|
Liquid Crystal Tunable Filter
A liquid crystal tunable filter (LCTF) is an optical filter that uses electronically controlled liquid crystal (LC) elements to transmit a selectable wavelength of light and exclude others. Often, the basic working principle is based on the Lyot filter but many other designs can be used. The main difference with the original Lyot filter is that the fixed wave plates are replaced by switchable liquid crystal wave plates. Optical systems LCTFs enable high image quality and allowing relatively easy integration with regard to optical system design and software control. However, they emit lower peak transmission values in comparison with conventional fixed-wavelength optical filters due to the use of multiple polarizing elements. This can be mitigated in some instances by using wider bandpass designs, since wider bandpass results in more light traveling through the filter. Some LCTFs are designed to tune to a limited number of fixed wavelengths such as the red, green, and blue (RGB) colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCTF New And Old VariSpec
A liquid crystal tunable filter (LCTF) is an optical filter that uses electronically controlled liquid crystal (LC) elements to transmit a selectable wavelength of light and exclude others. Often, the basic working principle is based on the Lyot filter but many other designs can be used. The main difference with the original Lyot filter is that the fixed wave plates are replaced by switchable liquid crystal wave plates. Optical systems LCTFs enable high image quality and allowing relatively easy integration with regard to optical system design and software control. However, they emit lower peak transmission values in comparison with conventional fixed-wavelength optical filters due to the use of multiple polarizing elements. This can be mitigated in some instances by using wider bandpass designs, since wider bandpass results in more light traveling through the filter. Some LCTFs are designed to tune to a limited number of fixed wavelengths such as the red, green, and blue ( RGB) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preclinical Imaging
Preclinical imaging is the visualization of living animals for research purposes, such as drug development. Imaging modalities have long been crucial to the researcher in observing changes, either at the organ, tissue, cell, or molecular level, in animals responding to physiological or environmental changes. Imaging modalities that are non-invasive and ''in vivo'' have become especially important to study animal models longitudinally. Broadly speaking, these imaging systems can be categorized into primarily morphological/anatomical and primarily molecular imaging techniques. Techniques such as high-frequency micro-ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) are usually used for anatomical imaging, while optical imaging (fluorescence and bioluminescence), positron emission tomography (PET), and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) are usually used for molecular visualizations. These days, many manufacturers provide multi-modal systems co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microscopy
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivariate Optical Computing
Multivariate optical computing, also known as molecular factor computing, is an approach to the development of compressed sensing spectroscopic instruments, particularly for industrial applications such as process analytical support. "Conventional" spectroscopic methods often employ multivariate and chemometric methods, such as multivariate calibration, pattern recognition, and classification, to extract analytical information (including concentration) from data collected at many different wavelengths. Multivariate optical computing uses an optical computer to analyze the data as it is collected. The goal of this approach is to produce instruments which are simple and rugged, yet retain the benefits of multivariate techniques for the accuracy and precision of the result. An instrument which implements this approach may be described as a multivariate optical computer. Since it describes an approach, rather than any specific wavelength range, multivariate optical computers m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
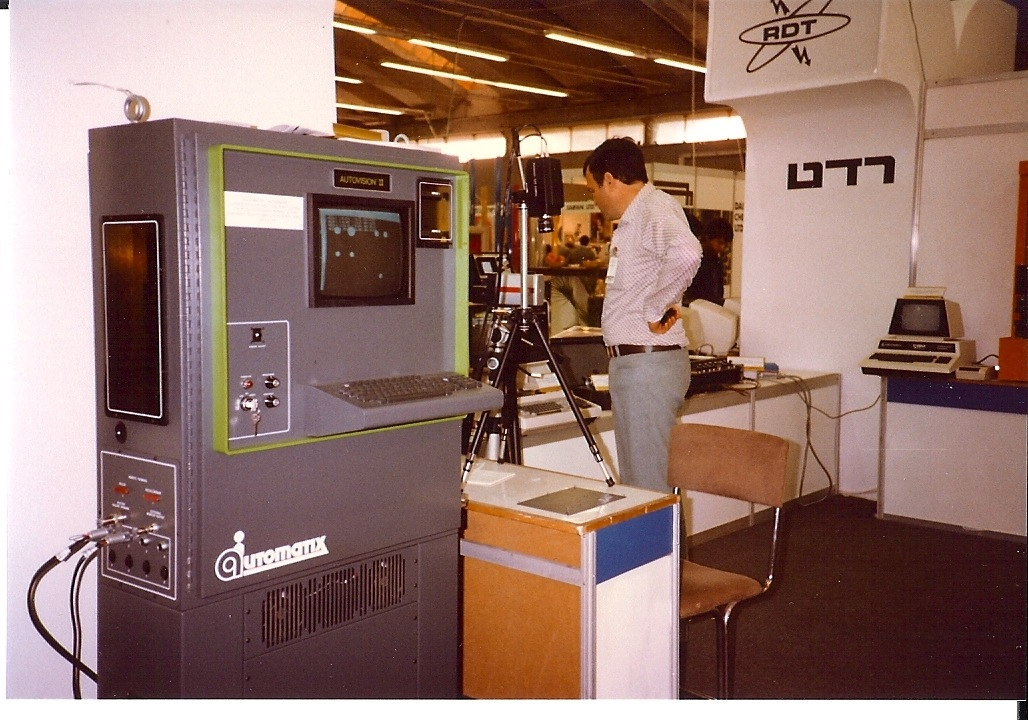
Machine Vision
Machine vision (MV) is the technology and methods used to provide imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision refers to many technologies, software and hardware products, integrated systems, actions, methods and expertise. Machine vision as a systems engineering discipline can be considered distinct from computer vision, a form of computer science. It attempts to integrate existing technologies in new ways and apply them to solve real world problems. The term is the prevalent one for these functions in industrial automation environments but is also used for these functions in other environment vehicle guidance. The overall machine vision process includes planning the details of the requirements and project, and then creating a solution. During run-time, the process starts with imaging, followed by automated analysis of the image and extraction of the requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acousto-optic Effect
Acousto-optics is a branch of physics that studies the interactions between sound waves and light waves, especially the diffraction of laser light by ultrasound (or sound in general) through an ultrasonic grating. Introduction Optics has had a very long and full history, from ancient Greece, through the renaissance and modern times. As with optics, acoustics has a history of similar duration, again starting with the ancient Greeks. In contrast, the acousto-optic effect has had a relatively short history, beginning with Brillouin predicting the diffraction of light by an acoustic wave, being propagated in a medium of interaction, in 1922. This was then confirmed with experimentation in 1932 by Debye and Sears, and also by Lucas and Biquard. The particular case of diffraction on the first order, under a certain angle of incidence, (also predicted by Brillouin), has been observed by Rytow in 1935. Raman and Nath (1937) have designed a general ideal model of interaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acousto-optic Modulator
An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell or an acousto-optic deflector (AOD), uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency). They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric transducer is attached to a material such as glass. An oscillating electric signal drives the transducer to vibrate, which creates sound waves in the material. These can be thought of as moving periodic planes of expansion and compression that change the index of refraction. Incoming light scatters (see Brillouin scattering) off the resulting periodic index modulation and interference occurs similar to Bragg diffraction. The interaction can be thought of as a three-wave mixing process resulting in Sum-frequency generation or Difference-frequency generation between phonons and photons. Principles of operation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobleach
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy. However, photobleaching may also be used prior to applying the (primarily antibody-linked) fluorescent molecules, in an attempt to quench autofluorescence. This can help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Photobleaching may also be exploited to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperspectral Imaging
Hyperspectral imaging collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifying materials, or detecting processes. There are three general branches of spectral imagers. There are push broom scanners and the related whisk broom scanners (spatial scanning), which read images over time, band sequential scanners (spectral scanning), which acquire images of an area at different wavelengths, and snapshot hyperspectral imaging, which uses a staring array to generate an image in an instant. Whereas the human eye sees color of visible light in mostly three bands (long wavelengths - perceived as red, medium wavelengths - perceived as green, and short wavelengths - perceived as blue), spectral imaging divides the spectrum into many more bands. This technique of dividing images into bands can be extended beyond the visibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
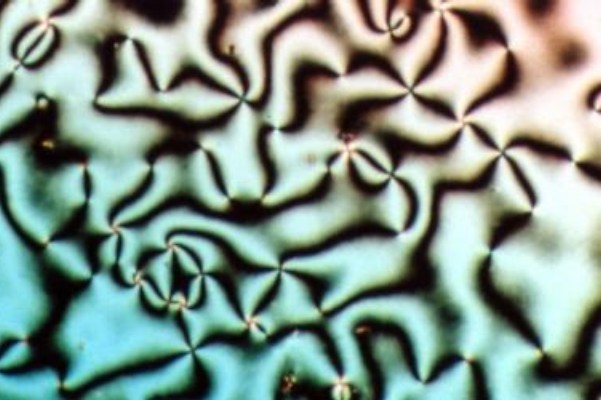
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |