|
List Of Cathedrals In Lithuania
This is the list of cathedrals in Lithuania sorted by Christian denominations, denomination. Roman Catholic Cathedrals of the Roman Catholicism in Lithuania, Roman Catholic Church in Lithuania:GCatholic.orgCathedrals Lithuania/ref> Eastern Orthodox Cathedrals of the Russian Orthodox Church: See also *List of cathedrals *List of cathedrals in Estonia *List of cathedrals in Latvia *List of cathedrals in Poland References {{Europe topic, List of cathedrals in, countries_only=yes Cathedrals in Lithuania, * Lists of cathedrals, Lithuania Lists of religious buildings and structures in Lithuania, Cathedrals Lists of tourist attractions in Lithuania, Cathedrals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedrals
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations with an episcopal hierarchy, such as the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches.New Standard Encyclopedia, 1998 by Standard Educational Corporation, Chicago, Illinois; page B-262c Church buildings embodying the functions of a cathedral first appeared in Italy, Gaul, Spain, and North Africa in the 4th century, but cathedrals did not become universal within the Western Catholic Church until the 12th century, by which time they had developed architectural forms, institutional structures, and legal identities distinct from parish churches, monastic churches, and episcopal residences. The cathedral is more important in the hierarchy than the church because it is from the cathedral that the bishop governs the area und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panevėžys
Panevėžys (; Latin: ''Panevezen''; pl, Poniewież; yi, פּאָנעװעזש, ''Ponevezh''; see also other names) is the fifth largest city in Lithuania. As of 2011, it occupied with 113,653 inhabitants. As defined by Eurostat, the population of Panevėžys functional urban area, that stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 127,471 (as of 2017) The largest multifunctional arena in Panevėžys, Cido Arena, hosted the Eurobasket 2011 group matches. The city is still widely known, if indirectly, in the Jewish world, for the eponymous Ponevezh Yeshiva. Coat of arms Historical facts allow to state that the first seal of the city of Panevėžys appeared when the city self-government was established. It is clear that until the end of the 18th century, Panevėžys did not have the right of self-government, therefore it could not had its coat of arms. All the preconditions for the establishment of self-government arose during the period of the Four-year Seimas (1788–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Vilkaviškis
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilkaviškis
Vilkaviškis () is a city in southwestern Lithuania, the administrative center of the Vilkaviškis District Municipality. It is located northwest from Marijampolė, at the confluence of of and rivers. The city got its name from the Vilkauja River. Initially named ''Vilkaujiškis'' the name was later changed to an easier-to-pronounce form, ''Vilkaviškis''. Until 1941 the city had a large Jewish community, which was killed by the German military and their local collaborators. This is the town from which the 2016 cost-of-living Cauliflower Revolution originated. Names The names of the town as it is called or was formerly called in other languages spoken by non-Lithuanian ethnic groups which have lived or live in or around the town include: pl, Wyłkowyszki; yi, Vilkovishk; german: Wilkowischken. Other spelling variants include ''Vilkavishkis'' and ''Wilkowyszki''. History The town was granted city rights in 1660 by the King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
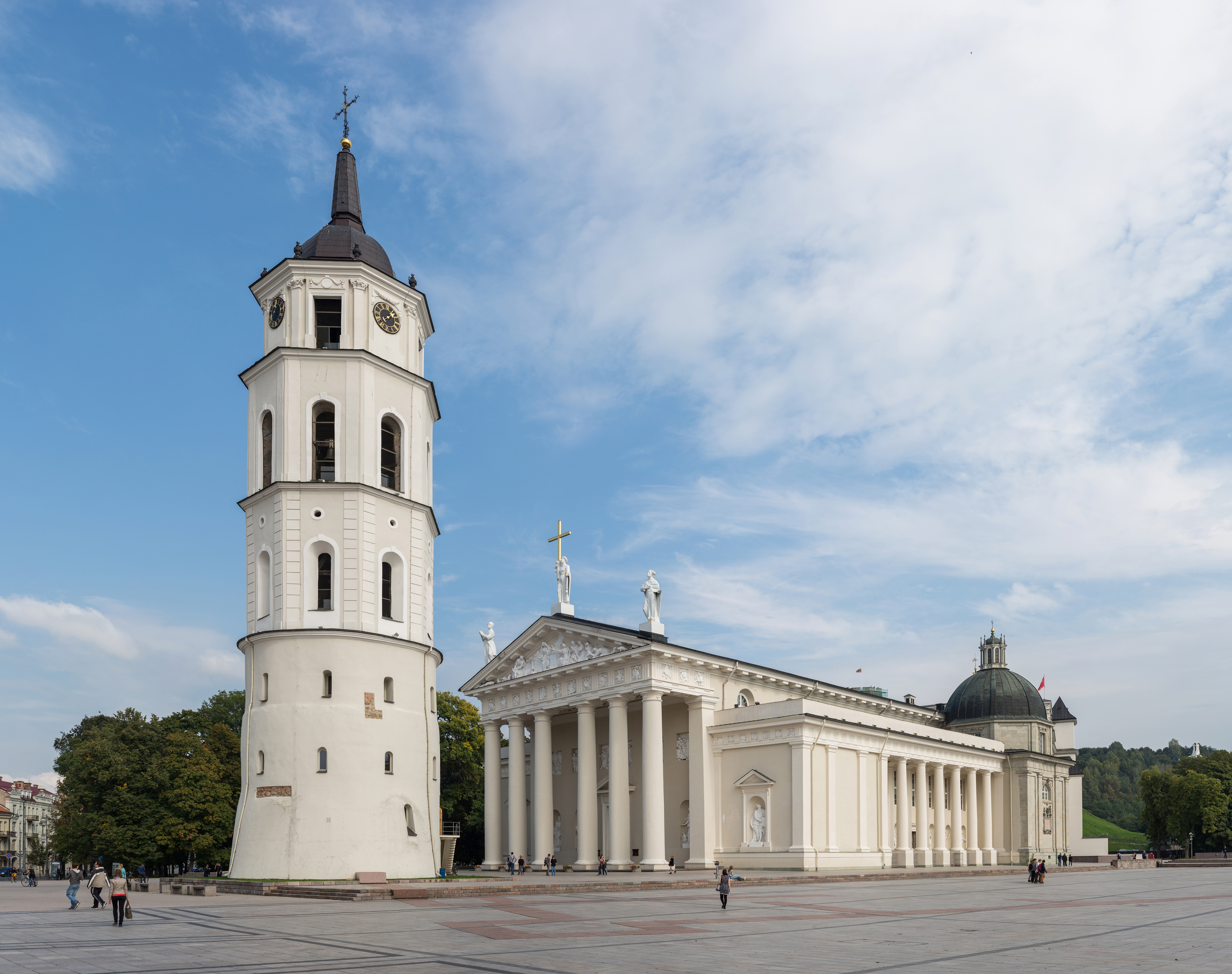
Vilkaviškis Cathedral
The Cathedral of the Visitation ( lt, Švč. M. Marijos Apsilankymo katedra) also called Vilkaviškis Cathedral is a religious building of the Catholic Church that serves as the cathedral of Vilkaviškis, Lithuania, and is the seat of the Diocese of Vilkaviškis. The church was built in Romanesque style, between 1870 and 1881 and was consecrated in 1884. With the erection of the Diocese of Vilkaviškis in 1926, the church was elevated to the rank of cathedral. The building suffered no major damage during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ..., however, the Russian authorities authorized their gradual dismantling to use their materials for civil construction. After the fall of communism in the country the cathedral was rebuilt from 1991 and the works were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telšiai Cathedral Exterior, Telšiai, Lithuania - Diliff
Telšiai (; Samogitian: ''Telšē'') is a city in Lithuania with about 21,499 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on the shores of Lake Mastis. Telšiai is one of the oldest cities in Lithuania, probably dating earlier than the 14th century. Between the 15th and 20th centuries, Telšiai became a district capital and between 1795 and 1802 it was included in the Vilnius Governorate. In 1873, Telšiai was transferred to the Kovno Governorate. Names The name Telšiai is a variant of the same Lithuanian language root (''-telš-'', ''-tilž-'') as Tilžė with the meaning connected to water. The name Telšiai or Telšē in Samogitian dialect of Lithuanian is derived from a verb ''telkšoti'' (literally, ''to be flooded with water'', ''to splash'', etc.). The name of Telšiai has been recorded in different forms and different languages throughout its history. Most of them are derived from ''Telšē'' in Samogitian dialect. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Telšiai
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telšiai
Telšiai (; Samogitian: ''Telšē'') is a city in Lithuania with about 21,499 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on the shores of Lake Mastis. Telšiai is one of the oldest cities in Lithuania, probably dating earlier than the 14th century. Between the 15th and 20th centuries, Telšiai became a district capital and between 1795 and 1802 it was included in the Vilnius Governorate. In 1873, Telšiai was transferred to the Kovno Governorate. Names The name Telšiai is a variant of the same Lithuanian language root (''-telš-'', ''-tilž-'') as Tilžė with the meaning connected to water. The name Telšiai or Telšē in Samogitian dialect of Lithuanian is derived from a verb ''telkšoti'' (literally, ''to be flooded with water'', ''to splash'', etc.). The name of Telšiai has been recorded in different forms and different languages throughout its history. Most of them are derived from ''Telšē'' in Samogitian dialect. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telšiai Cathedral
The Cathedral of St. Anthony of Padua ( lt, Telšių Šv. Antano Paduviečio katedra) is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Telšiai, Lithuania, seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Telšiai. History The history of the church dates back to 1624 when Deputy Chancellor of Lithuania Paweł Stefan Sapieha established a Franciscan monastery and built a wooden church on the Insula hill in the centre of Telšiai. A new spacious brick church was constructed between 1762 and 1794. It was consecrated in 1794 by the suffragan bishop of Samogitia, Fr Tadeusz Józef Bukaty ( lt, Tadas Juozapas Bukota). In 1802 renowned Vilnius architect Jan Boretti obliged to construct two towers and a narthex. However, due to unknown reasons he built only the narthex and failed to complete the work of towers. Franciscan monastery was dissolved in 1853 by the Russian tsar and the church became parish church. Romualdas Leščevskis became the first secular parish priest in 1854. The tower was built in 1859. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šiauliai 03
Šiauliai (; bat-smg, Šiaulē; german: Schaulen, ) is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 107,086. From 1994 to 2010 it was the capital of Šiauliai County. Names Šiauliai is referred to by various names in different languages: Samogitian ''Šiaulē'', Latvian ''Saule'' (historic) and ''Šauļi'' (modern), German (outdated) ''Schaulen'', Polish ''Szawle'', Russian Шавли (Shavli – historic) and Шяуля́й (Shyaulyai – modern), Yiddish שאַװל (Shavel). History The city was first mentioned in written sources as ''Soule'' in Livonian Order chronicles describing the Battle of Saule. Thus the city's founding date is now considered to be 22 September 1236, the same date when the battle took place, not far from Šiauliai. At first, it developed as a defence post against the raids by the Teutonic and Livonian Orders. After the Battle of Grunwald in 1410, the raids stopped and Šiauliai started to develop as an agricultural settlement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Šiauliai
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šiauliai
Šiauliai (; bat-smg, Šiaulē; german: Schaulen, ) is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 107,086. From 1994 to 2010 it was the capital of Šiauliai County. Names Šiauliai is referred to by various names in different languages: Samogitian ''Šiaulē'', Latvian ''Saule'' (historic) and ''Šauļi'' (modern), German (outdated) ''Schaulen'', Polish ''Szawle'', Russian Шавли (Shavli – historic) and Шяуля́й (Shyaulyai – modern), Yiddish שאַװל (Shavel). History The city was first mentioned in written sources as ''Soule'' in Livonian Order chronicles describing the Battle of Saule. Thus the city's founding date is now considered to be 22 September 1236, the same date when the battle took place, not far from Šiauliai. At first, it developed as a defence post against the raids by the Teutonic and Livonian Orders. After the Battle of Grunwald in 1410, the raids stopped and Šiauliai started to develop as an agricultural settlement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |