|
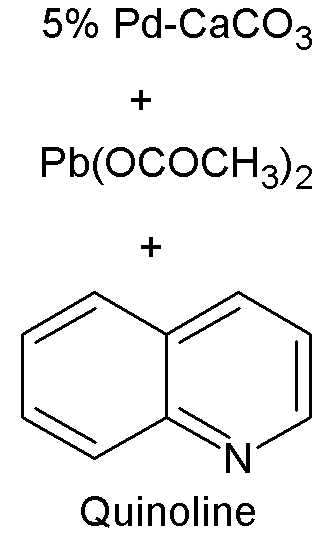
Lindlar's Catalyst
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulfate which is then poisoned with various forms of lead or sulfur. It is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes) and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar. Synthesis Lindlar catalyst is commercially available but may also be prepared by the reduction of palladium chloride in a slurry of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) followed by the addition of lead acetate. A variety of other "catalyst poisons" have been used, including lead oxide and quinoline. The palladium content of the supported catalyst is usually 5% by weight. Catalytic properties The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes). The lead serves to deactivate the palladium sites, further deactivation of the catalyst with quinoline or 3,6-dithia-1,8-octanediol enhances its selectivity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindlar Eng
Lindlar ( ) is a municipality in the Oberbergischer Kreis, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located about 30 km east of Cologne. Geography Lindlar is located between latitudes 50°58' and 51°5' N. and longitudes 7°15' and 7°28' E. The highest point at 361.8 ms is found near Oberlichtinghagen, the lowest at 110 ms near Oberbilstein. Neighbouring places Neighbouring towns are Gummersbach, Wipperfürth, Overath and Bergisch Gladbach, and the neighbouring municipalities are Engelskirchen, Marienheide and Kürten. Division of the municipality The municipality of Lindlar is made up of these main villages: Lindlar (local centre), Frielingsdorf, Linde, Hohkeppel, Schmitzhöhe, Hartegasse/Kapellensüng. The coat of arms of Lindlar The arms were granted on 6 August 1935. The arms show in the upper part the lion of the Counts of Berg and in the lower the balance as a symbol of justice. Lindlar had its own court in the County Berg. The arms are based on the old seal of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkynes
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumaric Acid
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer. Biosynthesis and occurrence It is produced in eukaryotic organisms from succinate in complex 2 of the electron transport chain via the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. It is one of two isomeric unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, the other being maleic acid. In fumaric acid the carboxylic acid groups are ''trans'' (''E'') and in maleic acid they are ''cis'' (''Z''). Fumaric acid is found in fumitory (''Fumaria officinalis''), bolete mushrooms (specifically ''Boletus fomentarius var. pseudo-igniarius''), lichen, and Iceland moss. Fumarate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maleic Acid
Maleic acid or ''cis''-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the ''cis''-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the ''trans''-isomer. It is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, maleic acid has few applications. Physical properties Maleic acid has a '' heat of combustion'' of -1,355 kJ/mol., 22.7 kJ/mol higher than that of fumaric acid. Maleic acid is more soluble in water than fumaric acid. The melting point of maleic acid (135 °C) is also much lower than that of fumaric acid (287 °C). Both properties of maleic acid can be explained on account of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding that takes place in maleic acid at the expense of intermolecular interactions, and that are not possible in fumaric acid for geometric reasons. Production and industrial applications In industry, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylenedicarboxylic Acid
Acetylenedicarboxylic acid or butynedioic acid is an organic compound (a dicarboxylic acid) with the formula C4H2O4 or . It is a crystalline solid that is soluble in diethyl ether. The removal of two protons yields the acetylenedicarboxylate dianion , which consists only of carbon and oxygen, making it an oxocarbon anion. Partial ionization yields the monovalent hydrogenacetylenedicarboxylate anion . The acid was first described in 1877 by Polish chemist Ernest Bandrowski. It can be obtained by treating α,β-dibromosuccinic acid with potassium hydroxide KOH in methanol or ethanol. The reaction yields potassium bromide and potassium acetylenedicarboxylate. The salts are separated and the latter is treated with sulfuric acid. Acetylenedicarboxylic acid is used in the synthesis of dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate, an important laboratory reagent. The acid is commonly traded as a laboratory chemical. It can also be reacted with sulfur tetrafluoride to produce hexafluoro-2-buty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syn Addition
In organic chemistry, syn- and anti-addition are different ways in which substituent molecules can be added to an alkene or alkyne. The concepts of syn and anti addition are used to characterize the different reactions of organic chemistry by reflecting the stereochemistry of the products in a reaction. The type of addition that occurs depends on multiple different factors of a reaction, and is defined by the final orientation of the substituents on the parent molecule. Syn and anti addition are related to the Markovnikov's rule for the orientation of a reaction, which refers to the bonding preference of different substituents for different carbons on an alkene or alkyne. In order for a reaction to follow Markovnikov's rule, the intermediate carbocation of the mechanism of a reaction must be on the more substituted carbon, allowing the substituent to bond to the more stable carbocation and the more substituted carbon. Syn addition is the addition of two substituents to the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospecific
In chemistry, stereospecificity is the property of a reaction mechanism that leads to different stereoisomeric reaction products from different stereoisomeric reactants, or which operates on only one (or a subset) of the stereoisomers."Overlap Control of Carbanionoid Reactions. I. Stereoselectivity in Alkaline Epoxidation," Zimmerman, H. E.; Singer, L.; Thyagarajan, B. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1959, 81, 108-116.Eliel, E., "Stereochemistry of Carbon Compound", McGraw-Hill, 1962 pp 434-436 In contrast, stereoselectivity is the property of a reactant mixture where a non-stereospecific mechanism allows for the formation of multiple products, but where one (or a subset) of the products is favored by factors, such as steric access, that are independent of the mechanism. A stereospecific mechanism ''specifies'' the stereochemical outcome of a given reactant, whereas a stereoselective reaction ''selects'' products from those made available by the same, non-specific mechanism acting on a giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PhC2HH2
PHC or PhC may refer to: Cities * Port Harcourt, Nigeria Courts *Peshawar High Court in Peshawar, Pakistan Education *Candidate of Philosophy (Candidatus/Candidata Philosophiae), an academic degree *Patrick Henry College, a college in Purcellville, Virginia, United States *Pacific Harbors Council Health care *Hawaii Prepaid Health Care Act * Partnership HealthPlan of California, a Medicaid health plan *Philippine Heart Center, hospital for heart illnesses in the Philippines *Primary health care * Primary Health Centre, health care provider in developing nations * PH Consulting SRL, health care industry consultants in LATAM **Primary Health Centre (India) Religion *Pentecostal Holiness Church *Perth Hebrew Congregation of Menora, Western Australia Science and technology *Password Hashing Competition *Polyhalogenated compound * Poly(hexamethylene carbonate) *Poly(hydridocarbyne) Transport *Port Harcourt International Airport, Nigeria, IATA code Entertainment *A Prairie Home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styrene
Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations have a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene and several copolymers. Approximately 25 million tonnes of styrene were produced in 2010, increasing to around 35 million tonnes by 2018. Natural occurrence Styrene is named after storax balsam (often commercially sold as ''styrax''), the resin of Liquidambar trees of the Altingiaceae plant family. Styrene occurs naturally in small quantities in some plants and foods (cinnamon, coffee beans, balsam tree (other), balsam trees and peanuts) and is also found in coal tar. History In 1839, the German apothecary Eduard Simon isolated a volatile liquid from the resin (called ''storax'' or ''styrax'' (Latin)) of the Liquidambar styraciflua, American sweetgu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |