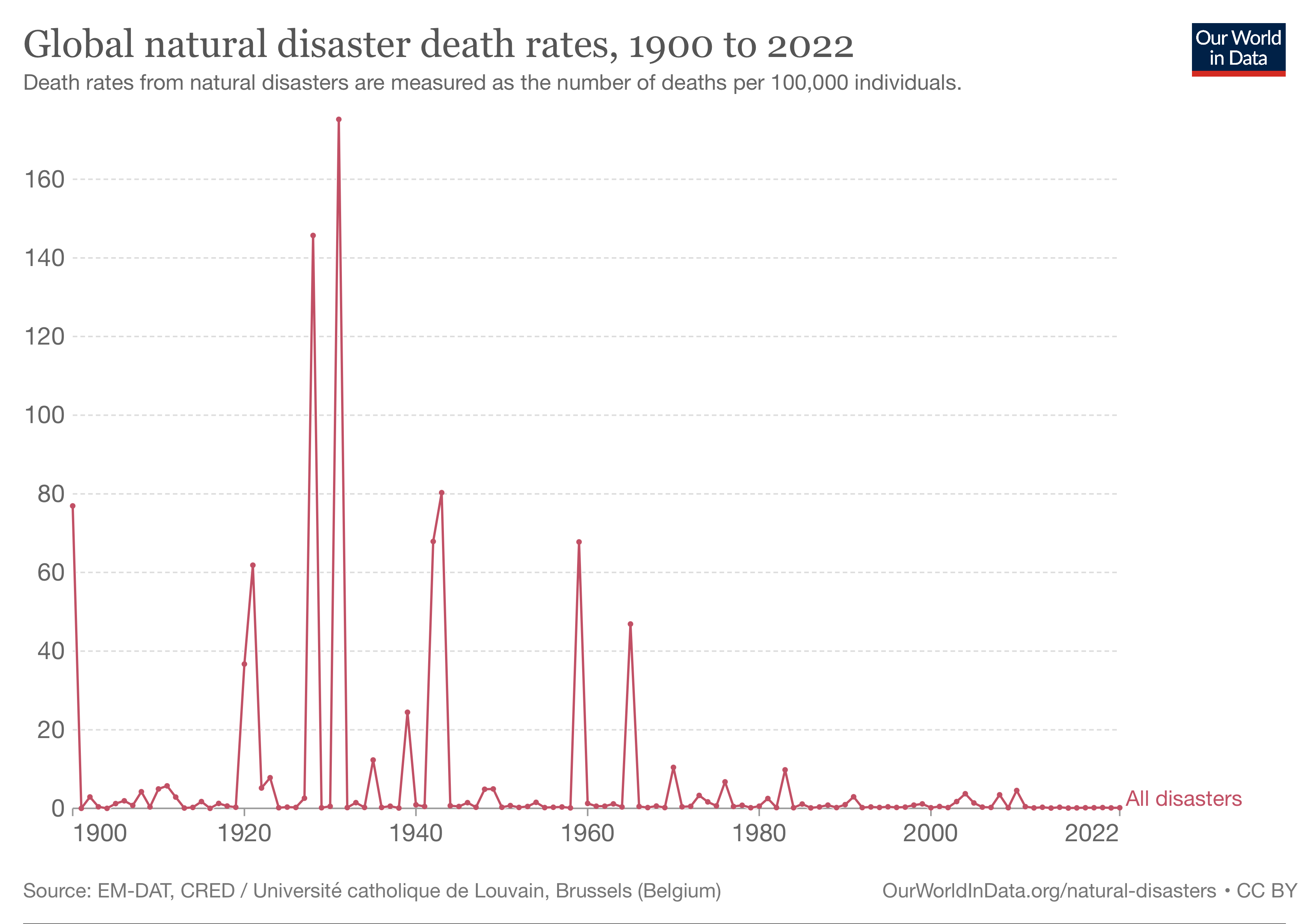
|
List Of Natural Disasters In The United Kingdom ...
This is a list of natural disasters in the British Isles. See also *List of disasters in Great Britain and Ireland by death toll *Climate of the United Kingdom *Geology of Great Britain *Geology of Ireland * Tsunamis affecting the British Isles *Drought in the United Kingdom *Floods in the United Kingdom References {{DEFAULTSORT:List of Natural Disasters in the British Isles List Natural disasters Natural disasters Natural Disasters Nat Nat or NAT may refer to: Computing * Network address translation (NAT), in computer networking Organizations * National Actors Theatre, New York City, U.S. * National AIDS trust, a British charity * National Archives of Thailand * National As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disaster
A natural disaster is "the negative impact following an actual occurrence of natural hazard in the event that it significantly harms a community". A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves some economic damage in its wake. The severity of the damage depends on the affected population's resilience and on the infrastructure available. Examples of natural hazards include: avalanche, coastal flooding, cold wave, drought, earthquake, hail, heat wave, hurricane ( tropical cyclone), ice storm, landslide, lightning, riverine flooding, strong wind, tornado, typhoon, tsunami, volcanic activity, wildfire, winter weather. In modern times, the divide between natural, man-made and man-accelerated disasters is quite difficult to draw. Human choices and activities like architecture, fire, resource management or even climate change potentially play a role in causing "natural disasters". In fact, the term "natural disaster" has been calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine Of 1315–1317
The Great Famine of 1315–1317 (occasionally dated 1315–1322) was the first of a series of large-scale crises that struck Europe early in the 14th century. Most of Europe (extending east to Russia and south to Italy) was affected. The famine caused many deaths over an extended number of years and marked a clear end to the period of growth and prosperity from the 11th to the 13th centuries. The Great Famine started with bad weather in spring 1315. Crop failures lasted through 1316 until the summer harvest in 1317, and Europe did not fully recover until 1322. Crop failures were not the only problem; cattle disease caused sheep and cattle numbers to fall as much as 80%. The period was marked by extreme levels of crime, disease, mass death, and even cannibalism and infanticide. The crisis had consequences for the Church, state, European society, and for future calamities to follow in the 14th century. Background Famines were familiar occurrences in medieval Europe. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |