|
List Of Mountain Types
Mountains and hills can be characterized in several ways. Some mountains are volcanoes and can be characterized by the type of lava and eruptive history. Other mountains are shaped by glacial processes and can be characterized by their shape. Finally, many mountains can be characterized by the type of rock that make up their composition. Types of mountains according to geology Glacially sculpted mountains and hills * Arête * Drumlin * Esker * Flyggberg * Nunatak * Pyramidal peak * Whaleback mountain Volcanic mountains * Cinder cone * Complex volcano * Guyot * Lava cone * Lava dome * Mud volcano * Pancake dome * Pyroclastic cone * Pyroclastic shield * Shield volcano * Stratovolcano * Subglacial mound * Submarine Volcano * Somma volcano * Tuya * Volcanic field * Volcanic plug Mountains with structure-controlled form * Bornhardt * Cuesta * Dome * Fault-block mountain * Fold mountain * Hogback * Homoclinal ridge * Table and mesa **Tepui (Guiana Highlands) * Traprock moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancake Dome
A pancake dome is an unusual type of lava dome found on the planet Venus. They are widely scattered on that planet and often form groups or clusters, though with smaller numbers of pancake domes in each group than is typical for the more common shield volcanos. They are commonly found near coronae and ''tesserae'' (large regions of highly deformed terrain, folded and fractured in two or three dimensions, believed to be unique to Venus) in the lowland plains. Pancake domes are between 10 and 100 times larger than volcanic domes formed on Earth. Description Pancake domes have a broad, flat profile similar to shield volcanoes and are thought to form from one large, slow eruption of viscous silica-rich lava. They usually have a central pit- or bowl-like feature similar to a volcanic crater, but it is thought that these pits form after the eruption as the lava cools and emits gas rather than being a vent from which the lava originated. The surface of pancake domes are covered with pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
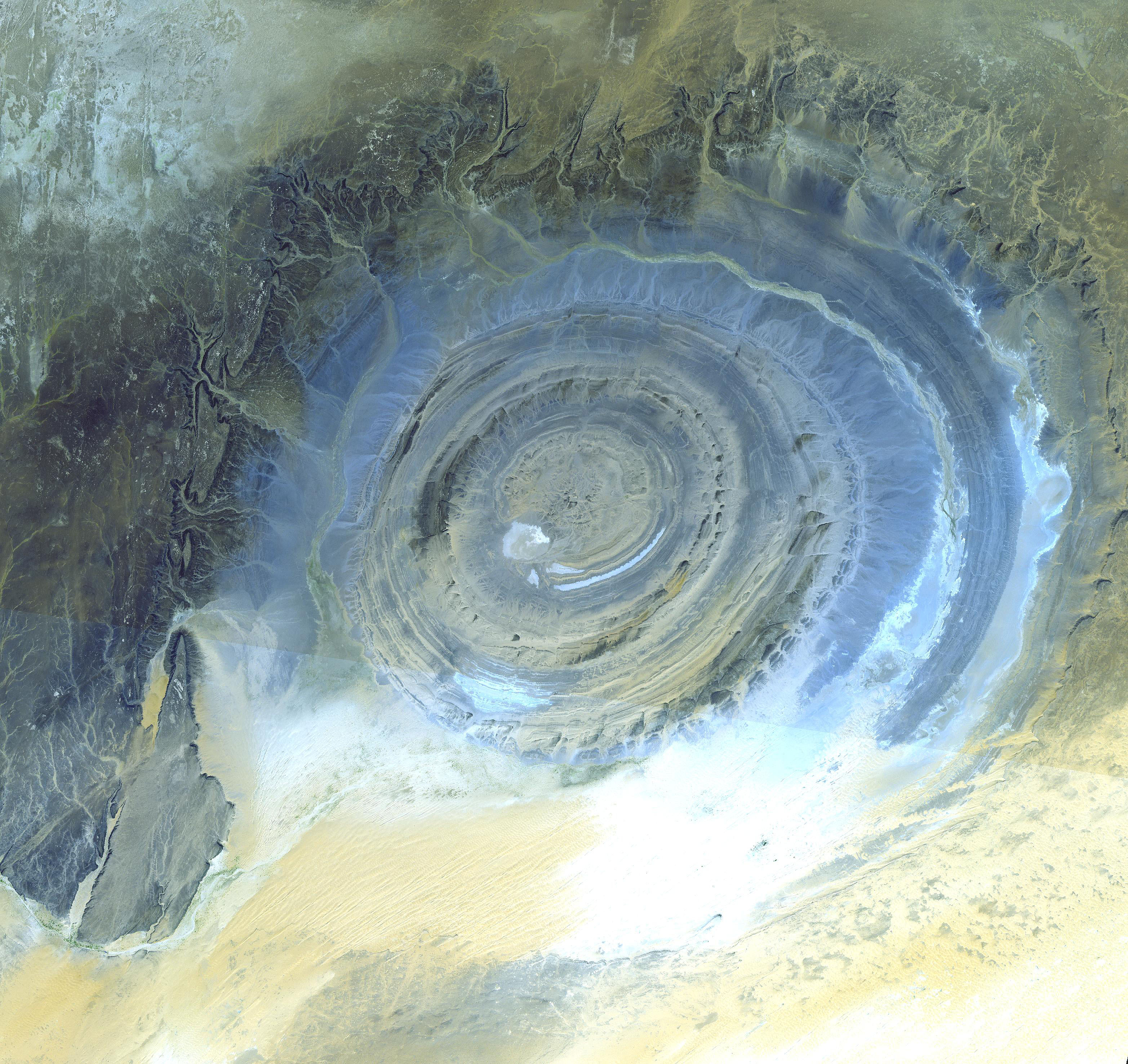
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology consisting of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, spherical-to- ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. However, a transect parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of strata. Consequently, if the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in plan view appears as a bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of deposition, then later deformed by the uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechanisms responsible for the formation of domes, the foremost of which are post-impact uplift, refolding, and diapirism. Post-impact uplift A complex crater, caused by collision of a hypervelocity body with another larger than itself, is typified by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer layer, the whole being tilted somewhat from the horizontal. This results in a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of resistant strata, called caprock. Where erosion has exposed the frontslope of this, a steep slope or escarpment occurs. The resulting terrain may be called scarpland. Definition In general usage, a cuesta is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope (backslope) on one side, and a steep slope (frontslope) on the other. The word is from Spanish: "flank or slope of a hill; hill, mount, sloping ground". In geology and geomorphology, cuesta refers specifically to an asymmetric ridge with a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of a resistant stratum or strata, called cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornhardt
A bornhardt () is a dome-shaped, steep-sided, bald rock outcropping at least in height and several hundred metres in width. They are named after Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946), a German geologist and explorer of German East Africa, who first described the feature. While ''bornhardt'' was originally used to sometimes denote a type of inselberg (literally island mountain—an isolated dome in an otherwise flat landscape), the term ''bornhardt'' is used in modern literature to refer to domed hills and mountains regardless of isolation; thus, not all bornhardts are inselbergs and not all inselbergs are bornhardts. Bornhardts are commonly composed of igneous rocks, often granites, but examples of gneiss, quartzite and arkose bornhardts exists. The Sugarloaf Mountain of Rio de Janeiro is a typical example of this landform and is the origin of the common bornhardt nickname "sugar loaf". Bornhardts are most easily seen in arid and semi-arid regions, but occur over a wide range of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Plug
A volcanic plug, also called a volcanic neck or lava neck, is a volcanic object created when magma hardens within a vent on an active volcano. When present, a plug can cause an extreme build-up of high gas pressure if rising volatile-charged magma is trapped beneath it, and this can sometimes lead to an explosive eruption. In a plinian eruption the plug is destroyed and ash is ejected. Glacial erosion can lead to exposure of the plug on one side, while a long slope of material remains on the opposite side. Such landforms are called crag and tail. If a plug is preserved, erosion may remove the surrounding rock while the erosion-resistant plug remains, producing a distinctive upstanding landform. Examples of volcanic plugs Africa Near the village of Rhumsiki in the Far North Province of Cameroon, Kapsiki Peak is an example of a volcanic plug and is one of the most photographed parts of the Mandara Mountains. Spectacular volcanic plugs are present in the center of La Gomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes such as cinder cones. Lava flows may also occur. They may occur as a monogenetic volcanic field or a polygenetic volcanic field. Description Alexander von Humboldt observed in 1823 that geologically young volcanoes are not distributed uniformly across the Earth's surface, but tend to be clustered into specific regions. Young volcanoes are rarely found within cratons, but are characteristic of subduction zones, rift zones, or in ocean basins. Intraplate volcanoes are clustered along hotspot traces. Within regions of volcanic activity, volcanic fields are clusters of volcanoes that share a common magma source. Scoria cones are particularly prone to cluster into volcanic fields, which are typically in diameter and consist of several tens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuya
A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period. As lava that erupts under a glacier cools very quickly and cannot travel far, it piles up into a steep-sided hill. If the eruption continues long enough, it either melts all the ice or emerges through the top of the ice and then creates normal-looking lava flows that make a flat cap on top of the hill. Discovering and dating the lava flows in a tuya has proven useful in reconstructing past glacial ice extents and thicknesses. Formation Tuyas are a type of subglacial volcano that consists of nearly horizontal beds of lava capping outward-dipping beds of fragmental volcanic rocks, and they often rise in isolation above a surrounding plateau. Tuyas are found in Iceland, British Columbia, the Santiam Pass region in Oregon, the Tyva Republic in eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
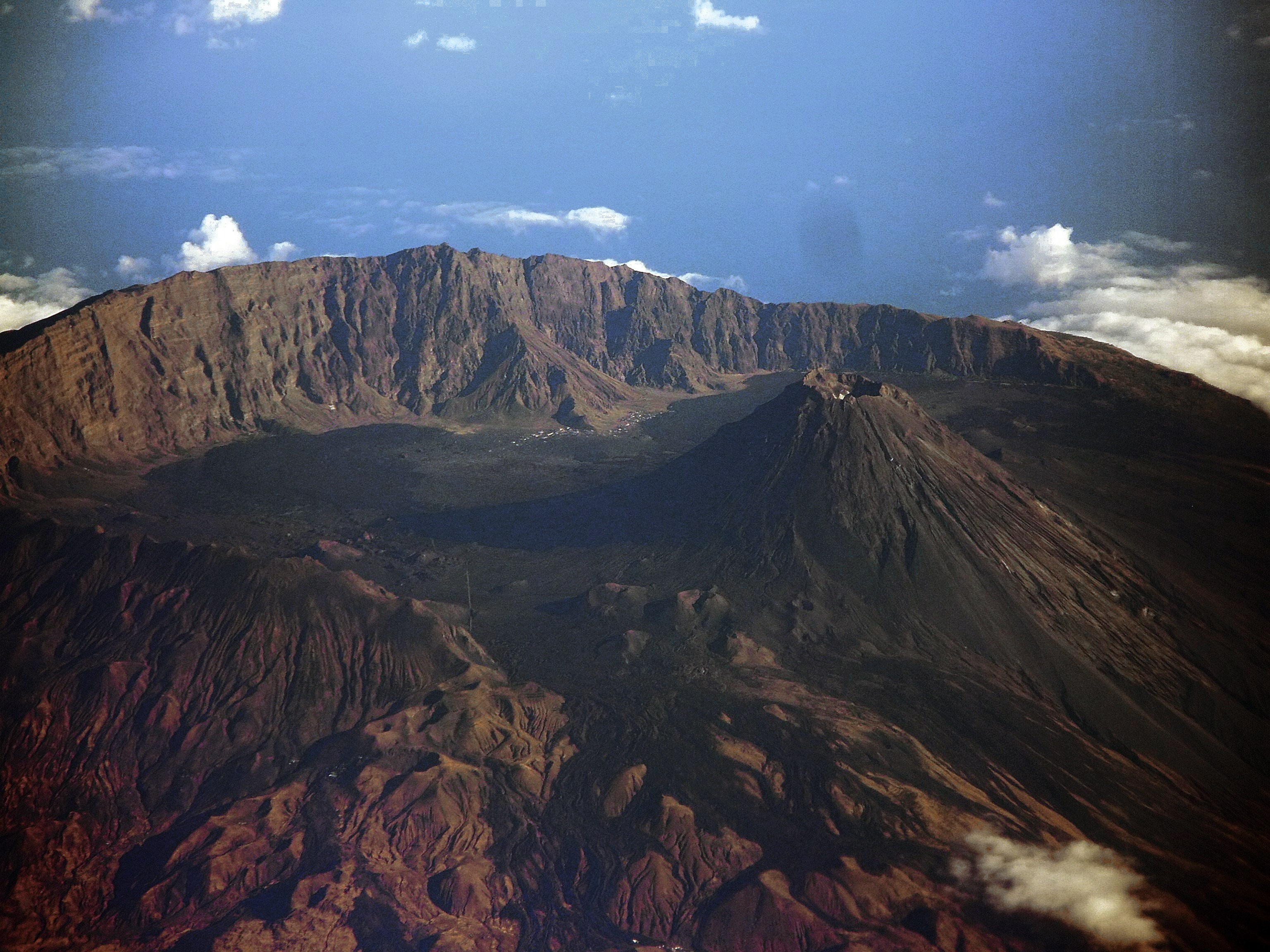
Somma Volcano
A somma volcano (also known as a sommian) is a volcano, volcanic caldera that has been partially filled by a new central volcanic cone, cone. The name comes from Mount Somma, a stratovolcano in southern Italy with a summit caldera in which the upper cone of Mount Vesuvius has grown. A number of Earth's best examples of somma volcanoes are found on Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula and the Kuril Islands that stretch south from Kamchatka to Hokkaidō (Japan). Some examples of somma volcanoes are the following: * Africa ** Pico do Fogo (Fogo, Cape Verde, Fogo Island, Cape Verde) ** Teide (Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain) * Americas ** Cosigüina (Chinandega, Nicaragua) ** Wizard Island (Oregon, United States) ** Lava domes (Mount St. Helens, Washington (state), Washington, United States) * Asia ** Ebeko (Paramushir Island, Kuril Islands, Russia) ** Gunung Baru Jari (Segara Anak caldera, Lombok, Indonesia) ** Kolokol Group: Kolokol, Berg, Borzov, Trezubetz (Urup Island, Kuril Islands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Volcano
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth.Martin R. Speight, Peter A. Henderson, "Marine Ecology: Concepts and Applications", John Wiley & Sons, 2013. . Although most submarine volcanoes are located in the depths of seas and oceans, some also exist in shallow water, and these can discharge material into the atmosphere during an eruption. The total number of submarine volcanoes is estimated to be over 1 million (most are now extinct) of which some 75,000 rise more than 1 km above the seabed. Only 119 submarine volcanoes in Earth's oceans and seas are known to have erupted during the last 11,700 years. Hydrothermal vents, sites of abundant biological activity, are commonly found near submarine volcanoes. Effe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subglacial Mound
A subglacial mound (SUGM) is a type of subglacial volcano. This type of volcano forms when lava erupts beneath a thick glacier or ice sheet. The magma forming these volcanoes was not hot enough to melt a vertical pipe right through the overlying glacial ice, instead forming hyaloclastite and pillow lava deep beneath the glacial ice field. Once the glaciers had retreated, the subglacial volcano would be revealed, with a unique shape as a result of their confinement within glacial ice. They are somewhat rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were formerly covered by continental ice sheets and also had active volcanism during the same period. They are found throughout Iceland, Antarctica and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Subglacial mounds can be mistaken for cinder cones because they may have a similar shape. An example of this confusion is Pyramid Mountain in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


