|
Linguistic Discrimination
Linguistic discrimination (also called glottophobia, linguicism and languagism) is unfair treatment of people which is based on their use of language and the characteristics of their speech, including their first language, their accent, the perceived size of their vocabulary (whether or not the speaker uses complex and varied words), their modality, and their syntax. For example, an Occitan speaker in France will probably be treated differently from a French speaker.The Legal Aid Society-Employment Law Center, & the ACLU Foundation of North California (2002). Language Discrimination: Your Legal Rights. http://www.aclunc.org/library/publications/asset_upload_file489_3538.pdf Based on a difference in use of language, a person may automatically form judgments about another person's wealth, education, social status, character or other traits, which may lead to discrimination. In the mid-1980s, linguist Tove Skutnabb-Kangas captured the idea of language-based discrimination as li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usage (language)
The usage of a language is the ways in which its written and spoken variations are routinely employed by its speakers; that is, it refers to "the collective habits of a language's native speakers", as opposed to idealized models of how a language works or (should work) in the abstract. For instance, Fowler characterized usage as "the way in which a word or phrase is normally and correctly used" and as the "points of grammar, syntax, style, and the choice of words." In the descriptive tradition of language analysis, by way of contrast, "correct" tends to mean functionally adequate for the purposes of the speaker or writer using it, and adequately idiomatic to be accepted by the listener or reader; usage is also, however, a concern for the prescriptive tradition, for which "correctness" is a matter of arbitrating style. Common usage may be used as one of the criteria of laying out prescriptive norms for codified standard language usage. Modern dictionaries are not generally p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Language
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by indigenous peoples. This language is from a linguistically distinct community that originated in the area. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is an official language of Bolivia. Also, national languages are not necessarily indigenous to the country. Many indigenous peoples worldwide have stopped passing on their ancestral languages to the next generation and have instead adopted the majority language as part of their acculturation into the majority culture. Furthermore, many indigenous languages have been subject to linguicide (language killing). Recognizing their vulnerability, the United Nations proclaimed 2019 the International Year of Indigenous Languages "to draw attention to the critical loss of indigenous languages and the urgent need to preserve, revitalize and promote indigenous languages." Disappearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriotic Propaganda (16627007085)
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to one's country. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings, language relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or historical aspects. It encompasses a set of concepts closely related to nationalism, mostly civic nationalism and sometimes cultural nationalism. Some manifestations of patriotism emphasize the "land" element in love for one's native land and use the symbolism of agriculture and the soil – compare ''Blut und Boden''. Terminology and usage An excess of patriotism in the defense of a nation is called chauvinism; another related term is ''jingoism''. The English word 'Patriot' derived from "Compatriot," in the 1590s, from Middle French "Patriote" in the 15th century. The French word's "Compatriote" and "Patriote" originated directly from Late Latin Patriota "fellow-countryman" in the 6th century. From Greek Patriotes "fellow countryman," from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation (RP) is the Accent (sociolinguistics), accent traditionally regarded as the Standard language, standard and most Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestigious form of spoken British English. For over a century, there has been argument over such questions as the definition of RP, whether it is geographically neutral, how many speakers there are, whether sub-varieties exist, how appropriate a choice it is as a standard and how the accent has changed over time. The name itself is controversial. RP is an accent, so the study of RP is concerned only with matters of pronunciation; other areas relevant to the study of language standards such as vocabulary, grammar and Style (sociolinguistics), style are not considered. History RP has most in common with the dialects of South East Midlands, namely London, Oxford and Cambridge. By the end of the 15th century, "Standard English" was established in the City of London, though it did not begin to resemble RP until the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
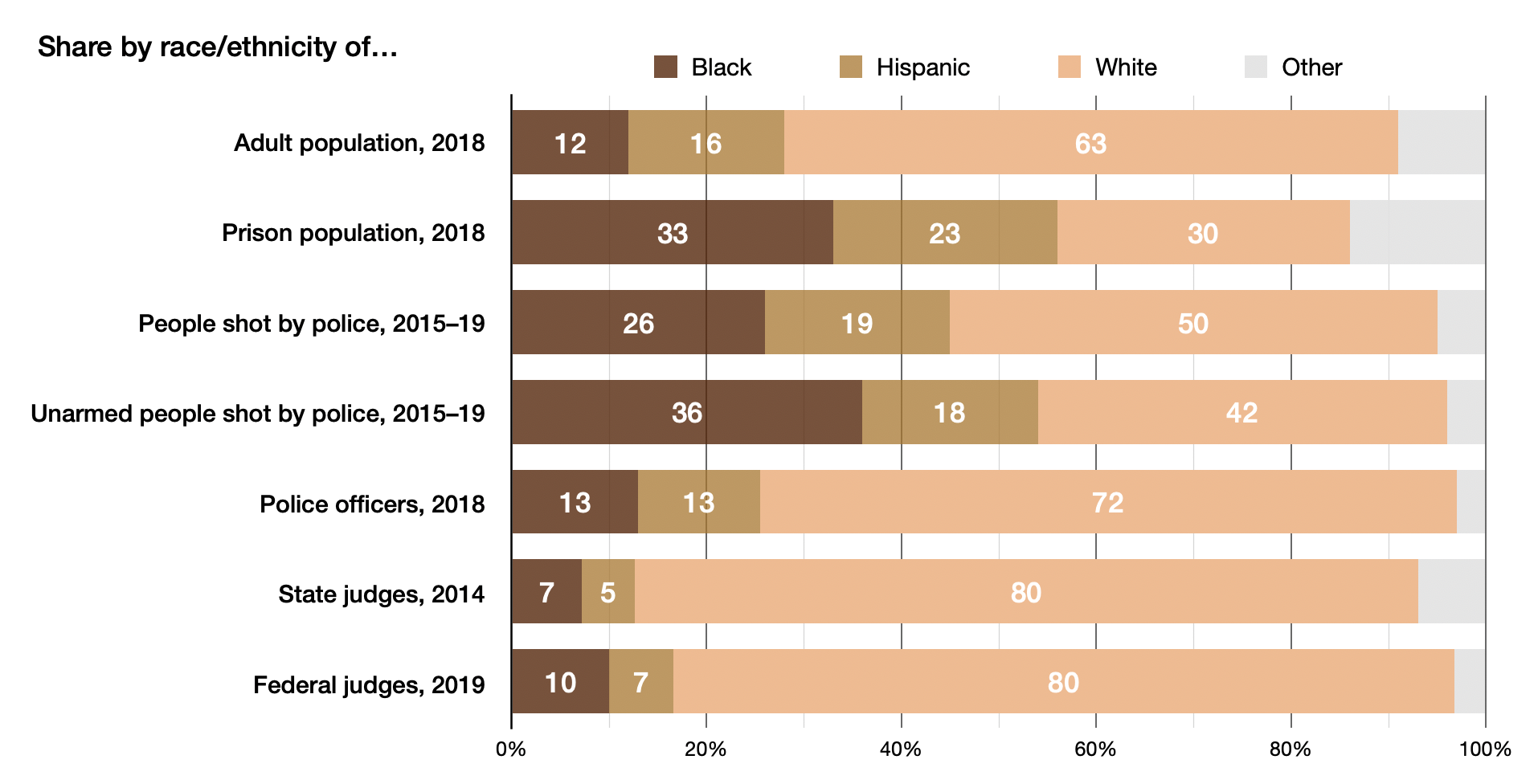
Racism In The United States
Racism in the United States comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are related to each other, are held by various people and groups in the United States, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions (including violence) at various times in the history of the United States against racial or ethnic groups. Throughout American history, white Americans have generally enjoyed legally or socially sanctioned privileges and rights, which have been denied to members of various ethnic or minority groups at various times. European Americans, particularly affluent white Anglo-Saxon Protestants, are said to have enjoyed advantages in matters of education, immigration, voting rights, citizenship, land acquisition, and criminal procedure. Racism against various ethnic or minority groups has existed in the United States since the early colonial era. Before 1865, most African Americans were enslaved and even afterwards, they have faced seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General American
General American English or General American (abbreviated GA or GenAm) is the umbrella accent of American English spoken by a majority of Americans. In the United States it is often perceived as lacking any distinctly regional, ethnic, or socioeconomic characteristics, but it encompasses a continuum of accents rather than a single unified accent. Americans with high education, or from the North Midland, Western New England, and Western regions of the country are the most likely to be perceived as having General American accents. The precise definition and usefulness of the term ''General American'' continue to be debated, and the scholars who use it today admittedly do so as a convenient basis for comparison rather than for exactness. Other scholars prefer the term Standard American English. Standard Canadian English accents are sometimes considered to fall under General American, especially in opposition to the United Kingdom's Received Pronunciation; in fact, typical Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestige (sociolinguistics)
In sociolinguistics, prestige is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally considered by a society to be the most "correct" or otherwise superior. In many cases, they are the standard form of the language, though there are exceptions, particularly in situations of covert prestige (where a non-standard dialect is highly valued). In addition to dialects and languages, prestige is also applied to smaller linguistic features, such as the pronunciation or usage of words or grammatical constructs, which may not be distinctive enough to constitute a separate dialect. The concept of prestige provides one explanation for the phenomenon of variation in form among speakers of a language or languages. The presence of prestige dialects is a result of the relationship between the prestige of a group of people and the language th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlanguage
An interlanguage is an idiolect that has been developed by a learner of a second language (L2) which preserves some features of their first language (L1), and can also overgeneralize some L2 writing and speaking rules. These two characteristics of an interlanguage result in the system's unique linguistic organization. An interlanguage is idiosyncratically based on the learners' experiences with the L2. It can "fossilize", or cease developing, in any of its developmental stages. It is claimed that several factors shape interlanguage rules, including L1 transfer, previous learning strategies, strategies of L2 acquisition, L2 communication strategies, and overgeneralization of L2 language patterns. Interlanguage is based on the theory that there is a dormant psychological framework in the human brain that is activated when one attempts to learn a second language. Interlanguage theory is often credited to Larry Selinker, who coined the terms "interlanguage" and "fossilization." Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Auxiliary Language
An international auxiliary language (sometimes acronymized as IAL or contracted as auxlang) is a language meant for communication between people from all different nations, who do not share a common first language. An auxiliary language is primarily a foreign language and often a constructed language. The concept is related to but separate from the idea of a '' lingua franca'' (or dominant language) that people must use to communicate. The term "auxiliary" implies that it is intended to be an additional language for communication between the people of the world, rather than to replace their native languages. Often, the term is used specifically to refer to planned or constructed languages proposed to ease international communication, such as Esperanto, Ido and Interlingua. It usually takes words from widely spoken languages. However, it can also refer to the concept of such a language being determined by international consensus, including even a standardized natural language (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Semantic Metalanguage
The natural semantic metalanguage (NSM) is a linguistic theory that reduces lexicons down to a set of semantic primitives. It is based on the conception of Polish professor Andrzej Bogusławski. The theory was formally developed by Anna Wierzbicka at Warsaw University and later at the Australian National University in the early 1970s, and Cliff Goddard at Australia's Griffith University. Approach The Natural Semantic Metalanguage (NSM) theory attempts to reduce the semantics of all lexicons down to a restricted set of semantic primitives, or primes. Primes are universal in that they have the same translation in every language, and they are primitive in that they cannot be defined using other words. Primes are ordered together to form explications, which are descriptions of semantic representations consisting solely of primes. Research in the NSM approach deals extensively with language and cognition, and language and culture. Key areas of research include lexical semantics, gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at the time. Today, the humanities are more frequently defined as any fields of study outside of professional training, mathematics, and the natural and social sciences. They use methods that are primarily critical, or speculative, and have a significant historical element—as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences;"Humanity" 2.b, ''Oxford English Dictionary'' 3rd Ed. (2003) yet, unlike the sciences, the humanities have no general history. The humanities include the studies of foreign languages, history, philosophy, language arts (literature, writing, oratory, rhetoric, poetry, etc.), performing arts ( theater, music, dance, etc.), and visual arts (painting, sculpture, photography, filmmaking, etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 19th century. In addition to sociology, it now encompasses a wide array of academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, human geography, linguistics, management science, communication science and political science. Positivist social scientists use methods resembling those of the natural sciences as tools for understanding society, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Interpretivist social scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its broader sense. In modern academic practice, researchers are often eclectic, using multiple methodologies (for instance, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_01.jpg)