|
List Of Convexity Topics
This is a list of convexity topics, by Wikipedia page. * Alpha blending - the process of combining a translucent foreground color with a background color, thereby producing a new blended color. This is a convex combination of two colors allowing for transparency effects in computer graphics. * Barycentric coordinates - a coordinate system in which the location of a point of a simplex (a triangle, tetrahedron, etc.) is specified as the center of mass, or barycenter, of masses placed at its vertices. The coordinates are non-negative for points in the convex hull. * Borsuk's conjecture - a conjecture about the number of pieces required to cover a body with a larger diameter. Solved by Hadwiger for the case of smooth convex bodies. * Bond convexity - a measure of the non-linear relationship between price and yield duration of a bond to changes in interest rates, the second derivative of the price of the bond with respect to interest rates. A basic form of convexity in finance. * Carath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Blending
In computer graphics, alpha compositing or alpha blending is the process of combining one image with a background to create the appearance of partial or full transparency. It is often useful to render picture elements (pixels) in separate passes or layers and then combine the resulting 2D images into a single, final image called the composite. Compositing is used extensively in film when combining computer-rendered image elements with live footage. Alpha blending is also used in 2D computer graphics to put rasterized foreground elements over a background. In order to combine the picture elements of the images correctly, it is necessary to keep an associated ''matte'' for each element in addition to its color. This matte layer contains the coverage information—the shape of the geometry being drawn—making it possible to distinguish between parts of the image where something was drawn and parts that are empty. Although the most basic operation of combining two images is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap, or upper convex. Definition A real-valued function f on an interval (or, more generally, a convex set in vector space) is said to be ''concave'' if, for any x and y in the interval and for any \alpha \in ,1/math>, :f((1-\alpha )x+\alpha y)\geq (1-\alpha ) f(x)+\alpha f(y) A function is called ''strictly concave'' if :f((1-\alpha )x + \alpha y) > (1-\alpha) f(x) + \alpha f(y)\, for any \alpha \in (0,1) and x \neq y. For a function f: \mathbb \to \mathbb, this second definition merely states that for every z strictly between x and y, the point (z, f(z)) on the graph of f is above the straight line joining the points (x, f(x)) and (y, f(y)). A function f is quasiconcave if the upper contour sets of the function S(a)=\ are convex sets. Properties Functions of a single variable # A differentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenchel's Inequality
In mathematics and mathematical optimization, the convex conjugate of a function is a generalization of the Legendre transformation which applies to non-convex functions. It is also known as Legendre–Fenchel transformation, Fenchel transformation, or Fenchel conjugate (after Adrien-Marie Legendre and Werner Fenchel). It allows in particular for a far reaching generalization of Lagrangian duality. Definition Let X be a real topological vector space and let X^ be the dual space to X. Denote by :\langle \cdot , \cdot \rangle : X^ \times X \to \mathbb the canonical dual pairing, which is defined by \left( x^*, x \right) \mapsto x^* (x). For a function f : X \to \mathbb \cup \ taking values on the extended real number line, its is the function :f^ : X^ \to \mathbb \cup \ whose value at x^* \in X^ is defined to be the supremum: :f^ \left( x^ \right) := \sup \left\, or, equivalently, in terms of the infimum: :f^ \left( x^ \right) := - \inf \left\. This definition can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenchel Conjugate
In mathematics and mathematical optimization, the convex conjugate of a function is a generalization of the Legendre transformation which applies to non-convex functions. It is also known as Legendre–Fenchel transformation, Fenchel transformation, or Fenchel conjugate (after Adrien-Marie Legendre and Werner Fenchel). It allows in particular for a far reaching generalization of Lagrangian duality. Definition Let X be a real topological vector space and let X^ be the dual space to X. Denote by :\langle \cdot , \cdot \rangle : X^ \times X \to \mathbb the canonical dual pairing, which is defined by \left( x^*, x \right) \mapsto x^* (x). For a function f : X \to \mathbb \cup \ taking values on the extended real number line, its is the function :f^ : X^ \to \mathbb \cup \ whose value at x^* \in X^ is defined to be the supremum: :f^ \left( x^ \right) := \sup \left\, or, equivalently, in terms of the infimum: :f^ \left( x^ \right) := - \inf \left\. This definition can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Point
In mathematics, an extreme point of a convex set S in a real or complex vector space is a point in S which does not lie in any open line segment joining two points of S. In linear programming problems, an extreme point is also called vertex or corner point of S. Definition Throughout, it is assumed that X is a real or complex vector space. For any p, x, y \in X, say that p x and y if x \neq y and there exists a 0 < t < 1 such that If is a subset of and then is called an of if it does not lie between any two points of That is, if there does exist and such that and The set of all extreme points of is denoted by Generalizations If is a subset of a vector space then a linear s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraph (mathematics)
In mathematics, the epigraph or supergraph of a function f : X \to \infty, \infty/math> valued in the extended real numbers \infty, \infty= \R \cup \ is the set, denoted by \operatorname f, of all points in the Cartesian product X \times \R lying on or above its graph. The strict epigraph \operatorname_S f is the set of points in X \times \R lying strictly above its graph. Importantly, although both the graph and epigraph of f consists of points in X \times \infty, \infty the epigraph consists of points in the subset X \times \R, which is not necessarily true of the graph of f. If the function takes \pm \infty as a value then \operatorname f will be a subset of its epigraph \operatorname f. For example, if f\left(x_0\right) = \infty then the point \left(x_0, f\left(x_0\right)\right) = \left(x_0, \infty\right) will belong to \operatorname f but not to \operatorname f. These two sets are nevertheless closely related because the graph can always be reconstructed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duality (optimization)
In mathematical optimization theory, duality or the duality principle is the principle that optimization problems may be viewed from either of two perspectives, the primal problem or the dual problem. If the primal is a minimization problem then the dual is a maximization problem (and vice versa). Any feasible solution to the primal (minimization) problem is at least as large as any feasible solution to the dual (maximization) problem. Therefore, the solution to the primal is an upper bound to the solution of the dual, and the solution of the dual is a lower bound to the solution of the primal. This fact is called weak duality. In general, the optimal values of the primal and dual problems need not be equal. Their difference is called the duality gap. For convex optimization problems, the duality gap is zero under a constraint qualification condition. This fact is called strong duality. Dual problem Usually the term "dual problem" refers to the ''Lagrangian dual problem'' but other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convexity (finance)
In mathematical finance, convexity refers to non-linearities in a financial model. In other words, if the price of an underlying variable changes, the price of an output does not change linearly, but depends on the second derivative (or, loosely speaking, higher-order terms) of the modeling function. Geometrically, the model is no longer flat but curved, and the degree of curvature is called the convexity. Terminology Strictly speaking, convexity refers to the second derivative of output price with respect to an input price. In derivative pricing, this is referred to as Gamma (Γ), one of the Greeks. In practice the most significant of these is bond convexity, the second derivative of bond price with respect to interest rates. As the second derivative is the first non-linear term, and thus often the most significant, "convexity" is also used loosely to refer to non-linearities generally, including higher-order terms. Refining a model to account for non-linearities is referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Set
In geometry, a subset of a Euclidean space, or more generally an affine space over the reals, is convex if, given any two points in the subset, the subset contains the whole line segment that joins them. Equivalently, a convex set or a convex region is a subset that intersects every line into a single line segment (possibly empty). For example, a solid cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary of a convex set is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval with the property that its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polytope
A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set contained in the n-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^n. Most texts. use the term "polytope" for a bounded convex polytope, and the word "polyhedron" for the more general, possibly unbounded object. Others''Mathematical Programming'', by Melvyn W. Jeter (1986) p. 68/ref> (including this article) allow polytopes to be unbounded. The terms "bounded/unbounded convex polytope" will be used below whenever the boundedness is critical to the discussed issue. Yet other texts identify a convex polytope with its boundary. Convex polytopes play an important role both in various branches of mathematics and in applied areas, most notably in linear programming. In the influential textbooks of Grünbaum and Ziegler on the subject, as well as in many other texts in discrete geometry, convex polytopes are often simply called "polytopes". Grünbaum points out that this is solely to avo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polygon
In geometry, a convex polygon is a polygon that is the boundary of a convex set. This means that the line segment between two points of the polygon is contained in the union of the interior and the boundary of the polygon. In particular, it is a simple polygon (not self-intersecting). Equivalently, a polygon is convex if every line that does not contain any edge intersects the polygon in at most two points. A strictly convex polygon is a convex polygon such that no line contains two of its edges. In a convex polygon, all interior angles are less than or equal to 180 degrees, while in a strictly convex polygon all interior angles are strictly less than 180 degrees. Properties The following properties of a simple polygon are all equivalent to convexity: *Every internal angle is strictly less than 180 degrees. *Every point on every line segment between two points inside or on the boundary of the polygon remains inside or on the boundary. *The polygon is entirely contained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
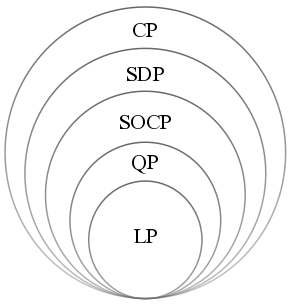
Convex Optimization
Convex optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets (or, equivalently, maximizing concave functions over convex sets). Many classes of convex optimization problems admit polynomial-time algorithms, whereas mathematical optimization is in general NP-hard. Convex optimization has applications in a wide range of disciplines, such as automatic control systems, estimation and signal processing, communications and networks, electronic circuit design, data analysis and modeling, finance, statistics ( optimal experimental design), and structural optimization, where the approximation concept has proven to be efficient. With recent advancements in computing and optimization algorithms, convex programming is nearly as straightforward as linear programming. Definition A convex optimization problem is an optimization problem in which the objective function is a convex function and the feasibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |