|
Lignum Crucis
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
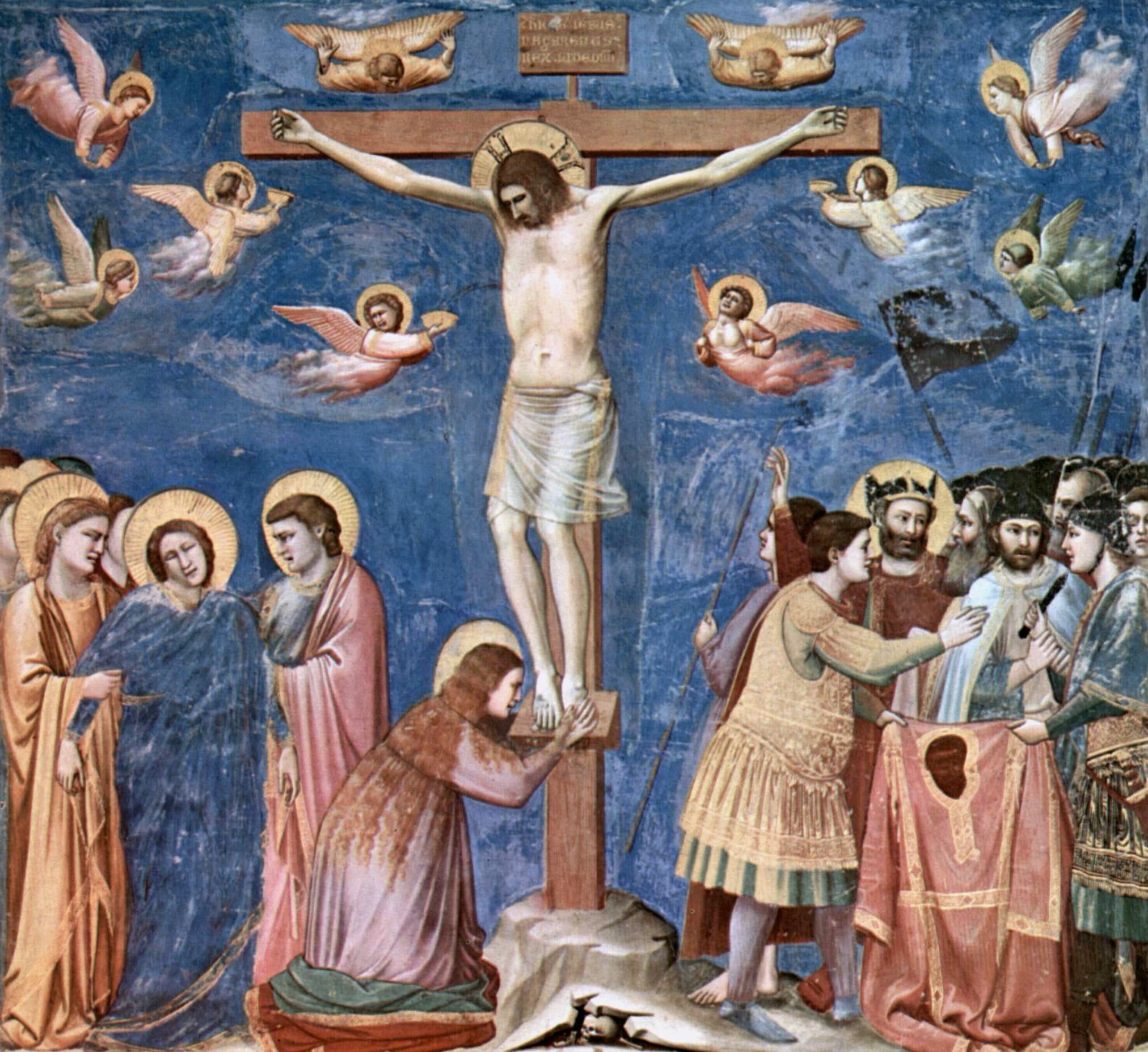
Giotto Crucifixion
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giotto's contemporary, the banker and chronicler Giovanni Villani, wrote that Giotto was "the most sovereign master of painting in his time, who drew all his figures and their postures according to nature" and of his publicly recognized "talent and excellence".Bartlett, Kenneth R. (1992). ''The Civilization of the Italian Renaissance''. Toronto: D.C. Heath and Company. (Paperback). p. 37. Giorgio Vasari described Giotto as making a decisive break with the prevalent Byzantine style and as initiating "the great art of painting as we know it today, introducing the technique of drawing accurately from life, which had been neglected for more than two hundred years".Giorgio Vasari, ''Lives of the Artists'', trans. George Bull, Penguin Classics, (196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impenitent Thief
The impenitent thief is a man described in the New Testament account of the Crucifixion of Jesus. In the Gospel narrative, two criminal bandits are crucified alongside Jesus. In the first two Gospels (Matthew and Mark), they both join the crowd in mocking him. In the version of the Gospel of Luke, however, one taunts Jesus about not saving himself and them, and the other (known as the penitent thief) asks for mercy. In apocryphal writings, the impenitent thief is given the name Gestas, which first appears in the Gospel of Nicodemus, while his companion is called Dismas. Christian tradition holds that Gestas was on the cross to the left of Jesus and Dismas was on the cross to the right of Jesus. In Jacobus de Voragine's ''Golden Legend'', the name of the impenitent thief is given as Gesmas. The impenitent thief is sometimes referred to as the "bad thief" in contrast to the good thief. The apocryphal Arabic Infancy Gospel refers to Gestas and Dismas as Dumachus and Titus, respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the University of Oxford, the oldest university in the English-speaking world; it has buildings in every style of English architecture since late Anglo-Saxon. Oxford's industries include motor manufacturing, education, publishing, information technology and science. History The history of Oxford in England dates back to its original settlement in the Saxon period. Originally of strategic significance due to its controlling location on the upper reaches of the River Thames at its junction with the River Cherwell, the town grew in national importance during the early Norman period, and in the late 12th century became home to the fledgling University of Oxford. The city was besieged during The Anarchy in 1142. The university rose to domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Of The Most Holy Trinity, Waterford
The Cathedral of the Most Holy Trinity is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Waterford and Lismore located in Barronstrand Street, Waterford City, Ireland. The cathedral is the oldest post-Reformation Catholic cathedral in Ireland, pre-dating the Catholic Emancipation Act of 1829 by some 36 years. History The cathedral was designed by John Roberts in 1793 and has the distinction of being the oldest post-Reformation cathedral of the Roman Catholic Church in Ireland. The cathedral was built under the direction of Rev. Dean Thomas Hearn, D.D., the cathedral dean. Roberts also designed Christ Church Cathedral, Waterford, and is said to have supervised the construction of the Catholic cathedral by attending the site every morning, and apparently 'died from the effects of a cold caught within the unfinished structure'. A chapel – known in the city as the 'Big Chapel' – had previously stood on the same ground, having been constructed there in 1693 at the heig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Folklore
Christian mythology is the body of myths associated with Christianity. The term encompasses a broad variety of legends and narratives, especially those considered sacred narratives. Mythological themes and elements occur throughout Christian literature, including recurring myths such as ascending to a mountain, the '' axis mundi'', myths of combat, descent into the Underworld, accounts of a dying-and-rising god, a flood myth, stories about the founding of a tribe or city, and myths about great heroes (or saints) of the past, paradises, and self-sacrifice. Various authors have also used it to refer to other mythological and allegorical elements found in the Bible, such as the story of the Leviathan. The term has been applied to myths and legends from the Middle Ages, such as the story of Saint George and the Dragon, the stories of King Arthur and his Knights of the Round Table, and the legends of the '' Parsival''. Multiple commentators have classified John Milton's epic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that salvation comes by divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, but disagree among themselves regarding the number of sacraments, the real presence of Christ in the Eucharist, and matters of ecclesiastica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of The East
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian Church, was an Eastern Christian church of the East Syriac Rite, based in Mesopotamia. It was one of three major branches of Eastern Christianity that arose from the Christological controversies of the 5th and 6th centuries, alongside the Oriental Orthodox Churches and the Chalcedonian Church. During the early modern period, a series of schisms gave rise to rival patriarchates, sometimes two, sometimes three. Since the latter half of the 20th century, three churches in Iraq claim the heritage of the Church of the East. Meanwhile, the East Syriac churches in India claim the heritage of the Church of the East in India. The Church of the East organized itself in 410 as the national church of the Sasanian Empire through the Council of Seleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Orthodox Church
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent one of its oldest branches. As some of the oldest religious institutions in the world, the Oriental Orthodox Churches have played a prominent role in the history and culture of Armenia, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Sudan, Western Asia and India. As autocephalous churches, its bishops are equal by virtue of episcopal ordination. Its doctrines recognizes the validity of only the first three ecumenical councils. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are composed of six autocephalous churches: the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, the Syriac Orthodox Church of Antioch, the Armenian Apostolic Church, the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, and the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church. They consider themselves to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Roman Catholic Church—the Pope—but the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognized by them as '' primus inter pares'' ("first among equals"), which may be explained as a representative of the church. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern and Southeastern Europe. The Eastern Orthodox Church officially calls itself the Orthodox Catholic Church. Eastern Orthodox theology is based on holy tradition, which incorporates the dogmatic decrees of the seven ecumenical councils, the Scriptures, and the teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynewulf
Cynewulf (, ; also spelled Cynwulf or Kynewulf) is one of twelve Old English poets known by name, and one of four whose work is known to survive today. He presumably flourished in the 9th century, with possible dates extending into the late 8th and early 10th centuries. Known for his religious compositions, Cynewulf is regarded as one of the pre-eminent figures of Anglo-Saxon Christian poetry. Posterity knows of his name by means of runic signatures that are interwoven into the four poems which comprise his scholastically recognized corpus. These poems are: ''The Fates of the Apostles'', ''Juliana'', ''Elene'', and ''Christ II'' (also referred to as ''The Ascension''). The four signed poems of Cynewulf are vast in that they collectively comprise several thousand lines of verse. In comparison, the one work attributed to Cædmon, ''Cædmon's Hymn'', is quite succinct at nine lines. Life Dialect Some basic statements can be made by examining such aspects as the spellings of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English Poetry
Old English literature refers to poetry and prose written in Old English in early medieval England, from the 7th century to the decades after the Norman Conquest of 1066, a period often termed Anglo-Saxon England. The 7th-century work ''Cædmon's Hymn'' is often considered as the oldest surviving poem in English, as it appears in an 8th-century copy of Bede's text, the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People''. Poetry written in the mid 12th century represents some of the latest post-Norman examples of Old English. Adherence to the grammatical rules of Old English is largely inconsistent in 12th-century work, and by the 13th century the grammar and syntax of Old English had almost completely deteriorated, giving way to the much larger Middle English corpus of literature. In descending order of quantity, Old English literature consists of: sermons and saints' lives; biblical translations; translated Latin works of the early Church Fathers; chronicles and narrative history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)

