|
List Of Bioluminescent Organisms
Bioluminescence is the production of light by living organisms. This list of bioluminescent organisms is organized by the environment, covering terrestrial, marine, and microorganisms. Terrestrial animals * flying squirrel *certain arthropods **fireflies **click beetle specific types (e.g. Pyrophorini, '' Balgus'', '' Campyloxenus'', etc.) ** glow worms ***railroad worms **certain mycetophilid flies **certain centipedes such as ''Geophilus carpophagus'' **certain millipedes such as '' Motyxia'' *a terrestrial mollusc (a tropical land snail) **''Quantula striata'' * annelids Marine animals Fish * Anglerfish * Gulper eel *Lanternfish *Marine hatchetfish *Midshipman fish * Pineconefish *Viperfish * Black dragonfish Invertebrates *Many cnidarians **Sea pens *** '' Renilla reniformis'' **coral **''Aequorea victoria'', a jellyfish *Certain Ctenophores or "comb jellies" *Certain echinoderms (e.g. Ophiurida) ** '' Amphiura filiformis'' ** '' Ophiopsila aranea'' ** '' Ophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omphalotus Nidiformis
''Omphalotus nidiformis'', or ghost fungus, is a gilled basidiomycete mushroom most notable for its bioluminescent properties. It is known to be found primarily in southern Australia and Tasmania, but was reported from India in 2012 and 2018. The fan or funnel shaped fruit bodies are up to across, with cream-coloured caps overlain with shades of orange, brown, purple, or bluish-black. The white or cream gills run down the length of the stipe, which is up to long and tapers in thickness to the base. The fungus is both saprotrophic and parasitic, and its fruit bodies are generally found growing in overlapping clusters on a wide variety of dead or dying trees. First described scientifically in 1844, the fungus has been known by several names in its taxonomic history. It was assigned its current name by Orson K. Miller, Jr. in 1994. Its epithet name is derived from the Latin ''nidus'' "nest", hence 'nest shaped'. Similar in appearance to the common edible oyster mushroom, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millipede
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from the Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery of ''Eumillipes persephone'', which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures. Most millipedes are slow-moving detritivores, eating decaying leaves and other dead plant matter. Some eat fungi or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiacanthus Atlanticus
''Idiacanthus atlanticus'', the black dragonfish, is a barbeled dragonfish of the family Stomiidae, found circumglobally in southern subtropical and temperate oceans between latitudes 25°S and 60°S, at depths down to . The species is sexually dimorphic: females are black with six stripes; males are brown, and lack the females' canine teeth, pelvic fins and barbel. Females are believed to make a diel vertical migration from deeper than by day to surface waters at night, whereas males do not migrate, remaining below at all times. Length is up to for the female, but only for the male. Black dragonfish are bioluminescent, but unlike most such predators, which use their light primarily to attract prey, they can see their own light. As a result, the fish can use their light to hunt. The light is nearly in the infrared Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viperfish
A viperfish is any species of marine fish in the genus ''Chauliodus''. Viperfishes are mostly found in the mesopelagic zone and are characterized by long, needle-like teeth and hinged lower jaws. A typical viperfish grows to lengths of . Viperfishes undergo diel vertical migration and are found all around the world in tropical and temperate oceans. Viperfishes possess photophores along the ventral side of their body, likely used to camouflage them by blending in with the less than 1% of light that reaches to below 200 meters depth. Although it may appear to be covered in scales, viperfishes do not possess scales. Rather, they are covered by a thick, transparent coating of unknown substance. Extremely large, fang-like teeth give the fish a slightly protruded lower jaw. Habitat Viperfishes live in meso- and bathypelagic environments where humans cannot easily make direct observations. Viperfishes engage in diel vertical migration, meaning they migrate up into more productive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineconefish
Pinecone fishes are small and unusual marine fish of the family ''Monocentridae''. The family contains just four species in two genera, one of which is monotypic. Their distribution is limited to tropical and subtropical waters of the Indo-Pacific. Pinecone fishes are popular subjects of public aquaria, but are both expensive and considered a challenge for the hobbyist to maintain. Description These fish are aptly named; their rounded, compressed bodies are completely covered (with the exception of the caudal peduncle) with very large, strong, platelike scales called scutes, which are fortified with prominent ridges. The first dorsal fin is composed of four to seven strong, disunited spines which vary in length; the second dorsal fin and anal fin are small, spineless and rounded, situated far back of the convex head. The pectoral fins are somewhat elongate and the caudal fin is truncate. Coloration is typically a yellow to orange, with the scales dramatically outlined in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midshipman Fish
A midshipman fish is any species of toadfish belonging to the genus ''Porichthys'' (in family Batrachoididae). Midshipman fish are distinguished by their photophores (organs which attract prey and after which they are named, being said to resemble the buttons of a naval uniform) and four lateral lines. Typical midshipman fishes, such as the plainfin midshipman (''Porichthys notatus''), are nocturnal and bury themselves in sand or mud in the intertidal zone during the day. At night they float just above the seabed. Some species have venomous dorsal spines and are capable of inflicting serious injuries if handled. Description Male midshipman fish have two morphs: type I and type II. Type I and type II males have different reproductive strategies, and can be distinguished from each other based on physical characteristics. Type I males are eight times larger in body mass, and have much larger vocal organs. Type II males’ reproductive organs are seven times larger in size than tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Hatchetfish
Marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes are small deep-sea mesopelagic ray-finned fish of the stomiiform subfamily Sternoptychinae. They should not be confused with the freshwater hatchetfishes, which are not particularly closely related Teleostei in the characiform family Gasteropelecidae. (2006): '' Fishes of the World'' (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p.209 The scientific name means "''Sternoptyx''-subfamily", from '' Sternoptyx'' (the type genus) + the standard animal family suffix "-inae". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''stérnon'' (στέρνον, "breast") + ''ptýx'' (πτύξ, "a fold/crease") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the Greek part in reference to the thorax shape of marine hatchetfishes. (2006)Family Sternoptychidae Version of 2006-OCT-10. Retrieved 2009-OCT-02. Description and ecology Found in tropical, subtropical and temperate waters of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, marine hatchetfishes range in size from ''Polyip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanternfish
Lanternfishes (or myctophids, from the Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represented by 246 species in 33 genera, and are found in oceans worldwide. Lanternfishes are aptly named after their conspicuous use of bioluminescence. Their sister family, the Neoscopelidae, are much fewer in number but superficially very similar; at least one neoscopelid shares the common name "lanternfish": the large-scaled lantern fish, '' Neoscopelus macrolepidotus''. Lanternfish are among the most widely distributed, diverse and populous vertebrates, with some estimates suggesting that they may have a total global biomass of 1.8 to 16 gigatonnes, accounting for up to 65% of all deep-sea fish biomass. Commercial fisheries for them exist off South Africa, in the sub-Antarctic, and in the Gulf of Oman. Description Lanternfish typically ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulper Eel
The saccopharyngiformes are a derived lineage of unusual eels within the order Anguilliformes, and includes families Cyematidae, Monognathidae, Eurypharyngidae, Saccopharyngidae, and the proposed family Neocyematidae. Most of the fish in this group are deep-dwelling and rarely seen, typically known from only a handful of specimens. Species include recognizable fish such as pelican eels, bobtail eels, and gulper eels. Some can live deep in the ocean, well into the aphotic zone, approximately 500–1800 meters deep. Extensive research has not been conducted on them due to being indirectly observed, with some species known only from their larvae. All families except for the exceptionally rare individuals of proposed family Neoceymatidae (known only from the Atlantic Ocean) are found in all major oceans. Description They have multiple internal differences from the rest of Anguilliformes. Notably, they have no symplectic bone, opercular bones, ribs, or swim bladders. Like many ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
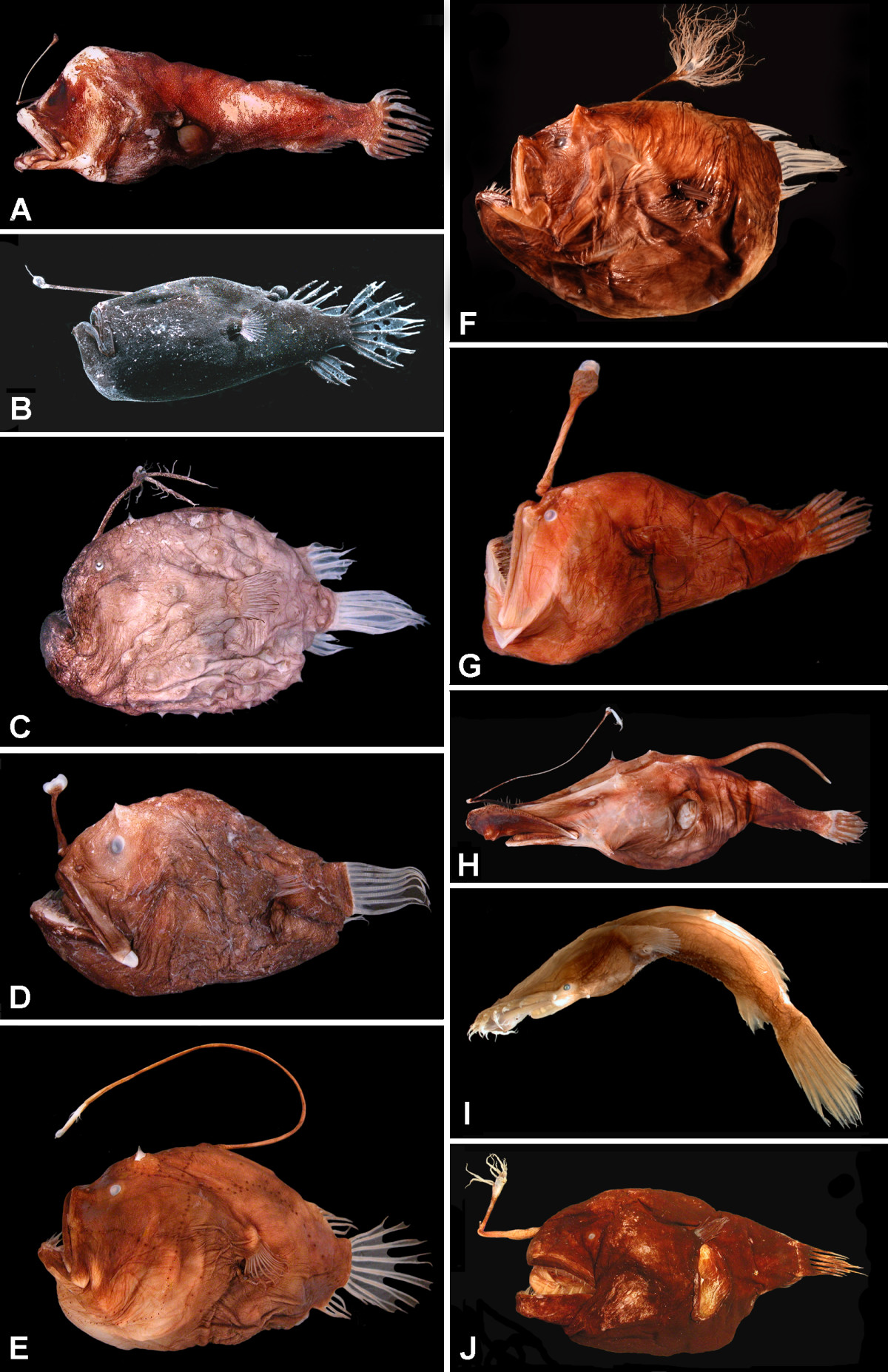
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of polycha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantula Striata
''Quantula striata'', also known as ''Dyakia striata'', is a species of medium-sized, air-breathing, tropical land snail. It is a terrestrial, pulmonate, gastropod mollusk in the family Dyakiidae. This species appears to be unique among terrestrial gastropods in that it is bioluminescent: Its eggs glow in the dark, and juveniles and most adults give off flashes of green light. It is the only species in the genus ''Quantula''.Tumpeesuwan C., Naggs F. & Panha S. (31 August 2007) "A new genus and new species of dyakiid snail (Pulmonata: Dyakiidae) from the Phu Phan range, northeastern Thailand". ''Raffles Bulletin of Zoology'55(2): 363-369PDF/ref> Distribution This species occurs in Singapore, Malaysia,Daston M. M. & Copeland J. (1993) "The luminescent organ and sexual maturity in ''Dyakia striata''". ''Malacologia'' 35(1):919abstract/ref> Cambodia, the Philippines, Fiji, and some islands in the Rhio Archipelago. Shell description The shell of this species is dextral (right-han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)