|
Ligninase
Lignin-modifying enzymes (LMEs) are various types of enzymes produced by fungi and bacteria that catalyze the breakdown of lignin, a biopolymer commonly found in the cell walls of plants. The terms ligninases and lignases are older names for the same class, but the name "lignin-modifying enzymes" is now preferred, given that these enzymes are not hydrolytic but rather oxidative (electron withdrawing) by their enzymatic mechanisms. LMEs include peroxidases, such as lignin peroxidase (), manganese peroxidase (), versatile peroxidase (), and many phenoloxidases of the laccase type. LMEs have been known to be produced by many species of white rot basidiomycetous fungi, including: ''Phanerochaete chrysosporium'', ''Ceriporiopsis subvermispora'', ''Trametes versicolor'', '' Phlebia radiata'', ''Pleurotus ostreatus'' and ''Pleurotus eryngii''. LMEs are produced not only by wood-white rotting fungi but also by litter-decomposing basidiomycetous fungi such as ''Agaricus bisporus'' (common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin Peroxidase
In enzymology, a lignin peroxidase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol + H2O2 \rightleftharpoons 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde + 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane-1,2-diol + H2O Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol and H2O2, whereas its 3 products are 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane-1,2-diol, and H2O. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on a peroxide as acceptor (peroxidases) and can be included in the broad category of ligninases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 1,2-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include diarylpropane oxygenase, ligninase I, diarylpropane peroxidase, LiP, diarylpropane:oxygen,hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase (C-C-bond-cleaving). It employs one cofactor, heme. Background Lignin is highly resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriporiopsis Subvermispora
''Ceriporiopsis'' is a genus of fungi in the family Phanerochaetaceae. The genus is widely distributed, and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains about 25 species. ''Ceriporiopsis'' was circumscribed in 1963 by Polish mycologist Stanislaw Domanski. The genus is a wastebasket taxon, containing "species that share common macroscopic and microscopic characteristics, but are not necessarily related." ''Ceriporiopsis'' species are crust fungi that cause a white rot. They have a monomitic hyphal system, containing only generative hyphae, and these hyphae have clamp connections. Species *'' Ceriporiopsis alboaurantia'' C.L.Zhao, B.K.Cui & Y.C.Dai (2014) – China *'' Ceriporiopsis albonigrescens'' Núñez, Parmasto & Ryvarden (2001) *'' Ceriporiopsis allantosporus'' Ryvarden (2016) – Colombia *'' Ceriporiopsis aurantitingens'' (Corner) T.Hatt. (2002) *'' Ceriporiopsis balaenae'' Niemelä (1985) *'' Ceriporiopsis carnegiae'' (D.V.Baxter) Gilb. & Ryvarden (1985) *'' Ceriporiopsis ceru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
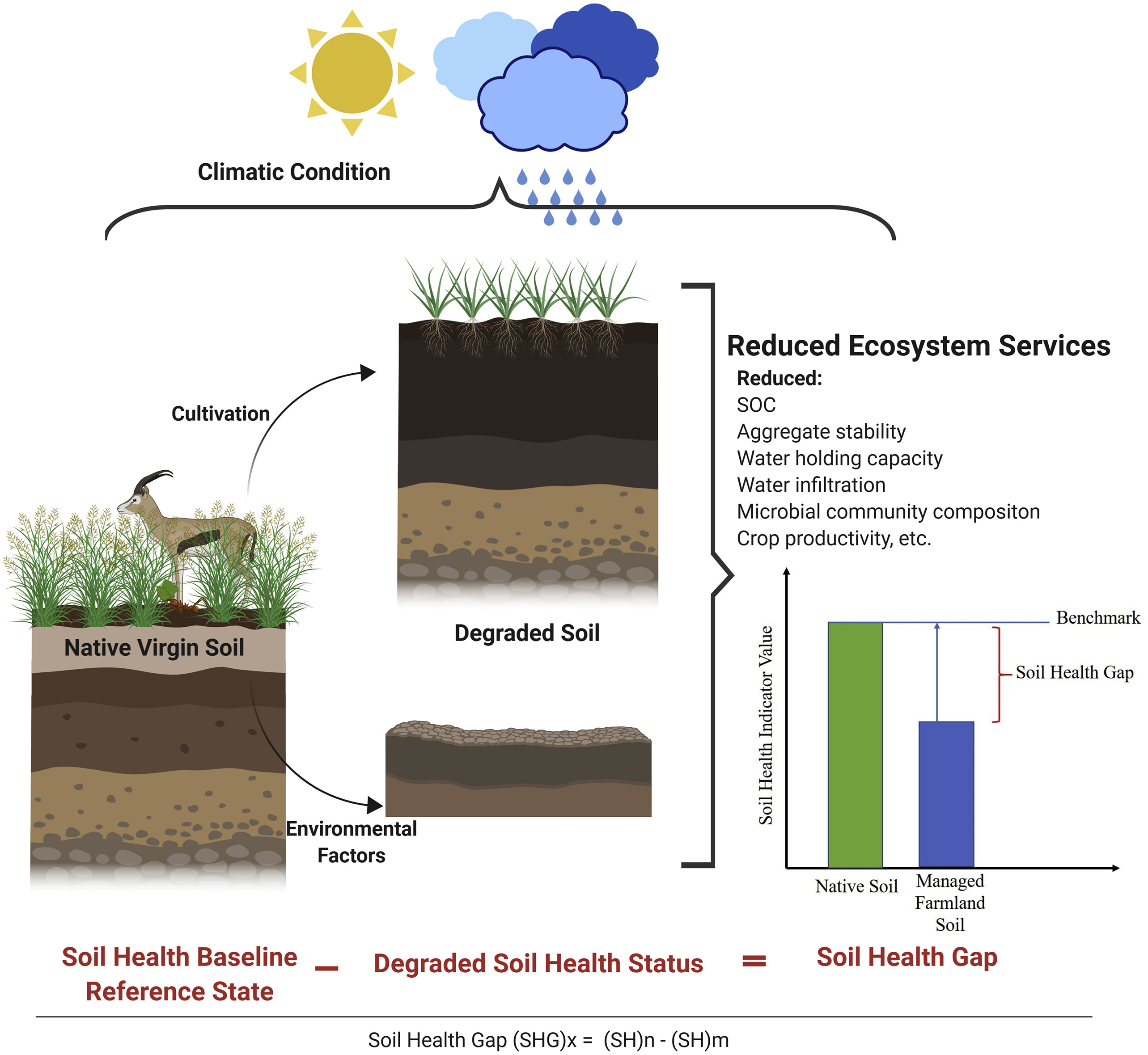
Soil Health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong together, as in microbiota, plants and animals. It is possible that a soil can be healthy in terms of eco-system functioning but not necessarily serve crop production or human nutrition directly, hence the scientific debate on terms and measurements. Soil health testing is pursued as an assessment of this status but tends to be confined largely to agronomic objectives, for obvious reasons. Soil health depends on soil biodiversity (with a robust soil biota), and it can be improved via soil management, especially by care to keep protective living covers on the soil and by natural (carbon-containing) soil amendments. Inorganic fertilizers do not necessarily damage soil health if 1) used at appropriate and not excessive rates and 2) if they b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration to and release from carbon sinks. Carbon sinks in the land and the ocean each currently take up about one-quarter of anthropogenic carbon emissions each year. Humans have disturbed the biological carbon cycle for many centuries by modifying land use, and moreover with the recent industrial-scale mining of fossil carbon (coal, petroleum and natural gas, gas extraction, and cement manufacture) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulase
Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4; systematic name 4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase) is any of several enzymes produced chiefly by fungi, bacteria, and protozoans that catalyze cellulolysis, the decomposition of cellulose and of some related polysaccharides: : Endohydrolysis of (1→4)-β-D-glucosidic linkages in cellulose, lichenin and cereal β-D-glucan The name is also used for any naturally occurring mixture or complex of various such enzymes, that act serially or synergistically to decompose cellulosic material. Cellulases break down the cellulose molecule into monosaccharides ("simple sugars") such as β-glucose, or shorter polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. Cellulose breakdown is of considerable economic importance, because it makes a major constituent of plants available for consumption and use in chemical reactions. The specific reaction involved is the hydrolysis of the 1,4-β-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, hemicellulose, lichenin, and cereal β-D-glucans. Because cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper. Smaller quantities are converted into a wide variety of derivative products such as cellophane and rayon. Conversion of cellulose from energy crops into biofuels such as cellulosic ethanol is under development as a renewable fuel source. Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and cotton. Some animals, particularly ruminants and termites, can digest cellulose with the help of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrocybe
''Agrocybe'' is a genus of mushrooms in the family Strophariaceae (previously placed in the Bolbitiaceae). The genus has a widespread distribution, and contains about 100 species. Distribution Mushroom cultivation began with the Romans and Greeks, who grew the small ''Agrocybe aegerita''. The Romans believed that fungi fruited when lightning struck. In Europe, toxic forms are not normally found, but ''Agrocybe molesta'' could be confused with poisonous white ''Agaricus'' species or with poisonous ''Amanita'' species. The edible southern species ''Agrocybe aegerita'' is commonly known as the Poplar mushroom, Chestnut mushroom or Velvet pioppino (Chinese: 茶樹菇). It is a white rot fungus and is a medium-sized agaric with a convex, almost flat, cap 3 to 10 cm in diameter. Underneath, it has numerous whitish radial plates adherent to the foot, later turning to a brownish-gray color, and light elliptic spores of 8-11 by 5-7 micrometres. The white fiber foot is generally cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coprinus
''Coprinus'' is a small genus of mushroom-forming fungi consisting of '' Coprinus comatus''the shaggy ink cap (British) or shaggy mane (American)and several of its close relatives. Until 2001, ''Coprinus'' was a large genus consisting of all agaric species in which the lamellae autodigested to release their spores. The black ink-like liquid this creates gave these species their common name "ink cap" (British) or "inky cap" (American). Molecular phylogenetic investigation found that ''Coprinus comatus'' was only a distant relative of the other members of ''Coprinus'', and was closer to genera in the Agaricaceae. Since ''Coprinus comatus'' is the type species of ''Coprinus'', only that species and its close relatives ''C. sterquilinus'' and ''C. spadiceisporus'' retained the name of the genus. The majority of species of ''Coprinus'' were therefore reclassified into three genera placed in Psathyrellaceae: ''Coprinellus'', ''Coprinopsis'', and '' Parasola''. ''Coprinus'' and these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaricus Bisporus
''Agaricus bisporus'' is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Eurasia and North America. It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state. ''A. bisporus'' is cultivated in more than seventy countries and is one of the most commonly and widely consumed mushrooms in the world. Names When immature and , this mushroom may be known as: * common mushroom * white mushroom * button mushroom * cultivated mushroom * table mushroom * champignon ( French for mushroom) When immature and , it may be known variously as: * Swiss brown mushroom * Roman brown mushroom * Italian brown mushroom * cremini/crimini mushroom * chestnut mushroom (not to be confused with '' Pholiota adiposa'') * baby bella When marketed in its mature state, the mushroom is brown with a cap measuring . This form is commonly sold under the names portobello, portabella, or portobella; the etymology is dispute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprotrophic Nutrition
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


