|
List Of Challenge Awards
This list of challenge awards is an index to articles about notable challenge awards, or inducement prize contests. A cash prize is given for the accomplishment of a feat, usually of engineering. Offered before 1900 Offered in 20th century Offered in 21st century See also * Inducement prize contest * Space elevator competitions * Competitions and prizes in biotechnology * Data science competition platform * Lists of awards Lists of awards cover awards given in various fields, including arts and entertainment, sports and hobbies, the humanities, science and technology, business, and service to society. A given award may be found in more than one list. Awards may be ... References {{reflist Challenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansari X-Prize Check
Ansari may refer to: People *Ansar (Islam), an Islamic term that literally means "helpers" and denotes the Medinan citizens that helped the Islamic prophet Muhammad after the Hijra *Ansari (nesba), people known as Ansari or Al-Ansari as a nesba *Ansari (surname), contemporary people known as Ansari or Al-Ansari as a surname **Banu Aws, one of the main Arab tribes of Medina which, along with the Khazraj, constituted the Ansar ("helpers") *Momin Ansari, a Muslim community, found mainly in the world and West and North India and the province of Sindh in Pakistan *Ansari, an alternate term for Alawites or Alawis Places *Ansari mountains, in Syria * Ansariye, Lebanon, a town in South Lebanon *Dupuk Ansari, a village in Khuzestan Province, Iran Other uses * Ansari X Prize, a former space competition *Ansar Imam Mahdi, a 21st-century Shia movement that believes Ahmad al-Hassan is the messenger of the 12th imam See also * Ansar (other) * Ansari (surname) Ansari or Al Ansari i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Mail
The ''Daily Mail'' is a British daily middle-market tabloid newspaper and news websitePeter Wilb"Paul Dacre of the Daily Mail: The man who hates liberal Britain", ''New Statesman'', 19 December 2013 (online version: 2 January 2014) published in London. Founded in 1896, it is the United Kingdom's highest-circulated daily newspaper. Its sister paper ''The Mail on Sunday'' was launched in 1982, while Scottish and Irish editions of the daily paper were launched in 1947 and 2006 respectively. Content from the paper appears on the MailOnline website, although the website is managed separately and has its own editor. The paper is owned by the Daily Mail and General Trust. Jonathan Harmsworth, 4th Viscount Rothermere, a great-grandson of one of the original co-founders, is the current chairman and controlling shareholder of the Daily Mail and General Trust, while day-to-day editorial decisions for the newspaper are usually made by a team led by the editor, Ted Verity, who succeede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kremer Prize
The Kremer prizes are a series of monetary awards, established in 1959 by the industrialist Henry Kremer. Royal Aeronautical Society Human Powered Flight Group The Royal Aeronautical Society's "Man Powered Aircraft Group" was formed in 1959 by the members of the Man Powered Group of the College of Aeronautics at Cranfield when they were invited to join the Society. Its title was changed from "Man" to "Human" in 1988 because of the many successful flights made by female pilots. Under the auspices of the Society, in 1959 the industrialist Henry Kremer offered the first Kremer prizes of £5,000 for the first human-powered aircraft to fly a figure-of-eight course round two markers half-a-mile apart. It was conditional that the designer, entrant pilot, place of construction and flight must all be British. In 1973 Kremer increased the prize to £50,000 and opened it to all nationalities, to stimulate interest. The first Kremer prize of £50,000 was won on 23 August 1977 by Dr. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Knuth
Donald Ervin Knuth ( ; born January 10, 1938) is an American computer scientist, mathematician, and professor emeritus at Stanford University. He is the 1974 recipient of the ACM Turing Award, informally considered the Nobel Prize of computer science. Knuth has been called the "father of the analysis of algorithms". He is the author of the multi-volume work ''The Art of Computer Programming'' and contributed to the development of the rigorous analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms and systematized formal mathematical techniques for it. In the process, he also popularized the asymptotic notation. In addition to fundamental contributions in several branches of theoretical computer science, Knuth is the creator of the TeX computer typesetting system, the related METAFONT font definition language and rendering system, and the Computer Modern family of typefaces. As a writer and scholar, Knuth created the WEB and CWEB computer programming systems designed to encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
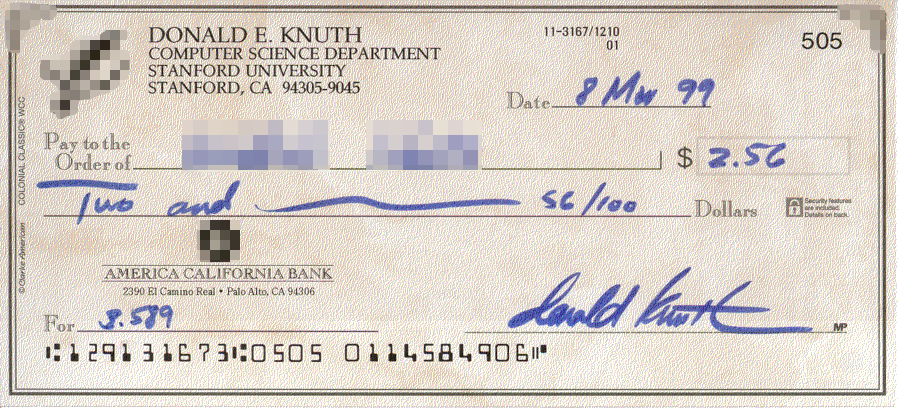
Knuth Reward Check
Knuth reward checks are checks or check-like certificates awarded by computer scientist Donald Knuth for finding technical, typographical, or historical errors, or making substantial suggestions for his publications. The ''MIT Technology Review'' describes the checks as "among computerdom's most prized trophies". History Initially, Knuth sent real, negotiable checks to recipients. He stopped doing so in October 2008 because of problems with check fraud. As a replacement, he started his own "Bank of San Serriffe", in the fictional nation of San Serriffe, which keeps an account for everyone who found an error since 2006. Knuth now sends out "hexadecimal certificates" instead of negotiable checks. , Knuth reported having written more than 2,000 checks, with an average value exceeding $8 per check.Donald Knuth (2002),All questions answered", ''Notices of the AMS'' 49(3): 318-324. , the total value of the checks signed by Knuth was over $20,000. Very few of these checks were actually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army CCDC Ground Vehicle Systems Center
The United States Army DEVCOM Ground Vehicle Systems Center (GVSC) (formerly United States Army Tank Automotive Research, Development and Engineering Center (TARDEC)), located in Warren, Michigan, is the United States Armed Forces' research and development facility for advanced technology in ground systems. It is part of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command (DEVCOM), a major subordinate command of the U.S. Army Futures Command. GVSC shares its facilities with the United States Army Tank-automotive and Armaments Command (TACOM). Current technology focus areas include Ground Vehicle Power and Mobility (GVPM), Ground System Survivability and Force Protection, among others. Laboratories It features a number of research laboratories, including: * Laser Protection Laboratory * Crew Station Systems Integration Laboratory * Robotic Systems Integration Laboratory * Ground Vehicle Simulation Laboratory — ride motion simulator, pintle motion based simulator, crew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Ground Vehicle Competition
The Intelligent Ground Vehicle Competition (IGVC) is an annual international robotics competition for teams of undergraduate and graduate students. Teams design and build an autonomous ground vehicle capable of completing several difficult challenges. The competition is well suited to senior design “capstone” courses as well as extracurricular design projects. The competition has taken place each year since 1993. The competition is normally held on the campus of Oakland University in Rochester, Michigan, although it has occasionally moved to other venues within the state of Michigan. Approximately 40 teams typically participate in this competition. Competition Overview The details of the competition change from year to year. In 2010 the competition included the following four events.“Official Competition Rules” retrieved from http://www.igvc.org/rules.html on July 31, 2010. # Design Competition: The design competition includes a written design report, an oral presentatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foresight Institute
The Foresight Institute (Foresight) is a San Francisco-based research non-profit that promotes the development of nanotechnology and other emerging technologies, such as safe AGI, biotech and longevity. Foresight runs four cross-disciplinary program tracks to research, advance, and govern maturing technologies for the long-term benefit of life and the biosphere: Molecular machines nanotechnology for building better materials, biotechnology for health extension, and computer science and crypto commerce for intelligent global cooperation. Foresight also runs a program on "existential hope", pushing forward the concept coined by Toby Ord and Owen Cotton-Barrett in their 2015 paper "Existential risk and Existential hope: Definitions", in which they wrote Foresight's stated strategy is to focus on creating a community that promotes beneficial uses of new technologies and reduce misuse and accidents potentially associated with them. Foresight runs a one-year Fellowship program aime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feynman Prize In Nanotechnology
The Feynman Prize in Nanotechnology is an award given by the Foresight Institute for significant advances in nanotechnology. Two prizes are awarded annually, in the categories of experimental and theoretical work. There is also a separate challenge award for making a nanoscale robotic arm and 8-bit adder. Overview The Feynman Prize consists of annual prizes in experimental and theory categories, as well as a one-time challenge award. They are awarded by the Foresight Institute, a nanotechnology advocacy organization. The prizes are named in honor of physicist Richard Feynman, whose 1959 talk ''There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom'' is considered by nanotechnology advocates to have inspired and informed the start of the field of nanotechnology. The annual Feynman Prize in Nanotechnology is awarded for pioneering work in nanotechnology, towards the goal of constructing atomically precise products through molecular machine systems. Input on prize candidates comes from both F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Erdős
Paul Erdős ( hu, Erdős Pál ; 26 March 1913 – 20 September 1996) was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered around discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics. Erdős published around 1,500 mathematical papers during his lifetime, a figure that remains unsurpassed. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erdős Problems
Erdős, Erdos, or Erdoes is a Hungarian surname. People with the surname include: * Ágnes Erdős (born 1950), Hungarian politician * Brad Erdos (born 1990), Canadian football player * Éva Erdős (born 1964), Hungarian handball player * József Erdős (born 1977), Hungarian entomologist * Mary Callahan Erdoes (born 1967), American banker * Paul Erdős (1913–1996), Hungarian mathematician * Richárd Erdős (1881–1912), Jewish Hungarian bass opera singer, father of Richard Erdoes * Richard Erdoes (1912–2008), Hungarian-Austrian born American artist * Sándor Erdős (born 1947), Hungarian fencer * Thomas Erdos (born 1965), Brazilian auto racing driver * Todd Erdos (born 1973), American middle-relief pitcher * Viktor Erdős (born 1987), Hungarian chess grandmaster See also * Erdő * Erdődy The House of Erdődy de Monyorókerék et Monoszló (also House of Erdödy) is the name of an old Hungarian- Croatian noble family with possessions in Hungary and Croatia. Eleva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dole
James Drummond Dole (September 27, 1877 – May 20, 1958), also known as the "Pineapple King", was an American industrialist who developed the pineapple industry in Hawaii. He established the Hawaiian Pineapple Company (HAPCO) which was later reorganized to become the Dole Food Company and now operates in over 90 countries. Dole was a cousin (once removed) of Sanford B. Dole, President of the Republic of Hawaii. Early life James Dole was born on September 27, 1877, in Jamaica Plain, Massachusetts (now part of Boston), to an American Puritan family long settled in the country since colonial America times. His father was Charles Fletcher Dole, a Unitarian minister, and his mother was Frances Drummond. His paternal great-grandfather was Wigglesworth Dole (1779–1845). His maternal grandfather was also a clergyman, James Drummond. Growing up, Dole attended Roxbury Latin School in Roxbury, Massachusetts, from which he graduated. In 1899, Dole obtained his bachelor's degree in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |