|
Linda Medlin
Linda Karen Medlin is a molecular biologist known for her work on diatoms. She is an elected member of the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters. Education and career Medlin has a B.S. from the University of Texas at Austin (1970), and an M.S. (1977) and a Ph.D.(1983) from Texas A&M University. She has worked at the Alfred-Wegener-Institute in Germany (1991-2009), Observatoire océanologique de Banyuls-sur-Mer in France (2009-2013), and the company Microbia Environment in France (2013-2016). As of 2008, she is an associate research fellow at the Marine Biological Association. Research Medlin's early work was with Greta Fryxell on the taxonomy of diatoms. She is known for her work on applying molecular tools to the study of phytoplankton, and she was the first to develop primers for polymerase chain reaction that targeted eukaryotic organisms, She applied this tool to taxonomic studies of multiple species of phytoplankton cultured in the laboratory. Her work extended into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picozoa
Picozoa, Picobiliphyta, Picobiliphytes, or Biliphytes are protists of a phylum of marine unicellular heterotrophic eukaryotes with a size of less than about 3 micrometers. They were formerly treated as eukaryotic algae and the smallest member of photosynthetic picoplankton before it was discovered they don't perform photosynthesis. The first species identified therein is ''Picomonas judraskeda''. They probably belong in the Archaeplastida as sister of the Rhodophyta. They were formerly placed within the cryptomonads-haptophytes assemblage. Discovery At the end of the 1990s the European project "Picodiv" clarified which organisms occur in picoplankton. In addition, for a period of two years, samples were taken in the Atlantic, in the Mediterranean, before the coast of Scotland, Alaska and Norway. Picobiliphyta were found particularly within the nutrient-poor ranges from cold coastal seas, where they can constitute up to 50 percent of the biomass. Affinities to other organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Molecular Biologists
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Norwegian Academy Of Science And Letters
Member may refer to: * Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon * Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set * In object-oriented programming, a member of a class ** Field (computer science), entries in a database ** Member variable, a variable that is associated with a specific object * Limb (anatomy), an appendage of the human or animal body ** Euphemism for penis * Structural component of a truss, connected by nodes * User (computing), a person making use of a computing service, especially on the Internet * Member (geology), a component of a geological formation * Member of parliament * The Members, a British punk rock band * Meronymy, a semantic relationship in linguistics * Church membership, belonging to a local Christian congregation, a Christian denomination and the universal Church * Member, a participant in a club or learned society A learned society (; also learned academy, scholarly society, or academic association) is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas A&M University Alumni
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both area (after Alaska) and population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the most populous city in Texas and the fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most populous in the state and seventh-largest in the U.S. Dallas–Fort Worth and Greater Houston are, respectively, the fourth- and fifth-largest metropolitan statistical areas in the country. Other major cities include Austin, the second most populous state capital in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas At Austin Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phycological Society
The International Phycological Society is a learned society of phycologists. It was established in 1960. The Society publishes a bimonthly academic journal An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and ... ''Phycologia''. References External links International Phycological Society "Phycologia" website {{authority control Learned societies of the United States Organizations established in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycological Society Of America
The Phycological Society of America (PSA) is a professional society, founded in 1946, that is dedicated to the advancement of phycology, the study of algae. The PSA is responsible for the publication of ''Journal of Phycology'' and organizes annual conferences among other events that aid in the advancement of related algal sciences. Membership in the Phycological Society of America is open to anyone from any nation who is concerned with the physiology, taxonomy, molecular biology, experimental biology, cell biology, and developmental biology of related algal sciences. As of 2012, membership was approximately 2,000 from 63 countries. Awards and Fellowships The PSA offers four honorary awards that are announced at the annual conference * The Harold C. Bold Award, established in 1973, the Bold Award is given for the outstanding graduate student paper(s) presented at the Annual Meeting as determined by the Bold Award Committee. * The Gerald W. Prescott Award, The Prescott Awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmful Algal Bloom
A harmful algal bloom (HAB) (or excessive algae growth) is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a " dead zone" which can cause fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. Harmful algal blooms in marine environments are often called "red tides". It is sometimes unclear what causes specific HABs as their occurrence in some locations appears to be entirely natural, while in others they appear to be a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
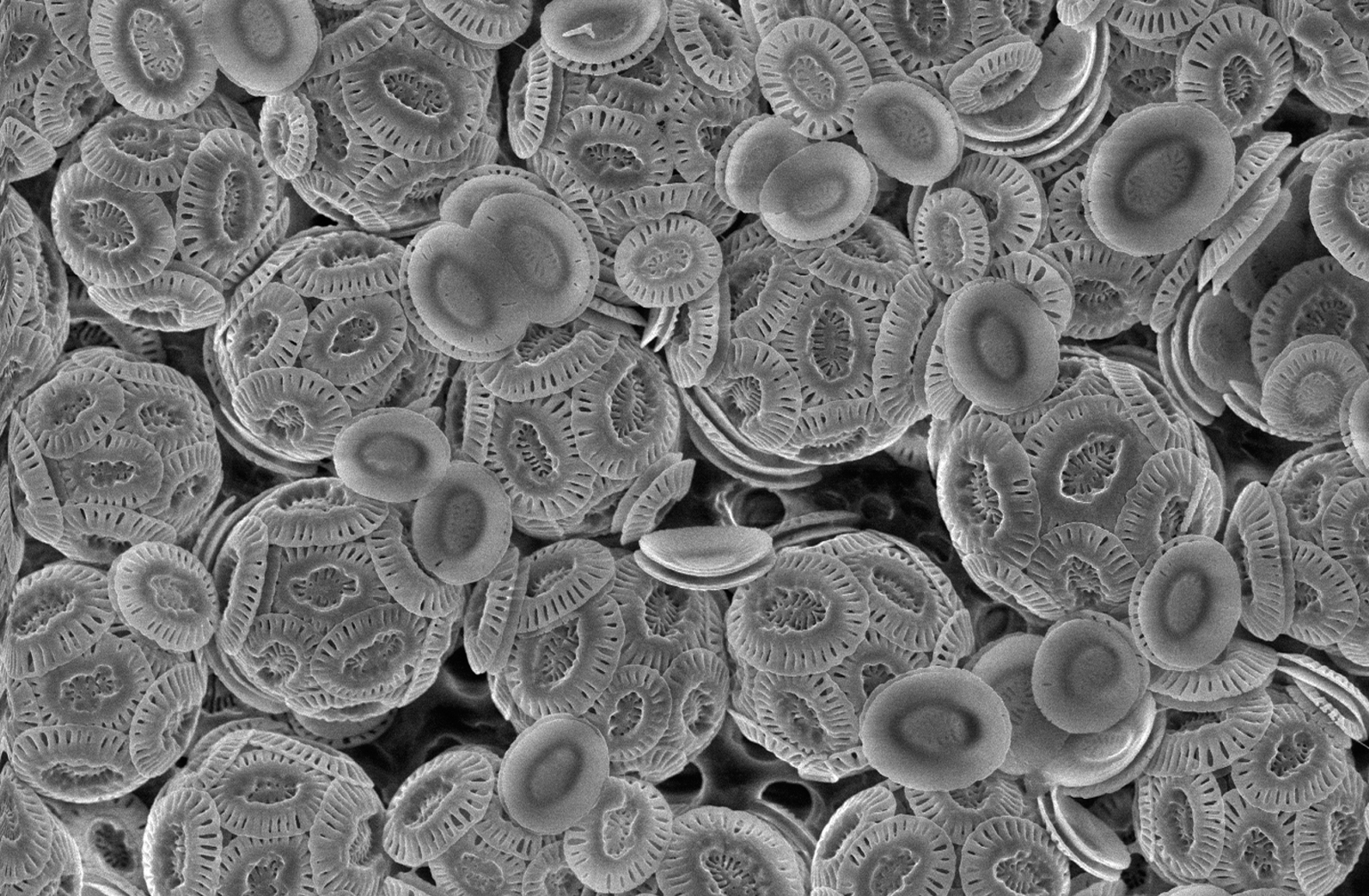
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's Five kingdom classification, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Academy Of Science And Letters
The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters ( no, Det Norske Videnskaps-Akademi, DNVA) is a learned society based in Oslo, Norway. Its purpose is to support the advancement of science and scholarship in Norway. History The Royal Frederick University in Christiania was established in 1811. The idea of a learned society in Christiania surfaced for the first time in 1841. The city of Trondhjem had no university, but had a learned society, the Royal Norwegian Society of Sciences and Letters, established in 1760. The purpose of a learned society in Christiania was to support scientific studies and aid publication of academic papers. The idea of the Humboldt-inspired university, where independent research stood strong, had taken over for the instrumental view of a university as a means to produce civil servants. The city already had societies for specific professions, for instance the Norwegian Medical Society which was founded in 1833. However, these societies were open for both acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)