|
List Of 1940s Jazz Standards
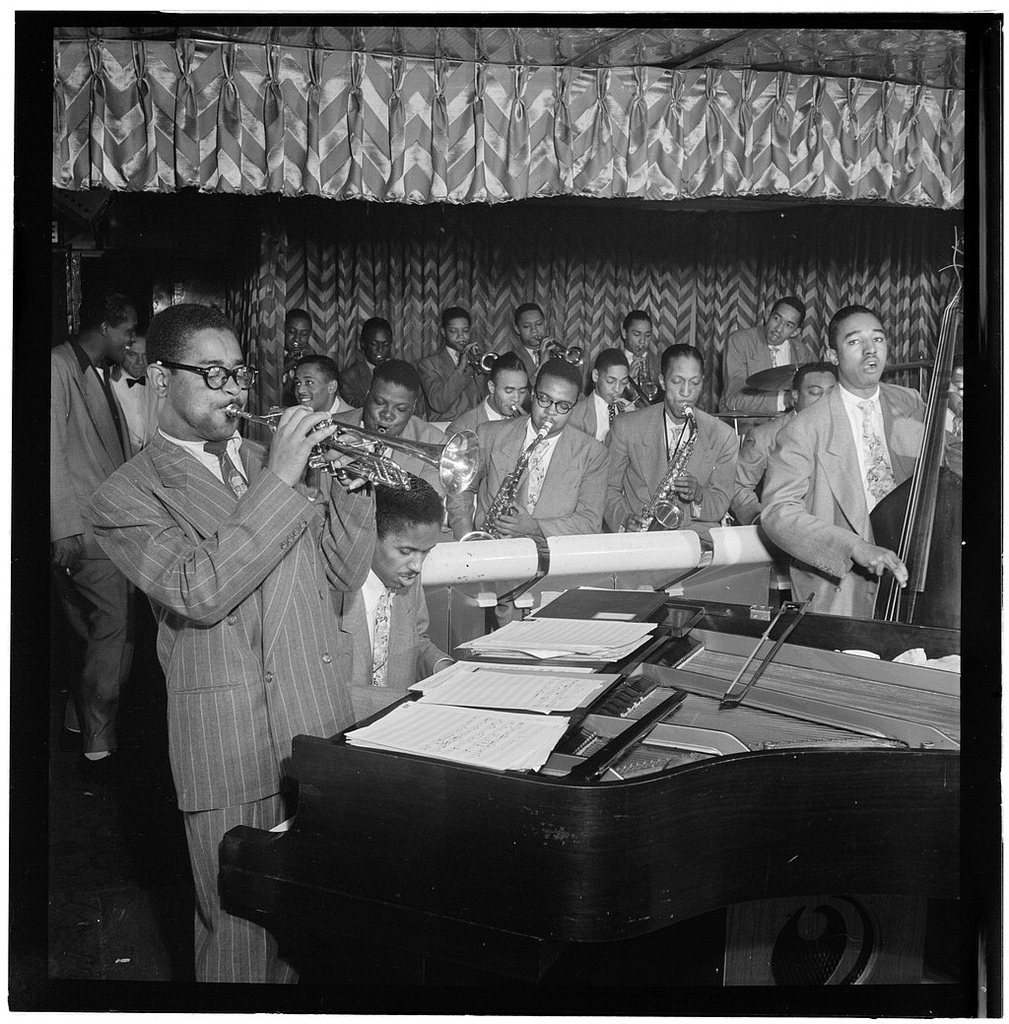
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz artists as part of the genre's musical repertoire. This list includes tunes written in the 1940s that are considered standards by at least one major fake book publication or reference work. The swing era lasted until the mid-1940s, and produced popular tunes such as Duke Ellington's "Cotton Tail" (1940) and Billy Strayhorn's "Take the 'A' Train" (1941). When the big bands struggled to keep going during World War II, a shift was happening in jazz in favor of smaller groups. Some swing era musicians, like Louis Jordan, later found popularity in a new kind of music, called "rhythm and blues", that would evolve into rock and roll in the 1950s. Bebop emerged in the early 1940s, led by Charlie Parker, Dizzy Gillespie, Thelonious Monk, and others. It appealed to a more specialized audience than earlier forms of jazz, with sophisticated harmonies, fast tempos, and often virtuoso music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz Musician Duke Ellington
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African Americans, African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional music, traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swung note, swing and blue notes, complex Chord (music), chords, Call and response (music), call and response vocals, polyrhythms and Jazz improvisation, improvisation. Jazz has roots in European harmony and African rhythmic rituals. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. Dixieland, New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphony, polyphonic Musical improvisation, improvisation. But jazz did not begin as a single musical traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizzy Gillespie
John Birks "Dizzy" Gillespie (; October 21, 1917 – January 6, 1993) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, composer, educator and singer. He was a trumpet virtuoso and improviser, building on the virtuosic style of Roy Eldridge but adding layers of harmonic and rhythmic complexity previously unheard in jazz. His combination of musicianship, showmanship, and wit made him a leading popularizer of the new music called bebop. His beret and horn-rimmed spectacles, scat singing, bent horn, pouched cheeks, and light-hearted personality provided one of bebop's most prominent symbols. In the 1940s, Gillespie, with Charlie Parker, became a major figure in the development of bebop and modern jazz. He taught and influenced many other musicians, including trumpeters Miles Davis, Jon Faddis, Fats Navarro, Clifford Brown, Arturo Sandoval, Lee Morgan, Chuck Mangione, and balladeer Johnny Hartman. He pioneered Afro-Cuban jazz and won several Grammy Awards. Scott Yanow wrote, "Dizzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avery Parrish
James Avery Parrish (January 24, 1917 – December 10, 1959) was an American jazz pianist, composer and arranger. He wrote and recorded " After Hours". Injuries from a bar fight in 1943 ended his career as a pianist. Early life Parrish was born in Birmingham, Alabama. His parents were Curley and Fannie G Parrish. Avery had at least one brother, who became an educator. Parrish graduated from Parker High School in Birmingham. According to a gossip columnist in 1935, Parrish was at that time married to singer Velma Middleton. Later life Parrish studied at the Alabama State Teachers College, where he played in the Bama State Collegians, an ensemble led by Erskine Hawkins. He remained in Hawkins's employ until 1942,"'Record Man' Returns to WOR Program" (May 9, 1942) ''The Pittsburgh Courier''. p. 20. and recorded with him extensively. Parrish wrote the music to " After Hours", and a 1940 recording of the tune with Hawkins's orchestra resulted in its becoming a jazz standard. He a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
After Hours (Avery Parrish Song)
"After Hours" is a blues piano composition composed by pianist Avery Parrish. It is usually played in G. The first recording of the song was by Parrish with the Erskine Hawkins Orchestra, on June 10, 1940, and was released on the Bluebird record label. It was an instant hit, and subsequently became a jazz standard. The song has been recorded many times by such diverse artists as Benny Goodman, Dizzy Gillespie with Sonny Rollins and Sonny Stitt, Woody Herman, Hazel Scott, Phineas Newborn, Hank Crawford, Buck Clayton, Ellis Marsalis, Roy Buchanan, Ryo Fukui, Muddy Waters and numerous others. The version used since 1984 as the theme song for the ''Jazz After Hours'' program on Public Radio International is a solo piano performance by Ray Bryant, recorded at the 1972 Montreux Jazz Festival. . jazzafterhours.org Retrieved August 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizzy Gillespie Playing Horn 1955
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness. Dizziness is a common medical complaint, affecting 20-30% of persons. Dizziness is broken down into 4 main subtypes: vertigo (~25-50%), disequilibrium (less than ~15%), presyncope (less than ~15%), and nonspecific dizziness (~10%). * Vertigo is the sensation of spinning or having one's surroundings spin about them. Many people find vertigo very disturbing and often report associated nausea and vomiting. * Presyncope describes lightheadedness or feeling faint; the name relates to syncope, which is actually fainting. * Disequilibrium is the sensation of being off balance and is most often characterized by frequent falls in a specific direction. This condition is not often associated with nausea or vomiting. * Non-specific dizziness may be psychiatric in origin. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
'Round Midnight (song)
"Round Midnight" (sometimes titled "Round About Midnight") is a 1943 composition by American jazz pianist Thelonious Monk that quickly became a jazz standard and has been recorded by a wide variety of artists. A version recorded by Monk's quintet was added to the Grammy Hall of Fame in 1993. It is one of the most recorded jazz standards composed by a jazz musician. Composition and Monk's first recording It is thought that Monk composed the song sometime in 1940 or 1941. However, Monk's longtime manager Harry Colomby claims the pianist may have written an early version around 1936 (at the age of 19). The song was copyrighted September 24, 1943 in C minor under the title "I Need You So", with lyrics by a friend of Monk's named Thelma Murray. The first recording was made by Cootie Williams on August 22, 1944, after the pianist Bud Powell persuaded Williams to record the tune. Monk first recorded the song on November 21, 1947. It later appeared on the Blue Note album '' Genius of Mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrapple From The Apple
"Scrapple from the Apple" is a bebop composition by Charlie Parker written in 1947, commonly recognized today as a jazz standard, written in F major. The song borrows its chord progression from " Honeysuckle Rose", a common practice for Parker, as he based many of his successful tunes over already well-known chord changes. While the A section is based on " Honeysuckle Rose", the B section or "middle eight" comes from the rhythm changes, which are based on George Gershwin's "I Got Rhythm". Other versions * Lenny Breau – '' Pickin' Cotten'' (1977, released 2001) * Sonny Criss with Tal Farlow – ''Up, Up, and Away'' (1967) * Miles Davis – ''Many Miles of Davis'' (1962) * Curtis Fuller – ''Jazz Conference Abroad'' (1962) * Dexter Gordon – ''Our Man in Paris'' (1963) * Jim Hall – ''Jim Hall Live!'' (1975) * Tom Harrell with Kenny Garrett and Kenny Barron – ''Moon Alley'' (1985) * Keith Jarrett – '' After the Fall'' (1998, released 2018) * Frank Morgan Quartet – ''Yard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yardbird Suite
"Yardbird Suite" is a bebop standard composed by jazz saxophonist Charlie Parker in 1946. The title combines Parker's nickname "Yardbird" (often shortened to "Bird") and a colloquial use of the classical music term " suite" (in a manner similar to such jazz titles as Lester Young's "Midnight Symphony" and Duke Ellington's "Ebony Rhapsody"). The composition uses an 32-bar AABA form. The "graceful, hip melody, became something of an anthem for beboppers." Three Charlie Parker recordings Although, as Bob Dorough wrote in the liner notes to the re-release of his album ''Yardbird Suite'', fans used to follow Parker everywhere he played and often taped his performances, there are only three known commercial recordings of Parker himself playing the tune. The first two were recorded with a septet at Radio Recorders in Hollywood on March 28, 1946. The session was supervised and produced by Ross Russell for his Dial Records label. Besides Parker on alto saxophone was Miles Davis on trump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology (composition)
"Anthropology" (also known as "Thriving from a Riff" or "Thriving on a Riff") is a bebop-style jazz composition that is credited to Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie. Parker stated in 1949 that Gillespie had played no part in its writing, and that others had added the trumpeter as co-composer. It is a contrafact, being based on the harmony of "I Got Rhythm". The first recording of the composition, then known as "Thriving from a Riff", was made on November 26, 1945, by an ensemble led by Parker. The other musicians were trumpeter Miles Davis, pianist Argonne Thornton, bassist Curley Russell, and drummer Max Roach. See also * List of jazz contrafacts * List of 1940s jazz standards Jazz standards are musical compositions that are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz artists as part of the genre's musical repertoire. This list includes tunes written in the 1940s that are considered standards by at least one majo ... * Charlie Parker's Savoy and Dial Sessions Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Night In Tunisia
"A Night in Tunisia" is a musical composition written by Dizzy Gillespie around 1940–42, while Gillespie was playing with the Benny Carter band. It has become a jazz standard. It is also known as "Interlude", and with lyrics by Raymond Leveen was recorded by Sarah Vaughan in 1944. Composition Gillespie called the tune "Interlude" and said "some genius decided to call it 'Night in Tunisia'". He said the tune was composed at the piano at Kelly's Stables in New York. He gave Frank Paparelli co-writer credit in compensation for some unrelated transcription work, but Paparelli had nothing to do with the song. "A Night in Tunisia" was one of the signature pieces of Gillespie's bebop big band, and he also played it with his small groups. In January 2004, The Recording Academy added the 1946 Victor recording by Gillespie to the Grammy Hall of Fame. On the album '' A Night at Birdland Vol. 1'', Art Blakey introduced his 1954 cover version with this statement: "At this time we'd like to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Peanuts
"Salt Peanuts" is a bebop tune reportedly composed by Dizzy Gillespie in 1942, credited "with the collaboration of" drummer Kenny Clarke. It is also cited as Charlie Parker's. The original lyrics have no exophoric meaning. Instead, they are a skat/bebop vocal which matches the octave note interval played predominantly throughout the song. The Pointer Sisters subsequently included vocalese lyrics for their rendition of Salt Peanuts as recorded on their That's a Plenty album. Composition "Salt Peanuts" is a contrafact of "I Got Rhythm": it has the same 32-bar AABA structure and harmony, but its melody is different. It is a simple piece – "a four-measure riff phrase played twice in each A section, and a slightly more complex bridge (which incorporates the ubiquitous 9–7–8 figure twice)". While the verbal exhortation "Salt Peanuts, Salt Peanuts!" is closely identified with Dizzy Gillespie, the musical motif upon which it is based predates Gillespie/Clarke. Glenn Miller record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtuoso
A virtuoso (from Italian ''virtuoso'' or , "virtuous", Late Latin ''virtuosus'', Latin ''virtus'', "virtue", "excellence" or "skill") is an individual who possesses outstanding talent and technical ability in a particular art or field such as fine arts, music, singing, playing a musical instrument, or composition. Meaning This word also refers to a person who has cultivated appreciation of artistic excellence, either as a connoisseur or collector. The plural form of ''virtuoso'' is either ''virtuosi'' or the Anglicisation ''virtuosos'', and the feminine forms are ''virtuosa'' and ''virtuose''. According to ''Music in the Western civilization'' by Piero Weiss and Richard Taruskin: ...a virtuoso was, originally, a highly accomplished musician, but by the nineteenth century the term had become restricted to performers, both vocal and instrumental, whose technical accomplishments were so pronounced as to dazzle the public. The defining element of virtuosity is the performance ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |