|
List Of United States War Department Forms
Forms of the United States War Department, Office of the Chief of Ordnance, are handbooks, descriptions, instructions, that would later be called technical manuals (TM's): a technical description of a cannon, machine-gun, rifle, pistol, revolver, some wagons and trucks belonging to the artillery and ammunition, also some field manuals (FM's). The forms have their own numbers, at least through no. 2050. List See also *United States Army Ordnance Corps *List of numbered documents of the United States Department of War From 1896 to 1929, the United States Department of War gave their publications a successive number, like other departments including the Department of Agriculture and Department of the Treasury. They were mostly (drill) regulations and other fie ... References External linksHathitrustonline library *Liberated Manuals online library {{Portal bar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Ordnance Corps
The United States Army Ordnance Corps, formerly the United States Army Ordnance Department, is a sustainment branch of the United States Army, headquartered at Fort Lee, Virginia. The broad mission of the Ordnance Corps is to supply Army combat units with weapons and ammunition, including at times their procurement and maintenance. Along with the Quartermaster Corps and Transportation Corps, it forms a critical component of the U.S. Army logistics system. The U.S. Army Ordnance Corps mission is to support the development, production, acquisition, and sustainment of weapon systems, ammunition, missiles, electronics, and ground mobility materiel during peace and war to provide combat power to the U.S. Army. The officer in charge of the branch for doctrine, training, and professional development purposes is the Chief of Ordnance. The current Chief of Ordnance is Brigadier General Michael B. Lalor. History Colonial period to War of Independence During the colonial era in Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
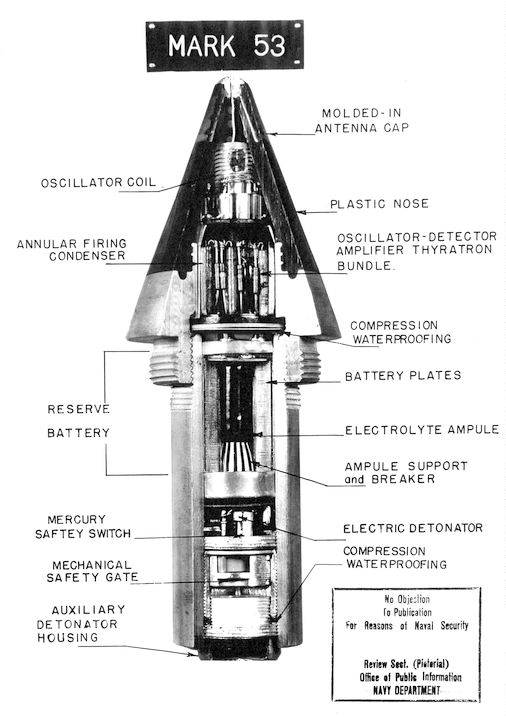
Fuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression Position Finder
The depression range finder (DRF) was a fire control device used to observe the target's range and bearing to calculate firing solutions when gun laying in coastal artillery. It was the main component of a vertical base rangefinding system. It was necessitated by the introduction of rifled artillery from the mid-19th century onwards, which had much greater ranges than the old smoothbore weapons and were consequently more difficult to aim accurately. The DRF was invented by Captain H.S.S. Watkin of the Royal Artillery in the 1870s and was adopted in 1881. It could provide both range and bearing information on a target. The device's inventor also developed a family of similar devices, among them the position finder, which used two telescopes as a horizontal base rangefinding system, around the same time; some of these were called electric position finders. Some position finders retained a depression range finding capability; some of these were called depression position finders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75 Mm Gun M1916
The 75 mm gun M1916 was a US Army field artillery piece used during and after World War I. It was used as an anti-aircraft gun as well as a field piece. It originated as the 3-inch gun M1913, which was soon modified to the 3-inch gun M1916, which was later altered to the subject weapon.Williford, pp. 80–83 History This weapon originated with the acquisition in 1912 of a 75 mm gun designed by Col. Deport of the French Army. The US Army wished to examine and adopt a split-trail carriage, which would allow a higher elevation for indirect fire and dropping shells into trenches. This carriage type was used on the prototype 3-inch model of 1913, which was later designated the 3-inch gun M1916 after a major carriage redesign, prompted by field trials of the M1913. By early 1917 only 34 weapons had been completed; one source traces this to the Ordnance Department developing the weapon without input from the Field Artillery, compounded by a complex top carriage intended to allow 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75 Mm Gun M1917
The 75 mm gun model of 1917 was an interim measure, based on the British QF 18-pounder, produced by the United States in World War I after it had decided to switch from to 75 mm calibre for its field guns. History The US decided early in World War I to switch from to 75 mm calibre for its field guns. Its preferred gun for re-equipment was the French 75 mm Model of 1897, but early attempts to produce it in the US using US commercial mass-production techniques failed, partly due to delays in obtaining necessary French plans, and then their being incomplete or inaccurate, and partly because US industry was not equipped to work to metric measurements. By 1917 US firms had produced 851 QF 18-pounders for export to Britain. Hence production of a 75 mm version offered a simple interim solution, being basically a copy of the British QF 18-pounder rechambered for French 75 mm ammunition, utilizing existing production capacity. It remains very similar to the 18-pound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BL 8-inch Howitzer Mk VI – VIII
The BL 8-inch howitzer Marks VI, VII and VIII (6, 7 and 8)Britain used Roman numerals to designate Marks (i.e. models) of ordnance until after World War II. Hence this article refers to the sixth, seventh and eighth models of British BL 8-inch howitzers were a series of British artillery siege howitzers on mobile carriages of a new design introduced in World War I. They were designed by Vickers in Britain and produced by all four British artillery manufacturers, but mainly by Armstrong, and one American company. They were the equivalents of the German 21 cm Morser 16 and in British service were used similarly to the BL 9.2-inch howitzer, but were quicker to manufacture, and more mobile. They delivered a shell to . They had limited service in the British Army in World War II before being converted to the new calibre. They also equipped a small number of Australian and Canadian batteries in World War I and by the US Army in that war. They were used in small numbers by other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Artillery Fire Control System
In the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps, the term fire control system was used to refer to the personnel, facilities, technology and procedures that were used to observe designated targets, estimate their positions, calculate firing data for guns directed to hit those targets, and assess the effectiveness of such fire, making corrections where necessary. Fire control instruments The Coast Artillery's early fire control instruments supported optical rangefinding and position finding, either horizontal base or vertical base, with both systems usually present for each fort. Early horizontal base rangefinding required two azimuth (a.k.a. bearing or deflection) instruments, preferably widely separated, and a communications system to transmit data to a plotting room and then to the guns. The instruments were often in bunkers called base end stations, as they defined the endpoints of a baseline. A base end station might be a two-story structure with a plotting room or other instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Machine Gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a Water cooling, water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and operate it: one fired, one fed the ammunition, the others helped to carry the weapon, its ammunition, and spare parts. It was in service from before the First World War until the 1960s, with air-cooled versions of it on many Allies of World War I, Allied World War I fighter aircraft. The weapon had a reputation for great solidity and reliability. Ian V. Hogg, in ''Weapons & War Machines'', describes an action that took place in August 1916, during which the British 100th Company of the Machine Gun Corps fired their ten Vickers guns to deliver sustained fire for twelve hours. Using 100 barrels, they fired a million rounds without breakdowns. "It was this absolute foolproof reliability which endeared the Vickers to every Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxim Gun
The Maxim gun is a recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first fully automatic machine gun in the world. The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historian Martin Gilbert, and was heavily used by colonial powers during the "Scramble for Africa". Afterwards, Maxim guns also saw extensive usage by different armies during the Russo-Japanese War, the First and Second World Wars, as well as by insurgent groups in contemporary conflicts. The Maxim gun was greatly influential in the development of machine guns, and it has multiple variants and derivatives. Design The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest recoil-operated firing systems in history. Energy from recoil acting on the breech block is used to eject each spent cartridge and insert the next one. Maxim's earliest designs used a 360-degree rotating cam to reverse the movement of the block, but this was later simplified to a toggle lock. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-inch M1902 Seacoast Gun
The 3-inch gun M1903 and its predecessors the M1898 and M1902 were rapid fire breech-loading artillery guns with a 360-degree traverse. In some references they are called "15-pounders" due to their projectile weight. They were originally emplaced from 1899 to 1917 and served until shortly after World War II. These 3-inch guns were placed to provide fire to protect underwater mines and nets against minesweepers, and also to protect against motor torpedo boats. In some documentation they are called "mine defense guns". The 3-inch guns were mounted on pedestal mounts (or a retractable "masking parapet" mount for the M1898) that bolted into a concrete emplacement that provided cover and safety for the gun's crew. History The 3-inch mine defense guns were part of a comprehensive plan of new fortifications specified by the Board of Fortifications of 1885. The new forts initially included guns up to 12-inch (305 mm) on disappearing carriages, to conceal the fort from observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 2 , an airline of Australia (IATA code QF)
* Qatar Foundation, a private, chartered, non-profit organization in the state of Qatar
* Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system
* Quick-firing gun, a sort of artillery piece
* Quiverfull, a movement of Christians who eschew all forms of birth control
* A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges (see British ordnance terms#QF)
* Quds Force an expeditionary warfare unit of IRGC
{{disambig
fr:QF ...
QF may stand for: * Qantas Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the world's third-oldest airline still in operation, having been founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

