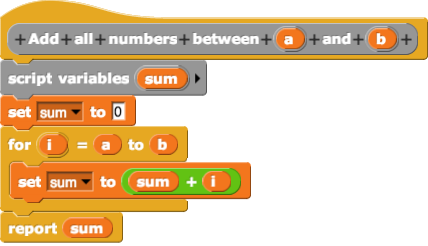
Graphical Programming
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS) is any programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements ''graphically'' rather than by specifying them ''textually''. A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs (known as ''dataflow'' or ''diagrammatic programming'') are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by users in an interactive way according to some specific spatial grammar for pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |