|
Line Of Sight
The line of sight, also known as visual axis or sightline (also sight line), is an imaginary line between a viewer/ observer/ spectator's eye(s) and a subject of interest, or their relative direction. The subject may be any definable object taken note of or to be taken note of by the observer, at any distance more than least distance of distinct vision. In optics, refraction of a ray due to use of lenses can cause distortion. Shadows, patterns and movement can also influence line of sight interpretation (as in optical illusions). The term "line" typically presumes that the light by which the observed object is seen travels as a straight ray, which is sometimes not the case as light can take a curved/angulated path when reflected from a mirror, refracted by a lens or density changes in the traversed media, or deflected by a gravitational field. Fields of study feature specific targets, such as vessels in navigation, marker flags or natural features in surveying, celestial objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imaginary Line
In general, an imaginary line is usually any sort of geometric line (more generally, curves) that has only an abstract definition and does not physically exist. They are often used to properly identify places on a map. Some outside geography do exist. A ''centerline'' is a nautical term for a line down the center of a vessel lengthwise. Examples Geography As a geographical concept, an imaginary line may serve as an arbitrary division, such as * Antarctic Circle * Arctic Circle * Border * International Date Line * Latitude, including the Equator, the Tropic of Capricorn and the Tropic of Cancer * Longitude, the Prime Meridian Any axis about which an object spins is an imaginary line. * Mason–Dixon line, which informally marks pieces of the borders of four U.S. states: Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia, once part of Virginia. Symbolically, the line separates the Northern United States from the Southern United States * Missouri Compromise Line * Time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gravitational Lens
A gravitational lens is matter, such as a galaxy cluster, cluster of galaxies or a point particle, that bends light from a distant source as it travels toward an observer. The amount of gravitational lensing is described by Albert Einstein's General relativity, general theory of relativity. If light is treated as Corpuscular theory of light, corpuscles travelling at the speed of light, Newtonian physics also predicts the bending of light, but only half of that predicted by general relativity. Orest Khvolson (1924) and Frantisek Link (1936) are generally credited with being the first to discuss the effect in print, but it is more commonly associated with Einstein, who made unpublished calculations on it in 1912 and published an article on the subject in 1936. In 1937, Fritz Zwicky posited that galaxy clusters could act as gravitational lenses, a claim confirmed in 1979 by observation of the Twin QSO SBS 0957+561. Description Unlike an lens (optics), optical lens, a point-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beyond Visual Line Of Sight
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Drone Warfare; 2024. e-ISBN (PDF) 978-3-11-074203-9.H. Pan; M. Zahmatkesh; F. Rekabi-Bana; F. Arvin; J. HuT-STAR: Time-Optimal Swarm Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage,F. Rekabi-Bana; Hu, J.; T. Krajník; Arvin, F.,Unified Robust Path Planning and Optimal Trajectory Generation for Efficient 3D Area Coverage of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Double Star
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes. This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a binary system of stars in mutual orbit, gravitationally bound to each other) or is an ''optical double'', a chance line-of-sight alignment of two stars at different distances from the observer. Binary stars are important to stellar astronomers as knowledge of their motions allows direct calculation of stellar mass and other stellar parameters. The only (possible) case of "binary star" whose two components are separately visible to the naked eye is the case of Mizar and Alcor (though actually a multiple-star system), but it is not known for certain whether Mizar and Alcor are gravitationally bound. Since the beginning of the 1780s, both professional and amateur double star observers have telescopically measured the distances and angles be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Line-of-sight Velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the vector displacement between the two points. It is formulated as the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity onto the relative direction or line-of-sight (LOS) connecting the two points. The radial speed or range rate is the temporal rate of the distance or range between the two points. It is a signed scalar quantity, formulated as the scalar projection of the relative velocity vector onto the LOS direction. Equivalently, radial speed equals the norm of the radial velocity, modulo the sign. In astronomy, the point is usually taken to be the observer on Earth, so the radial velocity then denotes the speed with which the object moves away from the Earth (or approaches it, for a negative radial velocity). Formulation Given a differentiable vector \mathbf r \in \mathbb^3 defining the instantaneous relative position of a target with respec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Non-line-of-sight Propagation
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) radio propagation occurs outside of the typical line-of-sight (LOS) between the transmitter and receiver, such as in ground reflections. Near-line-of-sight (also NLOS) conditions refer to partial obstruction by a physical object present in the innermost Fresnel zone. Obstacles that commonly cause NLOS propagation include buildings, trees, hills, mountains, and, in some cases, high voltage electric power lines. Some of these obstructions reflect certain radio frequencies, while some simply absorb or garble the signals; but, in either case, they limit the use of many types of radio transmissions, especially when low on power budget. Lower power levels at a receiver reduce the chance of successfully receiving a transmission. Low levels can be caused by at least three basic reasons: low transmit level, for example Wi-Fi power levels; far-away transmitter, such as 3G more than away or TV more than away; and obstruction between the transmitter and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Line-of-sight Propagation
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves can only travel in a direct visual path from the source to the receiver without obstacles. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line. The rays or waves may be diffracted, refracted, reflected, or absorbed by the atmosphere and obstructions with material and generally cannot travel over the horizon or behind obstacles. In contrast to line-of-sight propagation, at low frequency (below approximately 3 MHz) due to diffraction, radio waves can travel as ground waves, which follow the contour of the Earth. This enables AM radio stations to transmit beyond the horizon. Additionally, frequencies in the shortwave bands between approximately 1 and 30 MHz, can be refracted back to Earth by the ionosphere, called skywave or "skip" propagation, thus giving radio transmissions in this range a potentially global reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
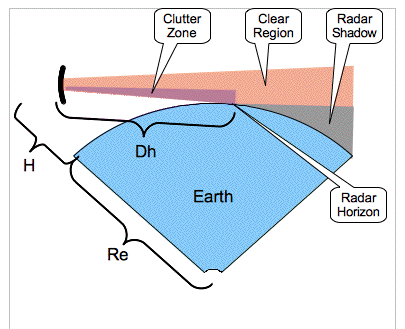
Radar Horizon
The radar horizon is a critical area of performance for air traffic, aircraft detection systems, defined by the distance at which the radar beam rises enough above the Earth's surface to make detection of a target at the lowest level possible. It is associated with the low elevation region of performance, and its geometry depends on terrain, radar height, and signal processing. This concept is associated with the notions of ''radar shadow'', the ''clutter zone'', and the ''clear zone''. Airborne objects can exploit the radar shadow zone and clutter zone to avoid radar detection by using a technique called nap-of-the-earth navigation. Definition Without taking into account the refraction through the atmosphere, the radar horizon would be the geometrical distance D_h from the radar to the horizon only taking into account the height H of the radar above sea-level, and the radius of the earth R_e (approximately 6.4·103 km): :D_h = \sqrt When H is small compared to R_e, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Line-of-sight (missile)
In missile guidance, line of sight (LOS) is the line directly between the launcher/tacker and the target, which must be in view. If the target is moving the missile is constantly manoeuvred to be on the line of sight as it changes, this results in the missile flying a curved path to the target (see command to line-of-sight). The same path is flown as in pursuit guidance but without the missile having a seeker. No ranger data is used in the control and no prediction of intercept location made. See also * Constant bearing, decreasing range * Index of aviation articles Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Articles related to aviation include: A Aviation accidents and incidents – Above Mean Sea Level (AMSL) – ADF – Acces ... Literature * Tactical and Strategic Missile Guidance, Paul Zarchan, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc. References * Missile operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |