|
List Of Indian Presidential Elections
The election of the President of India is an indirect election in which electoral college consisting of the elected members of both houses of parliament (M.P.s), the elected members of the State Legislative Assemblies (Vidhan Sabha) of all States and the elected members of the legislative assemblies (MLAs) of union territories with legislatures, i.e., National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, and Puducherry. The election process of the president is a more extensive process than of the prime minister who is also elected indirectly (not elected by people directly) by the Lok Sabha members only. Whereas President being the constitutional head with duties to protect, defend and preserve the constitution and rule of law in a constitutional democracy with constitutional supremacy, is elected in an extensive manner by the members of Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha and state legislative assemblies in a secret ballot procedure. Electoral college results See also * Election ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murmu is the 15th and current president, having taken office from 25 July 2022. The office of president was created when India officially became a republic on 26 January 1950 after gaining independence on 15th August 1947, when its constitution came into force. The president is indirectly elected by an electoral college comprising both houses of the Parliament of India and the legislative assemblies of each of India's states and territories, who themselves are all directly elected by the citizens. Article 53 of the Constitution of India states that the president can exercise their powers directly or by subordinate authority (with few exceptions), though all of the executive powers vested in the president are, in practice, exercised by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1952 Indian Presidential Election
The Election Commission of India held the first presidential elections of India on 2 May 1952. Dr. Rajendra Prasad won his first election with 507,400 votes (83.81%) over his nearest rival K. T. Shah who got 92,827 votes (15.3%). Schedule The election schedule was announced by the Election Commission of India on 4 April 1952. Results Source: Web archive of Election Commission of India website See also * 1952 Indian vice presidential election The first Indian vice presidential election was held in 1952. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan was elected unopposed as the first vice president. Had the election been contested by more than one candidate, the poll would have occurred on 12 May 1952. ... References {{Indian presidential elections 1952 elections in India Presidential elections in India May 1952 events in Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neelam Sanjiva Reddy
Neelam Sanjiva Reddy (; 19 May 1913 – 1 June 1996) was an Indian politician who served as the sixth President of India, serving from 1977 to 1982. Beginning a long political career with the Indian National Congress Party in the independence movement, he went on to hold several key offices in independent India — as Deputy Chief minister of Andhra state and the first Chief Minister of United Andhra Pradesh, a two-time Speaker of the Lok Sabha and a Union Minister— before becoming the Indian president. Born in present-day Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, Reddy completed his schooling at Adayar and joined the Government Arts College at Anantapur. He quit to become an Indian independence activist and was jailed for participating in the Quit India Movement. He was elected to the Madras Legislative Assembly in 1946 as a Congress party representative. Reddy became the deputy chief minister of Andhra State in 1953 and the first Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1956. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VV Giri 1974 Stamp Of India (cropped)
VV, V V, or v. v. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Vopli Vidopliassova, or VV, a Ukrainian rock band * Vicarious Visions, a video game company * V/V, a secondary chord in music * V.V., a character in ''Code Geass'' People * Alison Mosshart (born 1978), stage name VV, American singer with The Kills * Vasily Vorontsov (1847–1918), pseudonym VV, Russian economist and sociologist * Ville Valo (born 1976), or VV, Finnish musician Other uses * v/v (volume by volume), the volume fraction * VV, a phoneme or digraph for the letter " w" * Aerosvit Airlines, IATA code VV * Internal Troops of Russia (Russian: ''Vnutrenniye Voiska Ministerstva Vnutrennikh Del'') * Public Affairs (political party) (Czech: ''Věci veřejné''), a political party * Vorontsov-Vel'yaminov Interacting Galaxies, a catalogue of galaxies * Province of Vibo Valentia, Italy * V//V, the Intel Viiv platform initiative See also * * * Double V campaign, World War II slogan promoting democracy overseas African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1969 Indian Presidential Election
The Election Commission of India held indirect 5th presidential elections of India on 16 August 1969. Varahagiri Venkata Giri with 420,077 votes won in a runoff election over his rival Neelam Sanjeeva Reddy who got 405,427 votes. Schedule The election schedule was announced by the Election Commission of India on 14 July 1969. Results Source: Web archive of Election Commission of India website Giri won a majority of the votes in 11 of India's 17 state legislatures although the Congress Party was in power in 12. His campaign also had the backing of the Communists and other leftist parliamentary parties. Massive defections within the Congress Party resulted in Reddy winning only 268 first preference votes despite the Congress Parliamentary Party having a strength of 431. Background The Congress Parliamentary Board met on July 11, 1969, to discuss the presidential candidate. The Syndicate had already decided on nominating Sanjiva Reddy, whose affinity to them was well known. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
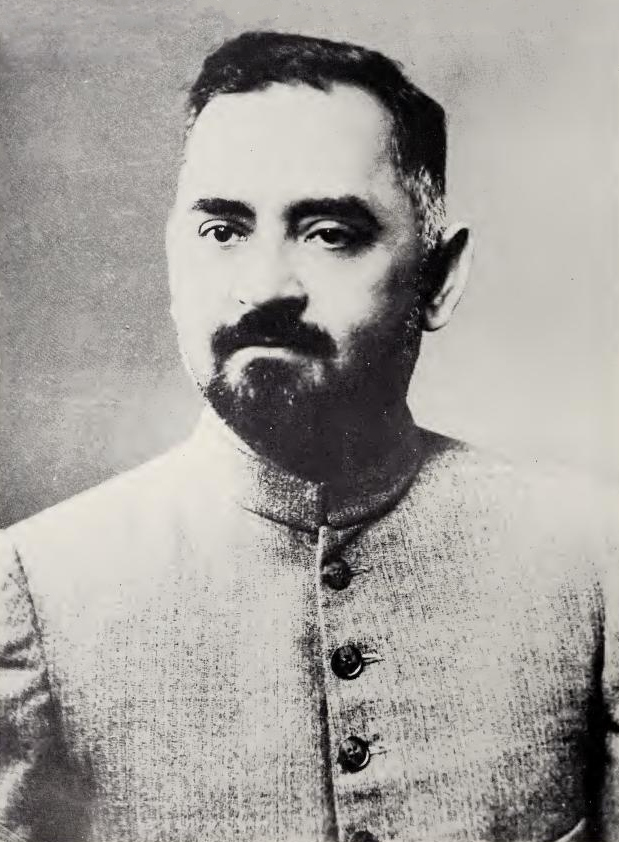
Koka Subba Rao
Koka Subba Rao (15 July 1902 – 6 May 1976) was the ninth Chief Justice of India (1966–1967). He also served as the Chief Justice of the Andhra Pradesh High Court. Early life He was born into a Velama family at Rajamahendravaram on the banks of Godavari River in present day Andhra Pradesh. His father, a lawyer, died early. Rao graduated from the Government Arts College, Rajamundry and studied law at Madras Law College. He was a good sportsman. Professional life He joined the office of his father-in-law, P. Venkata Raman Rao Naidu, who was junior of the Andhra Kesari Prakasam Pantulu. He was recruited as District Munsif and worked for a few months in Bapatla, Guntur district. After Venkata Raman Rao was elevated as Judge of Madras High Court, Subbarao partnered with gifted brother-in-law P. V. Rajamannar, who later became Advocate-General and Chief Justice of Madras High Court. They commanded the cream of legal work from all parts of composite Madras state. He was ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justice K
Justice, in its broadest sense, is the principle that people receive that which they deserve, with the interpretation of what then constitutes "deserving" being impacted upon by numerous fields, with many differing viewpoints and perspectives, including the concepts of moral correctness based on ethics, rationality, law, religion, equity and fairness. The state will sometimes endeavor to increase justice by operating courts and enforcing their rulings. Early theories of justice were set out by the Ancient Greek philosophers Plato in his work The Republic, and Aristotle in his Nicomachean Ethics. Advocates of divine command theory have said that justice issues from God. In the 1600s, philosophers such as John Locke said that justice derives from natural law. Social contract theory said that justice is derived from the mutual agreement of everyone. In the 1800s, utilitarian philosophers such as John Stuart Mill said that justice is based on the best outcomes for the greatest n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakir Husain (politician)
(8 February 1897 – 3 May 1969) known as Dr. Zakir Husain, was an Indian educationist and politician who served as President of India from 13 May 1967 until his death on 3 May 1969. Born into an Afridi Pashtun family in Hyderabad, Husain studied in Etawah, the Muhammadan Anglo-Oriental College, Aligarh and the University of Berlin from where he obtained a doctoral degree in economics. He was a founding member of the Jamia Milia Islamia of which he served as Vice-chancellor during 1926 to 1948. He was closely associated with Mahatma Gandhi and was chairman of the Basic National Education Committee which framed a new educational policy known as Nai Talim with its emphasis on free and compulsory education in the first language. Appointed Vice Chancellor of the Aligarh Muslim University in 1948, he helped retain it as a national institution of higher learning. For his services to education, he was awarded the Padma Vibhushan in 1954 and was a nominated member of the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Zakir Husain 1998 Stamp Of India (cropped)
President most commonly refers to: *President (corporate title) *President (education), a leader of a college or university *President (government title) President may also refer to: Automobiles * Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese full-size sedan * Studebaker President, a 1926–1942 American full-size sedan * VinFast President, a 2020–present Vietnamese mid-size SUV Film and television *'' Præsidenten'', a 1919 Danish silent film directed by Carl Theodor Dreyer * ''The President'' (1928 film), a German silent drama * ''President'' (1937 film), an Indian film * ''The President'' (1961 film) * ''The Presidents'' (film), a 2005 documentary * ''The President'' (2014 film) * ''The President'' (South Korean TV series), a 2010 South Korean television series * ''The President'' (Palestinian TV series), a 2013 Palestinian reality television show *''The President Show'', a 2017 Comedy Central political satirical parody sitcom Music *The Presidents (American soul band) *The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1967 Indian Presidential Election
The Election Commission of India held the indirect fourth presidential elections of India on 6 May 1967. Dr. Zakir Husain, with 471,244 votes, won the presidency over his rival Koka Subba Rao, who garnered 363,971 votes. Schedule The election schedule was announced by the Election Commission of India The Election Commission of India (ECI) is a constitutional body. It was established by the Constitution of India to conduct and regulate elections in the country. Article 324 of the Constitution provides that the power of superintendence, di ... on 3 April 1967. Results Source: Web archive of Election Commission of India website See also * 1967 Indian vice presidential election References {{Indian presidential elections 1967 elections in India Presidential elections in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan (; 5 September 1888 – 17 April 1975), natively Radhakrishnayya, was an Indian philosopher and statesman. He served as the 2nd President of India from 1962 to 1967. He also 1st Vice President of India from 1952 to 1962. He was the 2nd Ambassador of India to the Soviet Union from 1949 to 1952. He was also the 4th Vice-Chancellor of Banaras Hindu University from 1939 to 1948 and the 2nd Vice-Chancellor of Andhra University from 1931 to 1936. One of the most distinguished twentieth-century scholars of comparative religion and philosophy, Radhakrishnan held the King George V Chair of Mental and Moral Science at the University of Calcutta from 1921 to 1932 and Spalding Chair of Eastern Religion and Ethics at University of Oxford from 1936 to 1952. Radhakrishnan's philosophy was grounded in Advaita Vedanta, reinterpreting this tradition for a contemporary understanding. He defended Hinduism against what he called "uninformed Western criticism", c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photograph Of Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan Presented To First Lady Jacqueline Kennedy In 1962
A photograph (also known as a photo, image, or picture) is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor, such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are now created using a smartphone/ camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of what the human eye would see. The process and practice of creating such images is called photography. Etymology The word ''photograph'' was coined in 1839 by Sir John Herschel and is based on the Greek φῶς ('' phos''), meaning "light," and γραφή (''graphê''), meaning "drawing, writing," together meaning "drawing with light." History The first permanent photograph, a contact-exposed copy of an engraving, was made in 1822 using the bitumen-based " heliography" process developed by Nicéphore Niépce. The first photographs of a real-world scene, made using a camera obscura, followed a few years later at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
