|
List Of Insect-borne Diseases
This article contains a list of insect-borne diseases. They can take the form of parasitic worms, bacteria, protozoa, viruses, or the insects directly acting as a parasite. Insect-borne diseases Mosquitoes Mosquitoes are vectors for a large number of diseases, the large majority being viral in nature. Mosquito-borne viruses fall into four major groups: ''Bunyavirales'', ''Flaviviridae'', ''Togaviridae'', and ''Reoviridae''. They can present as either arbovirus encephalitis or viral hemorrhagic fevers. Other insects Direct parasites Insect-borne diseases See also * Arbovirus * List of diseases spread by invertebrates * Mosquito-borne disease * Robovirus * Tibovirus * Tick-borne disease Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and proto ... References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
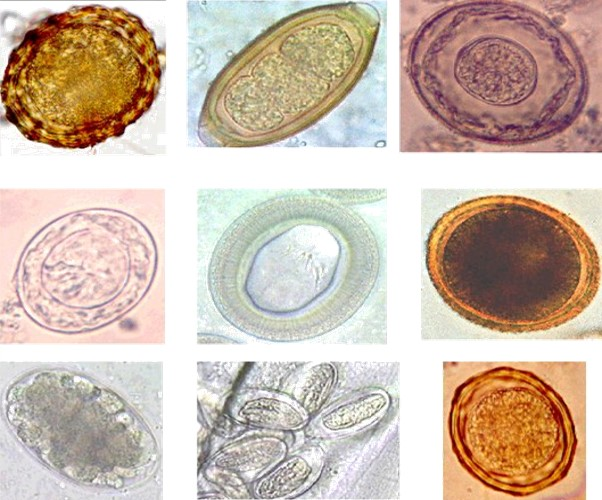
Parasitic Worm
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large Parasitism#Basic concepts, macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted helminth, soil-transmitted and intestinal parasite infection, infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are Parasitism#Basic concepts, endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living host (biology), hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tete Virus
''Tete orthobunyavirus'' is a bunyavirus found originally in Tete Province, Mozambique. It is a disease of animals and humans. Two forms, Bahig and Matruh viruses, were isolated from bird ticks including '' Hyalomma marginatum'', but elsewhere mosquitoes and biting midges Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, or biting midges, generally in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic. Ceratopogonidae are Holomet ... have been implicated as vectors. Subtypes *Bahig virus *Matruh virus *Tete virus SAAn3518 *Tsuruse virus *Weldona virus References Literature * Orthobunyaviruses {{Mozambique-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barmah Forest Virus
''Barmah Forest virus'' is an RNA virus in the genus ''Alphavirus''. This disease was named after the Barmah Forest in the northern Victoria region of Australia where it was first isolated in 1974. Or The first documented case in humans was in 1986. As of 2015, it has been found only in Australia. Although there is no specific treatment for infection with the Barmah Forest virus, the disease is non-fatal and most infected people recover.Barmah Forest Virus ''Queensland Health''. Queensland Government. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2012. The virus was discovered in 1974 in es in the |
Zika Fever
Zika fever, also known as Zika virus disease or simply Zika, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. Most cases have no symptoms, but when present they are usually mild and can resemble dengue fever. Symptoms may include fever, red eyes, joint pain, headache, and a maculopapular rash. Symptoms generally last less than seven days. It has not caused any reported deaths during the initial infection. Mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy can cause microcephaly and other brain malformations in some babies. Infections in adults have been linked to Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS). Zika fever is mainly spread via the bite of mosquitoes of the ''Aedes'' type. It can also be sexually transmitted and potentially spread by blood transfusions. Infections in pregnant women can spread to the baby. Diagnosis is by testing the blood, urine, or saliva for the presence of the virus's RNA when the person is sick, or the blood for antibodies after symptoms are present more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. In about 15% of people, within a day of improving the fever comes back, abdominal pain occurs, and liver damage begins causing yellow skin. If this occurs, the risk of bleeding and kidney problems is increased. The disease is caused by the yellow fever virus and is spread by the bite of an infected mosquito. It infects humans, other primates, and several types of mosquitoes. In cities, it is spread primarily by ''Aedes aegypti'', a type of mosquito found throughout the tropics and subtropics. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus ''Flavivirus''. The disease may be difficult to tell apart from other illnesses, especially in the early stages. To confirm a suspected case, blood-sample testing with polymerase chain reaction is required. A saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into a more severe dengue hemorrhagic fever, resulting in bleeding, low levels of blood platelets and blood plasma leakage, or into dengue shock syndrome, where dangerously low blood pressure occurs. Dengue is spread by several species of female mosquitoes of the ''Aedes'' genus, principally ''Aedes aegypti''. The virus has five serotypes; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications. A number of tests are available to confirm the diagnosis including detecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Nile Fever
West Nile fever is an infection by the West Nile virus, which is typically spread by mosquitoes. In about 80% of infections people have few or no symptoms. About 20% of people develop a fever, headache, vomiting, or a rash. In less than 1% of people, encephalitis or meningitis occurs, with associated neck stiffness, confusion, or seizures. Recovery may take weeks to months. The risk of death among those in whom the nervous system is affected is about 10 percent. West Nile virus (WNV) is usually spread by mosquitoes that become infected when they feed on infected birds, which often carry the disease. Rarely the virus is spread through blood transfusions, organ transplants, or from mother to baby during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding, but it otherwise does not spread directly between people. Risks for severe disease include being over 60 years old and having other health problems. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and blood tests. There is no human vaccine. The be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usutu Virus
Usutu virus (USUV) is a flavivirus belonging to the Japanese encephalitis complex, which is an emerging zoonotic arbovirus of concern because of its pathogenicity to humans and its similarity in ecology with other emerging arboviruses such as West Nile virus. It mainly infects ''Culex'' mosquitoes and birds; humans form a dead-end host. First identified in South Africa in 1959, the virus has caused outbreaks in birds across Europe since 1996. Nearly 50 cases in humans have been reported as of 2019, mainly in Europe. These are predominantly asymptomatic, but some people experience neurological symptoms. History USUV was first identified by Bruce McIntosh in '' Culex neavei'' mosquitoes in South Africa in 1959, and is named after the Usutu River. The virus was later identified in '' Mansonia aurites'' mosquitoes in Uganda. In 1996, USUV was identified outside Africa for the first time, causing significant mortality among Old World blackbirds in Italy. Only two human cases have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondweni Fever
Spondweni fever is an infectious disease caused by the Spondweni virus. It is characterized by a fever, chills, nausea, headaches, malaise and epistaxis. Transmitted by mosquitoes, it is found in sub-Saharan Africa and Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i .... References Viral diseases Tropical diseases Insect-borne diseases {{infectious-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Louis Encephalitis
Saint Louis encephalitis is a disease caused by the mosquito-borne Saint Louis encephalitis virus. Saint Louis encephalitis virus is related to Japanese encephalitis virus and is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. This disease mainly affects the United States, including Hawaii. Occasional cases have been reported from Canada, Mexico and the Caribbean, including the Greater Antilles, Trinidad and Tobago, and Jamaica. Signs and symptoms The majority of infections result in mild illness, including fever and headache. When infection is more severe the person may experience headache, high fever, neck stiffness, stupor, disorientation, coma, tremors, occasional convulsions and spastic paralysis. Fatality ranges from . Elderly people are more likely to have a fatal infection. Transmission Mosquitoes, primarily from the genus ''Culex'', become infected by feeding on birds infected with the Saint Louis encephalitis virus. The most common vector of this disease within the genus ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocio Viral Encephalitis
Rocio viral encephalitis is an epidemic flaviviral disease of humans first observed in São Paulo State, Brazil, in 1975. Low-level enzootic transmission is likely continuing in the epidemic zone, and with increased deforestation and population expansion, additional epidemics caused by Rocio virus are highly probable. If migratory species of birds are, or become involved in, the virus transmission cycle, the competency of a wide variety of mosquito species for transmitting Rocio virus experimentally suggest that the virus may become more widely distributed. The encephalitis outbreak in the western hemisphere caused by West Nile virus, a related flavivirus, highlights the potential for arboviruses to cause severe problems far from their source enzootic foci. The causative Rocio virus belongs to the genus ''Flavivirus'' (the same genus as the Zika virus) in family Flaviviridae and is closely related serologically to Ilhéus, St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis and Murray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray Valley Encephalitis Virus
''Murray Valley encephalitis virus'' (MVEV) is a zoonotic flavivirus endemic to northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. It is the causal agent of Murray Valley encephalitis (MVE; previously known as Australian encephalitis or Australian X disease). In humans, it can cause permanent neurological disease or death. MVEV is related to Kunjin virus, which has a similar ecology, but a lower morbidity rate. Although the arbovirus is endemic to Northern Australia, it has occasionally spread to the southern states during times of heavy rainfall during the summer monsoon season via seasonal flooding of the Murray-Darling River system. These outbreaks can be "...decades apart, with no or very few cases identified in between". Vector MVEV is a mosquito-borne virus that is maintained in a bird-mosquito-bird cycle. Water birds from the order Ciconiiformes, including herons and cormorants, provide the natural reservoir for MVEV. The major mosquito vector is ''Culex annulirostris''. Human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |