|
Lightwood–Albright Syndrome
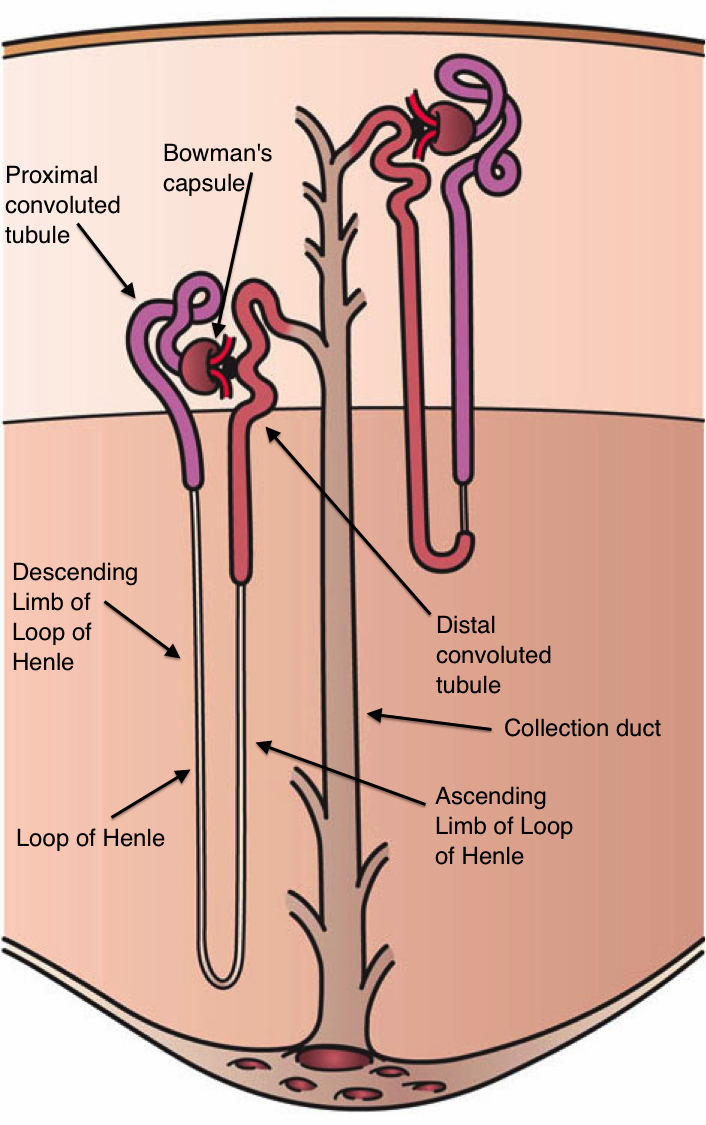
Lightwood–Albright syndrome is a neonatal form of renal tubular acidosis. It is characterized by distal renal tubular acidosis that occurs as a result of bicarbonate wasting and the inability to excrete hydrogen ions. By definition, it is a transient process and has no particular disease course. If untreated, it may lead to nephrocalcinosis and failure to thrive. It is also known as Lightwood Syndrome, Butler-Albright Syndrome, or Lightwood-Butler-Albright Syndrome. It is named for Reginald Cyril Lightwood and Fuller Albright.F. Albright, W. V. Consolazio, F. S. Coombs, J. H. Talbot; H. W. Sulkowitch. Metabolic studies and therapy in a case of nephrocalcinosis with rickets and dwarfism. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, 1940, 66: 7–33. Pathophysiology There is a genetic component to inheritance. While the disease can manifest without an inciting factor, most diagnoses come from an autosomal dominant and (less commonly) autosomal recessive form of inheritance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. In renal physiology, when blood is filtered by the kidney, the filtrate passes through the tubules of the nephron, allowing for exchange of salts, acid equivalents, and other solutes before it drains into the bladder as urine. The metabolic acidosis that results from RTA may be caused either by insufficient secretion of hydrogen ions (which are acidic) into the latter portions of the nephron (the distal tubule) or by failure to reabsorb sufficient bicarbonate ions (which are alkaline) from the filtrate in the early portion of the nephron (the proximal tubule). Although a metabolic acidosis also occurs in those with chronic kidney disease, the term RTA is reserved for individuals with poor urinary acidification in otherwise well-functioning kidneys. Several different types of RTA exist, which all have different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness and causes disability. Disuse causes rapid muscle atrophy and often occurs during injury or illness that requires immobilization of a limb or bed rest. Depending on the duration of disuse and the health of the individual, this may be fully reversed with activity. Malnutrition first causes fat loss but may progress to muscle atrophy in prolonged starvation and can be reversed with nutritional therapy. In contrast, cachexia is a wasting syndrome caused by an underlying disease such as cancer that causes dramatic muscle atrophy and cannot be completely reversed with nutritional therapy. Sarcopenia is age-related muscle atrophy and can be slowed by exercise. Finally, diseases of the muscles such as muscular dystrophy or myopathies can cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone deformities, bone pseudofractures and fractures, muscle spasms, or an abnormally curved spine. The most common cause of rickets is a vitamin D deficiency, although hereditary genetic forms also exist. This can result from eating a diet without enough vitamin D, dark skin, too little sun exposure, exclusive breastfeeding without vitamin D supplementation, celiac disease, and certain genetic conditions. Other factors may include not enough calcium or phosphorus. The underlying mechanism involves insufficient calcification of the growth plate. Diagnosis is generally based on blood tests finding a low calcium, low phosphorus, and a high alkaline phosphatase together with X-rays. Prevention for exclusively breastfed babies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an ''infant school'' is for children aged between four and seven. As a legal term, ''infancy'' is more lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Structurally, they (together with helium) have in common an outer s-orbital which is full; that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the decay chain of uranium and thorium and not as a primordial element. There have been experiments, all unsuccessful, to try to synthesize element 120, the next potential member of the group. Characteristics Chemical As with other groups, the members of this family show patterns in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowe Syndrome
Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (also called Lowe syndrome) is a rare X-linked recessive disorder characterized by congenital cataracts, hypotonia, intellectual disability, proximal tubular acidosis, aminoaciduria and low-molecular-weight proteinuria. Lowe syndrome can be considered a cause of Fanconi syndrome (bicarbonaturia, renal tubular acidosis, potassium loss and sodium loss). Signs and symptoms Boys with Lowe syndrome are born with cataracts in both eyes; glaucoma is present in about half of the individuals with Lowe syndrome, though usually not at birth. While not present at birth, kidney problems develop in many affected boys at about one year of age. Renal pathology is characterized by an abnormal loss of certain substances into the urine, including bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, amino acids, organic acids, albumin, calcium and L-carnitine. This problem is known as Fanconi-type renal tubular dysfunction. Genetics This syndrome is caused by mutations in the ''OCRL'' gene which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gitelman Syndrome
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by disease-causing variants in both alleles of the ''SLC12A3'' gene''.'' The ''SLC12A3'' gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter (also known as NCC, NCCT, or TSC), which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. The distal convoluted tubule of the kidney plays an important homeostatic role in sodium and chloride absorption as well as of the reabsorption of magnesium and calcium. Genetic mutations of NCC, lead to loss of function and subsequently, reduced transport of sodium and chloride via NCC. Secondary derangement of calcium, magnesium, and potassium concentrations are caused by secondary effects in the distal tubule and collecting duct. The effect is an electrolyte imbalance similar to that seen with thiazide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency
Adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA deficiency) is a metabolic disorder that causes immunodeficiency. It is caused by mutations in the ADA gene. It accounts for about 10–15% of all cases of autosomal recessive forms of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) among non-inbred populations. ADA deficiency can present in infancy, childhood, adolescence, or adulthood. Age of onset and severity is related to some 29 known genotypes associated with the disorder. It occurs in fewer than one in 100,000 live births worldwide. Signs and symptoms The main symptoms of ADA deficiency are pneumonia, chronic diarrhea, and widespread skin rashes. Affected children also grow much more slowly than healthy children and some have developmental delay. Most individuals with ADA deficiency are diagnosed with SCID in the first 6 months of life. An association with polyarteritis nodosa has been reported.Liebowitz J, Hellmann DB1, Schnappauf O (2019) Thirty years of followup in 3 patients with fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Paralysis
Periodic paralysis is a group of rare genetic diseases that lead to weakness or paralysis from common triggers such as cold, heat, high carbohydrate meals, not eating, stress or excitement and physical activity of any kind. The underlying mechanism of these diseases are malfunctions in the ion channels in skeletal muscle cell membranes that allow electrically charged ions to leak in or out of the muscle cell, causing the cell to depolarize and become unable to move. The symptoms of periodic paralysis can also be caused by hyperthyroidism, and are then labeled thyrotoxic periodic paralysis; however, if this is the underlying condition there are likely to be other characteristic manifestations, enabling a correct diagnosis. Types Periodic paralysis is an autosomal dominant myopathy with considerable variation in penetrance, leading to a spectrum of familial phenotypes (only one parent needs to carry the gene mutation to affect the children, but not all family members who share the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydipsia
Polydipsia is excessive thirst or excess drinking.Porth, C. M. (1990). ''Pathophysiology: Concepts of altered health states''. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott Company. The word derives from the Greek () "very thirsty", which is derived from (, "much, many") + (, "thirst"). Polydipsia is a nonspecific symptom in various medical disorders. It also occurs as an abnormal behaviour in some non-human animals, such as in birds. Causes Diabetes Polydipsia can be characteristic of diabetes mellitus, often as an initial symptom. It is observed in cases of poorly controlled diabetes, which is sometimes the result of low patient adherence to anti-diabetic medication. Diabetes insipidus ("tasteless" diabetes, as opposed to diabetes mellitus) can also cause polydipsia. Other physiological causes It can also be caused by a change in the osmolality of the extracellular fluids of the body, hypokalemia, decreased blood volume (as occurs during major hemorrhage), and other conditions that cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyuria
Polyuria () is excessive or an abnormally large production or passage of urine (greater than 2.5 L or 3 L over 24 hours in adults). Increased production and passage of urine may also be termed diuresis. Polyuria often appears in conjunction with polydipsia (increased thirst), though it is possible to have one without the other, and the latter may be a cause or an effect. Primary polydipsia may lead to polyuria. Polyuria is usually viewed as a symptom or sign of another disorder (not a disease by itself), but it can be classed as a disorder, at least when its underlying causes are not clear. Causes The most common cause of polyuria in both adults and children is uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, which causes osmotic diuresis, when glucose levels are so high that glucose is excreted in the urine. Water follows the glucose concentration passively, leading to abnormally high urine output. In the absence of diabetes mellitus, the most common causes are decreased secretion of aldosteron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basicity
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. They are slippery to the touch, can taste bitter and change the color of pH indicators (e.g., turn red litmus paper blue). In water, by altering the autoionization equilibrium, bases yield solutions in which the hydrogen ion activity is lower than it is in pure water, i.e., the water has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |