|
List Of World Heritage Sites In India
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) designates World Heritage Sites of outstanding universal value to cultural or natural heritage which have been nominated by countries which are signatories to the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty, are defined as natural heritage. India accepted the convention on 14 November 1977, making its sites eligible for inclusion on the list. , there are 40 World Heritage Sites located in India. Out of these, 32 are cultural, 7 are natural, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain " cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Victorian And Art Deco Ensemble Of Mumbai
The Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Bombay is a collection of 19th-century Victorian Revival public and 20th-century Mumbai Art Deco private buildings in the Fort precinct of Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. This ensemble was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2018. This buildings are set around the Oval Maidan, a large recreational ground that was once known as the Esplanade. The east of the Oval is flanked by the Victorian Gothic public buildings and the western side is flanked by the Art Deco buildings of Back bay Reclamation and Marine Drive. This nomination aims to safeguard a total of 94 buildings. The 19th century Victorian Gothic buildings that lie to the east of the Oval are mainly the Mumbai High Court, The University of Mumbai (Fort Campus) and The City Civil and Sessions Court (Housed in the Old Secretariat Building). This stretch also houses one of the landmarks of Mumbai, the Rajabai Clock Tower. The 20th century Art Deco buildings flank the western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
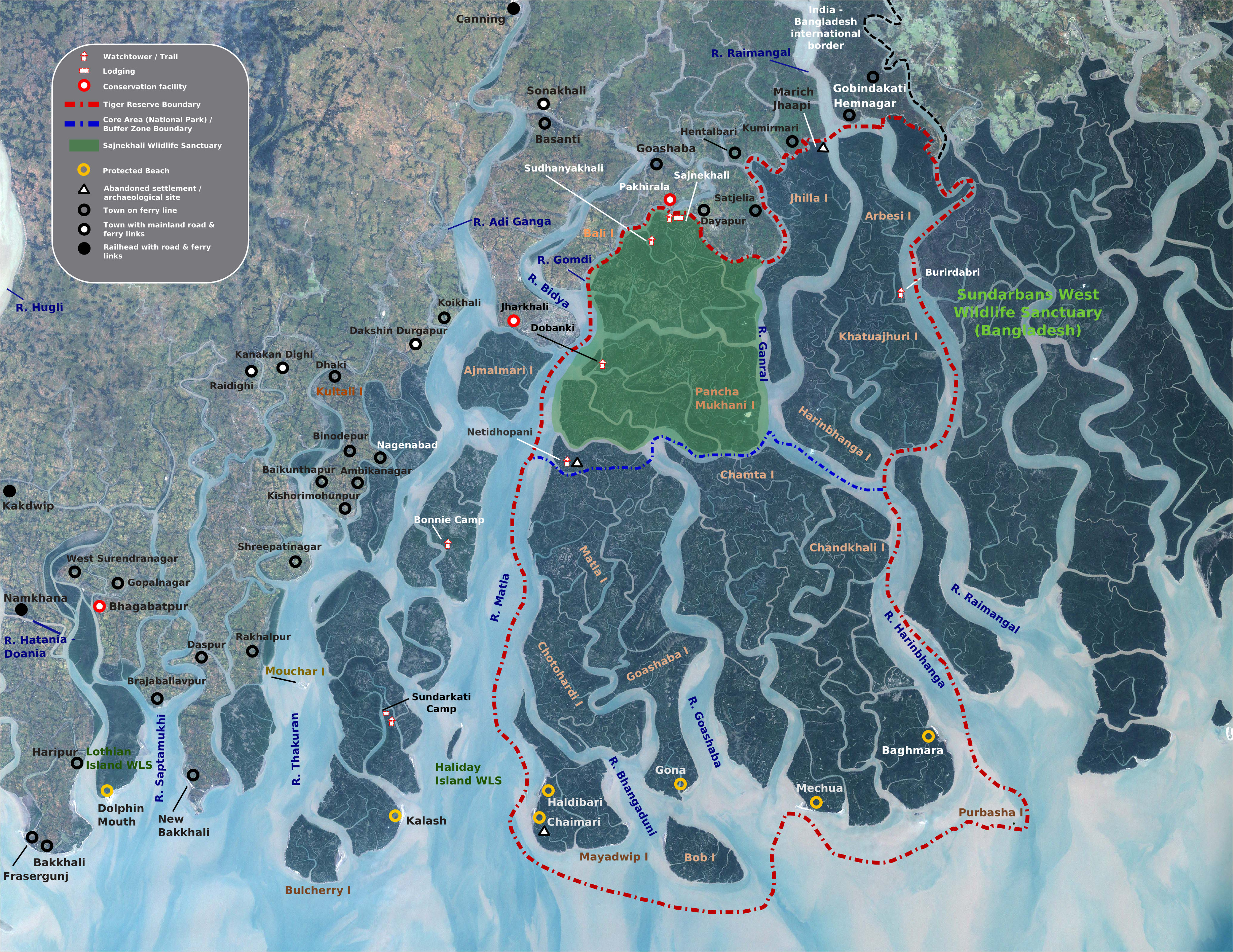
Sundarbans National Park
The Sundarbans National Park is a national park, tiger reserve and biosphere reserve in West Bengal, India. It is part of the Sundarbans on the Ganges Delta and adjacent to the Sundarban Reserve Forest in Bangladesh. It is located to south-west of the Bangladesh. The delta is densely covered by mangrove forests, and is one of the largest reserves for the Bengal tiger. It is also home to a variety of bird, reptile and invertebrate species, including the salt-water crocodile. The present Sundarban National Park was declared as the core area of Sundarban Tiger Reserve in 1973 and a wildlife sanctuary in 1977. On 4 May 1984 it was declared a national park. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site inscribed in 1987, and it has been designated as a Ramsar site since 2019. It is considered as a World Network of Biosphere Reserve (Man and Biosphere Reserve) from 1989. The first forest management division to have jurisdiction over the Sundarbans was established in 1869. In 1875 a large por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanda Devi And Valley Of Flowers National Parks
The Nanda Devi National Park and Valley of Flowers National Parks is an UNESCO World Heritage Site in Uttarakhand, India. It possesses of two core areas about 20 km apart, made up by the Nanda Devi National Park and the Valley of Flowers National Park, plus an encompassing Combined Buffer Zone. In 1988 the site was inscribed as ''Nanda Devi National Park (India)''. In 2005 it was expanded to encompass the Valley of Flowers National Park Valley of Flowers National Park is an Indian National parks of India, national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of Endemism, endemic alpine flowers and the var ... and a larger buffer zone and it was renamed to ''Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks''. The areas of the site are * - Nanda Devi National Park core area * - Valley of Flowers National Park core area * - Buffer zone References {{Uttarakhand 1988 establishments in Uttar Prades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic City Of Ahmadabad
The Historic City of Ahmadabad or Old Ahmedabad, the walled city of Ahmedabad in India, was founded by Ahmad Shah I of the Gujarat Sultanate in 1411. It remained the capital of the state of Gujarat for six centuries and later became the important political and commercial centre of Gujarat. Today, despite having become crowded and dilapidated, it still serves as the symbolic heart of metropolitan Ahmedabad. It was inscribed as the World Heritage City by UNESCO in July 2017. History The earliest settlements were situated south of the current old city and on the bank of Sabarmati river. It was known as Ashaval or Ashapalli. In the 11th century, Karna of the Chaulukya dynasty made the town his capital and named it Karnavati (Karna's town), Shrinagar (prosperous city), and Rajnagar (king's town). Ahmed Shah I laid the foundation of Bhadra Fort starting from Manek Burj, the first bastion of the city in 1411 which was completed in 1413. He also established the first square of the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konark Sun Temple
Konark Sun Temple is a (year 1250) Sun temple at Konark about northeast from Puri city on the coastline in Puri district, Odisha, India.Konark: India , Encyclopædia Britannica The temple is attributed to king of the about . Dedicated to the Hindu Sun God , what remains of the temple complex has the appearance of a high chariot with immense wheels and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Of Monuments At Pattadakal
Pattadakal, also called Paṭṭadakallu or Raktapura, is a complex of 7th and 8th century CE Hindu and Jain temples in northern Karnataka (India). Located on the west bank of the Malaprabha River in Bagalakote district, this UNESCO World Heritage Site is from Badami and about from Aihole, both of which are historically significant centres of Chalukya monuments.World Heritage Sites – Pattadakal – More Detail Archaeological Survey of India, Government of India (2012) The monument is a protected site under Indian law and is managed by the (ASI). UNESCO has described Pattadakal as "a harmonious ble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Himalayan National Park
The Great Himalayan National Park (GHNP) is a national park in India, located in Kullu region in the state of Himachal Pradesh. The park was established in 1984 and is spread over an area of 1171 km2; elevations within the park range between 1500 and 6000 m. The Great Himalayan National Park is a habitat to numerous flora and more than 375 fauna species, including approximately 31 mammals, 181 birds, 3 reptiles, 9 amphibians, 11 annelids, 17 mollusks and 127 insects. They are protected under the strict guidelines of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972; hence any sort of hunting is not permitted. In June 2014, the Great Himalayan National Park was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites, under the criterion of "outstanding significance for biodiversity conservation". Biogeography The GHNP is at the junction of world's two major biogeographic realms: the Indomalayan realm to the south and the Palearctic realm to the north. The temperate forest flora-fauna of GHN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darjeeling Himalayan Railway
The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, also known as the DHR or the Toy Train, is a narrow-gauge, gauge railway that runs between New Jalpaiguri and Darjeeling in the Indian state of West Bengal. Built between 1879 and 1881, it is about long. It climbs from about above sea level at New Jalpaiguri to about at Darjeeling, using six Zig zag (railway), zig zags and five Loop line (railway), loops to gain altitude. Six diesel locomotives handle most of the scheduled service, with daily tourist trains from Darjeeling to Ghum, West Bengal, Ghum – India's highest railway station – and the steam-hauled ''Red Panda'' service from Darjeeling to Kurseong. Steam-enthusiast specials are hauled by vintage British-built DHR B Class, B-Class steam locomotives. The railway's headquarters are at Kurseong. On 5 December 1999, UNESCO declared the DHR a World Heritage Site. Two more railway lines were later added, and the site became known as one of the mountain railways of India. History Siligur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilgiri Mountain Railway
The Nilgiri Mountain Railway (NMR) is a railway in Nilgiris district, Tamil Nadu, India, built by the British in 1908. The railway is operated by the Southern Railway and is the only rack railway in India. The railway relies on its fleet of steam locomotives. NMR switched to diesel locomotives on the section between Coonoor and Udhagamandalam. Local people and visitors led a campaign to return to steam locomotives in this section. In July 2005, UNESCO added the Nilgiri Mountain Railway as an extension to the World Heritage Site of Darjeeling Himalayan Railway. The site then became known as Mountain Railways of India. History In 1854, plans were made to build a mountain railway from Mettupalayam to the Nilgiri Hills. However, it took the decision-makers 45 years to cut through the bureaucratic red tape and complete the construction. The line was completed and opened for traffic in June 1899. It was operated first by the Madras Railway under an agreement with the government. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |