|
List Of Longest Novels
This is a list of the novels over 500,000 words published through a mainstream publisher. Traditionally, '' Artamène ou le Grand Cyrus'' has been considered the longest novel, but it has been surpassed by at least one novel, or two depending on the criterion used to determine the length. Originally published (1649–1654) in ten parts, each part in three volumes, ''Artamène'' is generally attributed to Madeleine de Scudéry. Compiling a list of longest novels yields different results depending on whether pages, words, or characters are counted. Length of a book is typically associated with its size—specifically page count—leading many to assume the largest and thickest book equates to its length. Word count is a direct way to measure the length of a novel in a manner unaffected by variations of format and page size; however, translating the story into different languages and dialects results in different word counts. Comparison of methods There are at least three ways to det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artamène
''Artamène ou le Grand Cyrus'' (English: ') is a novel sequence, originally published in ten volumes in the 17th century. The title pages credit the work to French writer Georges de Scudéry, but it is usually attributed to his sister and fellow writer Madeleine. At 1,954,300 words, it is considered one of the longest novels ever published. "Scudery’s major classical references and source-material comes from Herodotus’ ''Histories'' and Xenophon's ''Cyropaedia''. Other sources include Plutarch, Justin, Polyaenus, Pliny, Ovid, Strabon, and the Bible." However, it is a roman à clef ''Roman à clef'' (, anglicised as ), French for ''novel with a key'', is a novel about real-life events that is overlaid with a façade of fiction. The fictitious names in the novel represent real people, and the "key" is the relationship ... about contemporary personages. References External links Artamène.org: the entire novel available onlineArtamene and Ibrahim* contemporary En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devta (novel)
''Devta'' ( ''deotā'', "devata, deity") is a serialized fantasy thriller novel written in the Urdu language by Mohiuddin Nawab. It was published monthly for 33 years in the Pakistani magazine ''Suspense Digest'' from February 1977 to January 2010. ''Devta'' is the fictional autobiography of Farhad Ali Taimoor, a man who gained telepathy, telepathic powers. The author Mohiuddin Nawab, a well-known social story writer of Pakistan, has written more than 500 stories, both short stories and novel-length, mostly published in ''Suspense Digest'', a monthly magazine published in Karachi and available in Pakistan, India, and elsewhere in the world where Urdu is spoken. He has also written screenplays for film and television. Spanning 49 volumes and an estimated 2,450,000 words, (9,800,000 estimated characters with and without spaces. 6898.1 Pages) ''Devta'' is the longest continuously-published story on record. It was started in February 1977 and appeared every month in ''Suspense Diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
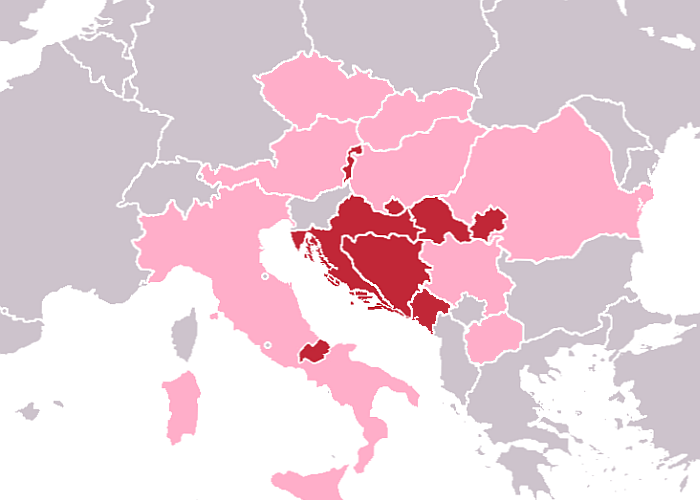
Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia. Due to political, social and economic reasons, many Croats migrated to North and South America as well as New Zealand and later Australia, establishing a diaspora in the aftermath of World War II, with grassroots assistance from earlier communities and the Roman Catholic Church. In Croatia (the nation state), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Language
Croatian (; ' ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official and literary standard of Croatia and one of the official languages of the European Union. Croatian is also one of the official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and a recognized minority language in Serbia and neighboring countries. Standard Croatian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Serbian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin. In the mid-18th century, the first attempts to provide a Croatian literary standard began on the basis of the Neo-Shtokavian dialect that served as a supraregional ''lingua franca'' pushing back regional Chakavian, Kajkavian, and Shtokavian vernaculars. The decisive role was played by Croatian Vukovians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Školska Knjiga
Školska knjiga (lit. ''Schoolbook'', ) is one of the largest publishing companies in Croatia , image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capit .... It was established in 1950. Until the mid-1990s it had a virtual monopoly on publishing schoolbooks and this remains its core business. References External links * Publishing companies established in 1950 Publishing companies of Croatia Educational book publishing companies 1950 establishments in Yugoslavia 1950 establishments in Croatia Companies based in Zagreb {{Publish-corp-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marija Jurić Zagorka
Marija Jurić (; 2 March 1873 – 30 November 1957), known by her pen name Zagorka (), was a Croatian journalist, writer and women's rights activist. She was the first female journalist in Croatia and is among the most read Croatian writers. Early life and education Marija Jurić was born on 2 March 1873 in the village of Negovec in the family of Ivan Jurić and Josipa Domin. She had two brothers and a sister. Baptized in a Catholic church on 3 March 1873, she was given the baptismal name Mariana. She later spoke of her family as being wealthy but unhappy. She spent her childhood in Hrvatsko Zagorje on the Golubovec estate owned by Baron Geza Rauch which her father managed. She was educated by private tutors alongside baron Rauch's children. Zagorka attended elementary school in Varaždin were she stood out as very intelligent and talented, finishing all grades with the highest marks. Although her father wanted to send her to Switzerland to attend high school, which baron Rauch a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language spoken country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warre B
{{surname ...
Warre is a surname, and may refer to: *Edmond Warre (1837–1920), English rower and head master of Eton College *Émile Warré, French beekeeper who invented the Warré Hive *Francis Warre Warre-Cornish (1839–1916), British scholar and writer *Felix Warre (1879–1953), English rower *Sir Henry Warre (1819-1898), British Army officer *Richard Warre (c. 1649 – 1730), English official *Sir William Warre (1784–1853), British Army officer See also *Warre baronets * *Warr (surname) Warr is a surname, and may refer to: People * Antony Warr (1913-1995), English rugby union player * Augustus Frederick Warr (1847–1908), English lawyer and Conservative party politician * Charles Warr (1892–1969), Church of Scotland m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred A
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *''Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album ''Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England *Alfred Music, an American music publisher *Alfred University, New York, U.S. *The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario * Alfred Island, Nunavut * Mount Alfred, British Columbia United States * Alfred, Maine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Romains
Jules Romains (born Louis Henri Jean Farigoule; 26 August 1885 – 14 August 1972) was a French poet and writer and the founder of the Unanimism literary movement. His works include the play '' Knock ou le Triomphe de la médecine'', and a cycle of works called ''Les Hommes de bonne volonté (Men of Good Will)''. Sinclair Lewis called him one of the six best novelists in the world. He was nominated for the Nobel prize in literature sixteen times. Life Jules Romains was born in Saint-Julien-Chapteuil in the Haute-Loire but went to Paris to attend first the Lycée Condorcet and then the prestigious École Normale Supérieure. He was close to the Abbaye de Créteil, a utopian group founded in 1906 by Charles Vildrac and René Arcos, which brought together, among others, the writer Georges Duhamel, the painter Albert Gleizes and the musician Albert Doyen. He received his agrégation in philosophy in 1909. In the interwar years, he pleaded the cause of pacifism and a united Europe ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Men Of Good Will
''Les Hommes de bonne volonté'' () is an epic roman-fleuve by French writer Jules Romains, published in 27 volumes between 1932 and 1946. It has been classified both as a novel cycle and a novel and, at two million words and 7,892 pages, has been cited as one of the longest novels ever written. Plot The volumes, written in chronological order from volume one, ''Le 6 octobre'', through volume twenty-seven, ''Le 7 octobre'', between them cover 6 October 1908 through 7 October 1933 in French life—an average of one volume per year, book-ended by one volume each for two particular days. The plot is expansive and features a large cast of characters, rather than narrowly focusing on individuals, but the two principals are Pierre Jallez, a poet loosely based on Romains, and Jean Jerphanion, a teacher who later goes into politics. They meet in volume 2 starting at the École Normale Supérieure and become friends. Jerphanion marries a woman named Odette and lives happily with her, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Williamson
Henry William Williamson (1 December 1895 – 13 August 1977) was an English writer who wrote novels concerned with wildlife, English social history and ruralism. He was awarded the Hawthornden Prize for literature in 1928 for his book ''Tarka the Otter''. He was born in London, and brought up in a semi-rural area where he developed his love of nature, and nature writing. He fought in World War I and, having witnessed the Christmas truce and the devastation of trench warfare, he developed first a pacifist ideology, then fascist sympathies. He moved to Devon after World War II and took up farming and writing; he wrote many other novels. He married twice. He died in a hospice in Ealing in 1977, and was buried in North Devon. Early years Henry Williamson was born in Brockley in south-east London to bank clerk William Leopold Williamson (1865-1946) and Gertrude Eliza (1867-1936; née Leaver). In early childhood his family moved to Ladywell, and he received a grammar school educati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)