|
Lilienfeld Radiation
Lilienfeld radiation, named after Julius Edgar Lilienfeld, is electromagnetic radiation produced when electrons hit a metal surface. The Smith–Purcell effect is believed to be a variant of Lilienfeld radiation. Lilienfeld radiation is shown as Transition radiation by Vitaly Ginzburg and Ilya Frank Ilya Mikhailovich Frank (russian: Илья́ Миха́йлович Франк; 23 October 1908 – 22 June 1990) was a Soviet winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1958 jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Igor Y. Tamm, also of the ... in 1945 References Particle physics Electromagnetic radiation {{electromagnetism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld (April 18, 1882 – August 28, 1963) was an Austro-Hungarian, and later American (where he moved in 1921) physicist and electrical engineer, who was credited with the first patent on the field-effect (FET) (1925). Because of his failure to publish articles in learned journals and because high-purity semiconductor materials were not available yet, his FET patent never achieved fame, causing confusion for later inventors. Early life Lilienfeld was born into a German-speaking Ashkenazi Jewish family in Lemberg (present-day Lviv) in the Austrian part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Education Between 1900 and 1904, Lilienfeld studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität (renamed Humboldt University in 1949), in Berlin, where he received his Ph.D. on February 18, 1905. In 1905, he started work at the physics institute at Leipzig University as an untenured professor. Career Lilienfeld's early career, at the University of Leipzig, saw him conduct impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Light, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Classical electromagnetism, Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric field, electric and magnetic fields. Depending on the frequency of oscillation, different wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum are produced. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted ''c''. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The position of an electromagnetic wave w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
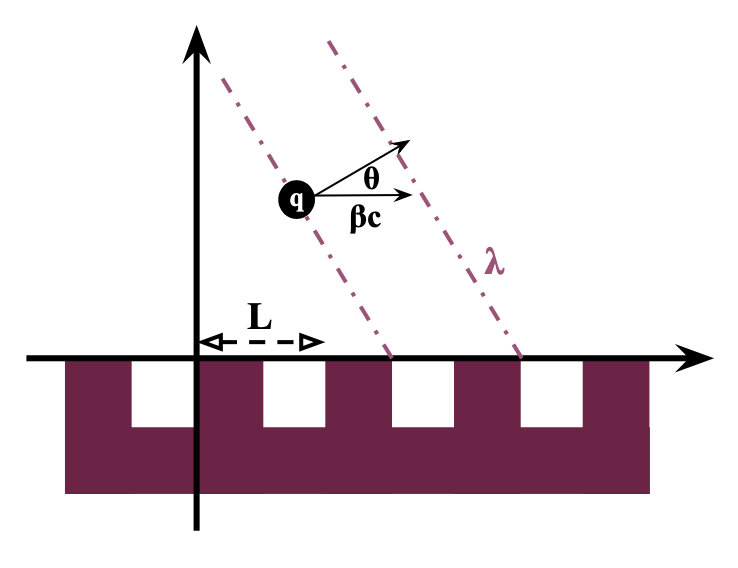
Smith–Purcell Effect
The Smith–Purcell effect was the precursor of the free-electron laser (FEL). It was studied by Steve Smith, a graduate student under the guidance of Edward Purcell. In their experiment, they sent an energetic beam of electrons very closely parallel to the surface of a ruled optical diffraction grating, and thereby generated visible light. Smith showed there was negligible effect on the trajectory of the inducing electrons. Essentially, this is a form of Cherenkov radiation where the phase velocity of the light has been altered by the periodic grating. However, unlike Cherenkov radiation, there is no minimum or threshold particle velocity. Smith–Purcell radiation is particularly attractive for applications involving non-destructive beam diagnostics (bunch-length diagnostics in accelerators for example) and especially as a viable THz radiation source, which has further broad-range uses in diverse and high-impact fields like materials sciences, biotechnology, security and communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Radiation
Transition radiation (TR) is a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle passes through inhomogeneous media, such as a boundary between two different media. This is in contrast to Cherenkov radiation, which occurs when a charged particle passes through a homogeneous dielectric medium at a speed greater than the phase velocity of electromagnetic waves in that medium. History Transition radiation was demonstrated theoretically by Ginzburg and Frank in 1945. They showed the existence of Transition radiation when a charged particle perpendicularly passed through a boundary between two different homogeneous media. The frequency of radiation emitted in the backwards direction relative to the particle was mainly in the range of visible light. The intensity of radiation was logarithmically proportional to the Lorentz factor of the particle. After the first observation of the transition radiation in the optical region, many early studies indicated that the applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitaly Ginzburg
Vitaly Lazarevich Ginzburg, ForMemRS (russian: Вита́лий Ла́заревич Ги́нзбург, link=no; 4 October 1916 – 8 November 2009) was a Russian physicist who was honored with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2003, together with Alexei Abrikosov and Anthony Leggett for their "pioneering contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids." His career in physics was spent in the former Soviet Union and was one of the leading figure in former Soviet program of nuclear weapons, working towards designs of the thermonuclear devices. He became a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and succeeded Igor Tamm as head of the Department of Theoretical Physics of the Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FIAN). In his later life, Ginzburg become an outspoken atheist and was critical of clergy's influence in Russian society. Biography Vitaly Ginzburg was born to a Jewish family in Moscow on 4 October 1916— the son of an enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Frank
Ilya Mikhailovich Frank (russian: Илья́ Миха́йлович Франк; 23 October 1908 – 22 June 1990) was a Soviet winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1958 jointly with Pavel Alekseyevich Cherenkov and Igor Y. Tamm, also of the Soviet Union. He received the award for his work in explaining the phenomenon of Cherenkov radiation. He received the Stalin prize in 1946 and 1953 and the USSR state prize in 1971. Life and career Ilya Frank was born on 23 October 1908 in St. Petersburg. His father, Mikhail Lyudvigovich Frank, was a talented mathematician descended from a Jewish family, while his mother, Yelizaveta Mikhailovna Gratsianova, was a Russian Orthodox physician. His father participated in the student revolutionary movement, and as a result was expelled from Moscow University. After the October Revolution, he was reinstated and appointed professor. Ilya's uncle, Semyon Frank, a noted Russian philosopher, wasn't as fortunate and was expelled from the USSR in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |