|
List Of Countries By Irreligion
Irreligion, which may include deism, agnosticism, ignosticism, anti-religion, atheism, skepticism, ietsism, spiritual but not religious, freethought, anti-theism, apatheism, non-belief, pandeism, secular humanism, non-religious theism, pantheism, panentheism, and New age, varies in the countries around the world. According to reports from the Worldwide Independent Network/Gallup International Association's (WIN/GIA) four global polls: in 2005, 77% were a religious person and 4% were "convinced atheists"; in 2012, 23% were not a religious person and 13% were "convinced atheists"; in 2015, 22% were not a religious person and 11% were "convinced atheists"; and in 2017, 25% were not a religious person and 9% were "convinced atheists". According to the Pew Research Centre in 2012, 16% of the world is "religiously unaffiliated", which "include atheists, agnostics and people who do not identify with any particular religion in surveys"; of that overall category, many may still hold some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and antitheism. Social scientists tend to define irreligion as a purely naturalist worldview that excludes a belief in anything supernatural. The broadest and loosest definition, serving as an upper limit, is the lack of religious identification, though many non-identifiers express metaphysical and even religious beliefs. The narrowest and strictest is subscribing to positive atheism. According to the Pew Research Center's 2012 global study of 230 countries and territories, 16% of the world's population does not identify with any religion. The population of the religiously unaffiliated, sometimes referred to as "nones", has grown significantly in recent years. Measurement of irreligiosity requires great cultural sensitivity, especially outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
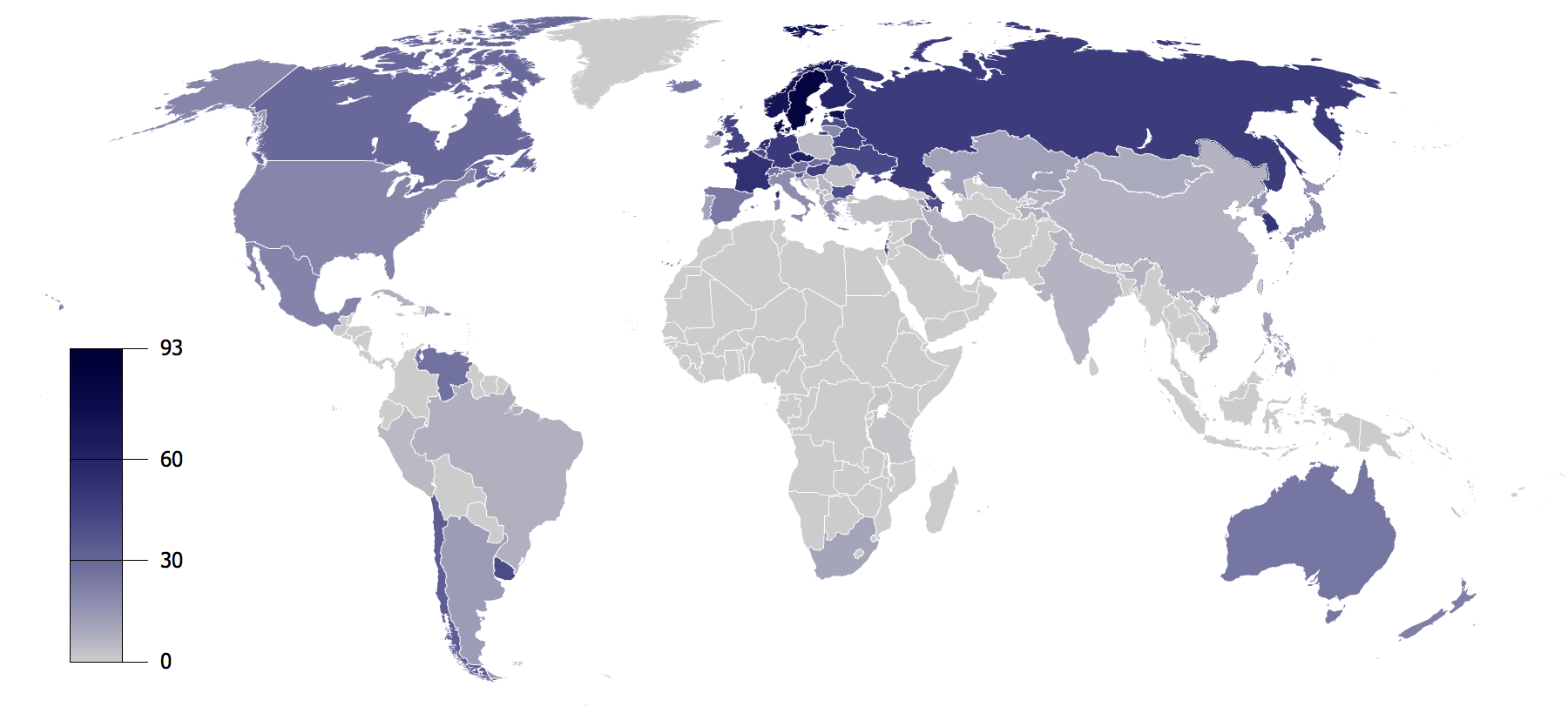
Countries By Percentage Of Unaffiliated–Pew Research 2010
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the country of Wales is a component of a multi-part sovereign state, the United Kingdom. A country may be a historically sovereign area (such as Korea), a currently sovereign territory with a unified government (such as Senegal), or a non-sovereign geographic region associated with certain distinct political, ethnic, or cultural characteristics (such as the Basque Country). The definition and usage of the word "country" is flexible and has changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. The largest country by area is Russia, while the smallest is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Belgium
Irreligion in Belgium pertains to citizens of Belgium that are atheist, agnostic, or otherwise unaffiliated with any religion. Irreligion is the second most common religious stance in Belgium, following Catholicism. History The Constitution of Belgium guaranteed the right to freedom of religion when it was enacted in 1831. Articles 19-21 provide for protections of secularism: the Constitution of Belgium guarantees the freedom of worship and its public practice, forbids the obligation of any religious practices, and disallows government intervention or involvement in a religion's leadership. The First School War was a dispute between Catholicism and secularism in schools in the 1880s. The dispute was revived in the Second School War in the 1950s. Demographics Religion has declined in Belgium, though Catholicism still remains large among the Belgian population. As of 2018, 29.3% of Belgians are irreligious. 20.2% of Belgians identify as not religious, while 9.1% identify as ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Bangladesh
Irreligion in Bangladesh is rare and uncommon publicly. A Gallup (company), Gallup survey from 2014 - 2015 found that approximately less than 1% of Bangladeshis identified as convinced atheists. Bangladesh has 166.3 million people as of 2021 estimation. Persecution of irreligious people Many secularist or irreligious bloggers who supported the anti-Islamist 2013 Shahbag protests, protests occurred came under attack following the protests. Amnesty International noted with concern the rise in communal violence against religious minorities, including 2013 Bangladesh anti-Hindu violence, attacks on Hindus. In early April 2013, the police began arresting bloggers for hurting religious sentiments. Four bloggers, Subrata Adhikary Shuvo, Russell Parvez, Mashiur Rahman Biplob and Asif Mohiuddin (who was still recovering from his wounds), were arrested within days of one another. The blog, Amar Blog, was also taken down. A religious group called Hefazat-e-Islam Bangladesh called for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Azerbaijan
Irreligion in Azerbaijan is open to interpretation according to differing censuses and polls. Although Islam is the predominant faith in Azerbaijan, religious affiliation is nominal in Azerbaijan and percentages for actual practicing adherents are much lower. It is difficult to quantify the number of atheists or agnostics in Azerbaijan as they are not officially counted in the census of the country. Research and statistics According to a study conducted by the Caucasus Research Resource Centers, in 2010, approximately 2,000 people were interviewed, of which 28% answered that religion is "an extremely important" part of their life. Two years later, the survey was conducted again, but only about 1800 people were interviewed, of which 33% reported that religion is an extremely important part of their life. In addition, another 44% claimed that religion is a "fairly important" part of their daily lives. The remaining 23% claimed that religion is a relatively important or completely i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Australia
Atheism, agnosticism, scepticism, freethought, secular humanism or general irreligion are increasing in Australia. Post-war Australia has become a highly secularised country. Religion does not play a major role in the lives of much of the population. In the country's 2021 census, 38.9% of Australians (or 9,886,957 people) selected either "no religion" or specified their form of irreligion, almost nine percent higher (and 2,846,240 more people) than the . 7.2% did not state their religion, or gave an unclear response, meaning that over 46% of Australians did not state a religious affiliation in the 2021 census, a 6.4% increase from the last census. When asked of their religious affiliation in the 2016 census, 29.6% of Australians (or 6,933,708 people) selected "no religion." This is more than seven percent higher (and 2,240,546 more people), than in the . Additionally in 2016, another 0.5% instead opted to specify their form of irreligion, writing it in under "other," hence resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Albania
Irreligion, atheism and agnosticism are present among Albanians (see religion in Albania), along with the predominant faiths of Islam and Christianity. The majority of Albanians lead a secular life and reject religious considerations to shape or condition their way of life. Irreligion in Albania arose after a period of rising anti-clericalism and secularization in the context of the rising Albanian nationalism in the late Ottoman Empire. While authors in this period had at times used invective against religion, the first public advocate of abandoning religion itself was Ismet Toto in 1934 followed by works by Anastas Plasari in 1935. Beginning in 1946 under communist rule in Albania, religion was first curtailed, and then public religious practice was outlawed in 1967 with the adoption of state atheism by Enver Hoxha although some private practice survived, and remained so until restrictions were first eased in 1985 and then removed in 1990 under his successor Ramiz Alia. Polli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In Afghanistan
According to a study by Humanists International (HI), Afghanistan is one of the seven countries in the world (the other six being Iran, the Maldives, Mauritania, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and Sudan) where being an atheist or a convert can lead to a death sentence. According to the 2012 WIN-Gallup Global Index of Religion and Atheism report, Afghanistan ranks among the countries where people are least likely to admit to being an atheist. Apostasy persecuted by Muslims Apostasy is a crime under the sharia of Afghanistan, quote: "Others point out that no one has been executed for apostasy in Afghanistan even under the Taleban ... two Afghan editors accused of blasphemy both faced the death sentence, but one claimed asylum abroad and the other was freed after a short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Zuckerman
Philip Joseph Zuckerman (born June 26, 1969) is a professor of sociology and secular studies at Pitzer College in Claremont, California. He specializes in the sociology of substantial secularity. He is the author of several books, including ''Living the Secular Life'' (2014), ''What It Means to be Moral'' (2019) and ''Society Without God'' (2008) for which he won ''ForeWord Magazine's'' silver book of the year award, and ''Faith No More'' (2011). Early life and education Born on June 26, 1969, to secular Ashkenazi Jewish parents in Los Angeles, California, Zuckerman grew up in Pacific Palisades and studied at Santa Monica College. He transferred to the University of Oregon in Eugene, and there earned a Bachelor of Arts (1992), Master of Arts (1995), and Doctor of Philosophy (1998), all in sociology. Career Zuckerman is a professor of sociology and secular studies at Pitzer College in Claremont, California. He is also an affiliated adjunct professor at Claremont Graduate Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentsu
Dentsu Inc. ( ja, 株式会社電通 ''Kabushiki-gaisha Dentsū'' or 電通 ''Dentsū'' for short) is a Japanese international advertising and public relations joint stock company headquartered in Tokyo. Dentsu is currently the largest advertising agency in Japan and the fifth largest advertising agency network in the world in terms of worldwide revenues. Dentsu does business with almost every major institution in Japan, accounting for about 28 percent of the national advertising budget. Its connections to the government are so tight that ''The New York Times'' referred to Dentsu as "the unofficial communications department of the governing Liberal Democratic Party", and it has also been likened to the CIA on account of its reach. History Dentsu was originally established as and by Hoshiro Mitsunaga. In 1906, Telegraphic Service Co. became . The next year, Japan Advertising Ltd. merged with Japan Telegraphic Communication Co., Ltd. to create advertising and communicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It also conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, random sample survey research and panel based surveys, media content analysis, and other empirical social science research. The Pew Research Center does not take policy positions, and is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts. History In 1990, the Times Mirror Company founded the Times Mirror Center for the People & the Press as a research project, tasked with conducting polls on politics and policy. Andrew Kohut became its director in 1993, and The Pew Charitable Trusts became its primary sponsor in 1996, when it was renamed the Pew Research Center for the People & the Press. In 2004, the trust established the Pew Research Center in Washington, D.C. In 2013, Kohut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pew Research Centre
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It also conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, random sample survey research and panel based surveys, media content analysis, and other empirical social science research. The Pew Research Center does not take policy positions, and is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts. History In 1990, the Times Mirror Company founded the Times Mirror Center for the People & the Press as a research project, tasked with conducting polls on politics and policy. Andrew Kohut became its director in 1993, and The Pew Charitable Trusts became its primary sponsor in 1996, when it was renamed the Pew Research Center for the People & the Press. In 2004, the trust established the Pew Research Center in Washington, D.C. In 2013, Kohut st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |