|
List Of Gadfly Petrels
This is a list of the birds that belong to the group gadfly petrels. They are all from the genus '' Pterodroma'' and belong to the family Procellariidae. * ''Pterodroma macroptera'', great-winged petrel, breeds and ranges on islands of the southern oceansClements, J. (2007) * ''Pterodroma gouldi'', grey-faced petrel, breeds on islands off the coast of the North Island, New Zealand, and off the coast of southwestern Australia * ''Pterodroma neglecta'', Kermadec petrel, breeds on islands of the south Pacific from New Zealand to Easter Island, Juan Fernández Islands, San Ambrosio, and San Félix ** ''Pterodroma neglecta neglecta'' breeds on south Pacific islands from New Zealand to Easter Island ** ''Pterodroma neglecta juana'' breeds on Juan Fernández Islands, San Ambrosio, and San Félix * ''Pterodroma magentae'', magenta petrel, breeds on Chatham Islands * ''Pterodroma arminjoniana'', herald petrel breeds on Raine Island, Tonga, French Polynesia to Easter Island, Trindade Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadfly Petrel
The gadfly petrels or ''Pterodroma'' are a genus of about 35 species of petrels, part of the seabird order Procellariiformes. The gadfly petrels are named for their speedy weaving flight, as if evading gadflies ( horseflies). The flight action is also reflected in the name ''Pterodroma'', from Ancient Greek ''pteron'', "wing" and ''dromos'', "runner". The short, sturdy bills of these medium to large petrels are adapted for soft prey that they pick from the ocean surface. They have twisted intestines for digesting marine animals that have unusual biochemistries. Their complex wing and face marking are probably for interspecific recognition. These birds nest in colonies on islands and are pelagic when not breeding. One white egg is laid usually in a burrow or on open ground. They are nocturnal at the breeding colonies. While generally wide-ranging, most ''Pterodroma'' species are confined to a single ocean basin (e.g. Atlantic), and vagrancy is not as common amongst the genus as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. As of 2021, according to Johnson's Tribune, Tonga has a population of 104,494, 70% of whom reside on the main island, Tongatapu. The country stretches approximately north-south. It is surrounded by Fiji and Wallis and Futuna (France) to the northwest; Samoa to the northeast; New Caledonia (France) and Vanuatu to the west; Niue (the nearest foreign territory) to the east; and Kermadec (New Zealand) to the southwest. Tonga is about from New Zealand's North Island. First inhabited roughly 2,500 years ago by the Lapita civilization, Tonga's Polynesian settlers gradually evolved a distinct and strong ethnic identity, language, and culture as the Tongan people. They were quick to establish a powerful footing acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zino's Petrel
Zino's petrel (''Pterodroma madeira'') or the freira, is a species of small seabird in the gadfly petrel genus, endemic to the island of Madeira. This long-winged petrel has a grey back and wings, with a dark "W" marking across the wings, and a grey upper tail. The undersides of the wings are blackish apart from a triangle of white at the front edge near the body, and the belly is white with grey flanks. It is very similar in appearance to the slightly larger Fea's petrel, and separating these two Macaronesian species at sea is very challenging. It was formerly considered to be a subspecies of the soft-plumaged petrel, ''P. mollis'', but they are not closely related, and Zino's was raised to the status of a species because of differences in morphology, calls, breeding behaviour and mitochondrial DNA. It is Europe's most endangered seabird, with breeding areas restricted to a few ledges high in the central mountains of Madeira. Zino's petrel nests in burrows which are visited only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henderson Island (Pitcairn Islands)
Henderson Island (formerly also San Juan Bautista and Elizabeth Island) is an uninhabited island in the south Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Pitcairn Island Group, together with Pitcairn, Oeno, and Ducie Islands. Measuring , it has an area of and is located northeast of Pitcairn Island. It has poor soil and little fresh water, and is unsuitable for agriculture. There are three beaches on the northern end and the remaining coast comprises steep (mostly undercut) cliffs up to in height. In 1902, it was annexed to the Pitcairn Islands colony, which is now a British Overseas Territory. Henderson is one of the last two raised coral atolls in the world whose ecosystems remain relatively unaffected by human contact, along with Aldabra in the Indian Ocean. In 1988, it was designated a World Heritage Site by the United Nations. Ten of its 51 flowering plants, all four of its land birds and about a third of the identified insects and gastropods are endemic – a remarkable diversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henderson Petrel
The Henderson petrel (''Pterodroma atrata'') is a ground-nesting species of gadfly petrel in the family Procellariidae. Adults measure on average 37 cm. It has a uniform grey-brown plumage. These birds are endangered. It is found in the Pitcairn Islands, and possibly in French Polynesia, though confusion over the taxon makes reports of this species in the Marquesas, Tuamotus, Australs and Gambiers uncertain. Breeding colonies formerly existed on Ducie Island, but were wiped out by invasive rats by 1922. It is now believed to nest uniquely on Henderson island, which was declared a World Heritage Site in 1988. The International Union for Conservation of Nature classifies it as closely related to ''Pterodroma arminjoniana'' and ''Pterodroma heraldica''. Its natural habitat is the moist subtropical scrub found on that island. The endangered habitat of this species was identified in 2007 as requiring urgent action to restore it. During Captain Cook's first voyage, Dani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillip Island (Norfolk Island)
Phillip Island is an island located south of Norfolk Island in the Southwest Pacific, and is part of the Norfolk Island group. It was named in 1788 by Lieutenant Philip Gidley King after Arthur Phillip, the first Governor of New South Wales. Phillip Island is part of the Australian external territory of Norfolk Island, and is included in Norfolk Island National Park, as is neighbouring Nepean Island and about 10 percent of Norfolk Island proper. A National Parks hut located near the centre of the island houses a small rotating group of around four people for much of the year. Otherwise the island is uninhabited. Phillip Island has an area of , measuring from west to east and from north to south, with the highest point, Jacky Jacky, being above sea level. It is roughly shaped like a hairdryer with the nozzle pointing east. The island is of volcanic origin, made of basaltic tuff and lava dating from the Miocene epoch. Phillip Island is included on the Register of the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Howe Island
Lord Howe Island (; formerly Lord Howe's Island) is an irregularly crescent-shaped volcanic remnant in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It lies directly east of mainland Port Macquarie, northeast of Sydney, and about southwest of Norfolk Island. It is about long and between wide with an area of , though just of that comprise the low-lying developed part of the island. Along the west coast is a sandy semi-enclosed sheltered coral reef lagoon. Most of the population lives in the north, while the south is dominated by forested hills rising to the highest point on the island, Mount Gower (). The Lord Howe Island Group comprises 28 islands, islets, and rocks. Apart from Lord Howe Island itself, the most notable of these is the volcanic and uninhabited Ball's Pyramid about to the southeast of Howe. To the north lies a cluster of seven small uninhabited islands called the Admiralty Group. The first repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
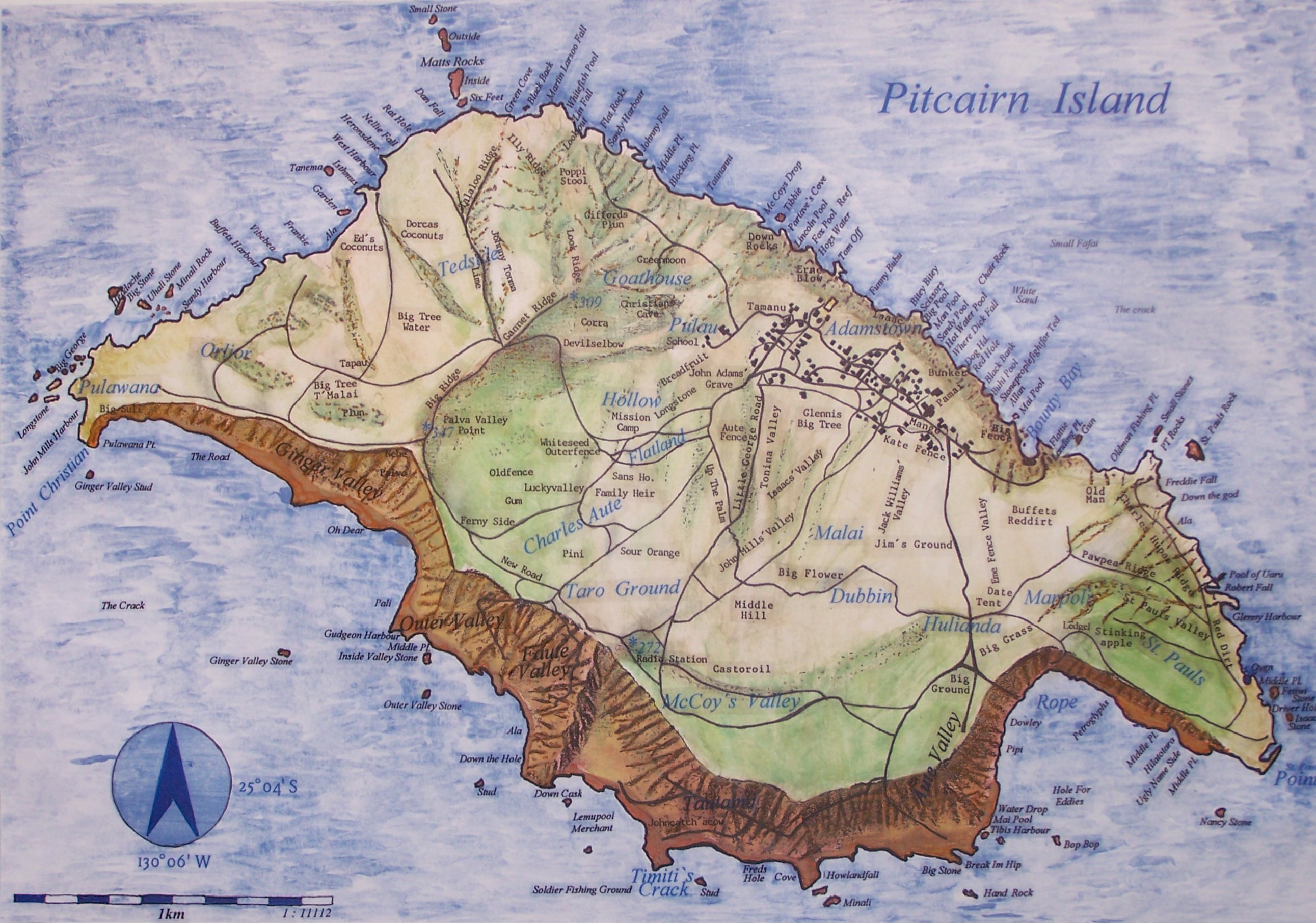
Pitcairn Island
Pitcairn Island is the only inhabited island of the Pitcairn Islands, of which many inhabitants are descendants of mutineers of HMS ''Bounty''. Geography The island is of volcanic origin, with a rugged cliff coastline. Unlike many other South Pacific islands, it is not surrounded by coral reefs that protect the coast. The only access to the island is via a small pier on Bounty Bay. Adamstown is the sole settlement. Pawala Valley Ridge is the island's highest point at 346 m above sea level. The volcanic soil and tropical climate with abundant rainfall make the soil productive. The average temperature ranges from 19 to 24°C. The annual rainfall is 1,800 mm. As there are no rivers or lakes, drinking water is collected from the rain with cisterns. Fauna Indigenous fauna consists of insects and lizards. Since their introduction, rats have become an invasive species. A large number of seabirds nest along the steep shorelines. Due to the absence of coral reefs, fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austral Islands
The Austral Islands (french: Îles Australes, officially ''Archipel des Australes;'' ty, Tuha'a Pae) are the southernmost group of islands in French Polynesia, an overseas country of the French Republic in the South Pacific. Geographically, they consist of two separate archipelagos, namely in the northwest the Tupua'i islands (french: Îles Tubuaï) consisting of the Îles Maria, Rimatara, Rūrutu, Tupua'i Island proper and Ra'ivāvae, and in the southeast the Bass Islands (french: Îles basses) composed of the main island of Rapa Iti and the small Marotiri (also known as Bass Rocks or Îlots de Bass). Inhabitants of the islands are known for their pandanus fiber weaving skills. The islands of Maria and Marotiri are not suitable for sustained habitation. Several of the islands have uninhabited islets or rocks off their coastlines. Austral Islands' population is 6,965 on almost . The capital of the Austral Islands administrative subdivision is Tupua'i. History Whaling ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuamotu Archipelago
The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands (french: Îles Tuamotu, officially ) are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending (from northwest to southeast) over an area roughly the size of Western Europe. Their combined land area is . This archipelago's major islands are Anaa, Fakarava, Hao and Makemo. The Tuamotus have approximately 16,000 inhabitants. The islands were initially settled by Polynesians, and modern Tuamotuans have inherited from them a shared culture and the Tuamotuan language. The Tuamotus are a French overseas collectivity. History The early history of the Tuamotu islands is generally unknown. Archaeological findings suggest that the western Tuamotus were settled from the Society Islands as early as 900 CE or as late as 1200 CE. DNA evidence suggests that they were settled about 1110 CE. On the islands of Rangiroa, Manihi and Mataiva, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murphy's Petrel
Murphy's petrel (''Pterodroma ultima'') is a species of seabird and a member of the gadfly petrels. The bird is 15 inches in length, with a 35-inch wingspan and weigh about 13 ounces. It was described by Robert Cushman Murphy in 1949, which is the source of the species' common name. Distribution Very little is known about this species of petrel. It was not until the 1980s that it was determined that these petrels might be regular visitors far offshore of North America. It occurs in the South Pacific, nesting on rocky islets and cliffs off tropical oceanic islands in the Austral, Tuamotu, and Pitcairn groups. The bird has been recorded off the coast of the Hawaiian Islands and well off the Pacific Coast of the United States and in the southern Gulf of Alaska. Most reports of Murphy's petrels are over 40 miles offshore and the species reportedly has one of the greatest foraging ranges of any breeding seabird References * "National Geographic" ''Field Guide to the Birds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |