|
Light-weight Linux Distribution
A light-weight Linux distribution is one that uses lower memory and/or has less processor-speed requirements than a more "feature-rich" Linux distribution. The lower demands on hardware ideally result in a more responsive machine, and/or allow devices with fewer system resources (e.g. older or embedded hardware) to be used productively. The lower memory and/or processor-speed requirements are achieved by avoiding software bloat, i.e. by leaving out features that are perceived to have little or no practical use or advantage, or for which there is no or low demand. The perceived weight of a Linux distribution is strongly influenced by the desktop environment included with that distribution. Accordingly, many Linux distributions offer a choice of editions. For example, Canonical hosts several variants ("flavors") of the Ubuntu distribution that include desktop environments other than the default GNOME or the deprecated Unity. These variants include the Xubuntu and Lubuntu distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubuntu 20
Lubuntu ( ) is a lightweight Linux distribution based on Ubuntu and uses the LXQt desktop environment in place of Ubuntu's GNOME desktop. Lubuntu was originally touted as being "lighter, less resource hungry and more energy-efficient", but now aims to be "a functional yet modular distribution focused on getting out of the way and letting users use their computer". Lubuntu originally used the LXDE desktop, but moved to the LXQt desktop with the release of Lubuntu 18.10 in October 2018, due to the slow development of LXDE, losing support for GTK 2 as well as the more active and stable LXQt development without GNOME dependencies. The name ''Lubuntu'' is a portmanteau of ''LXQt'' and ''Ubuntu''. The LXQt name derives from the merger of the LXDE and Razor-qt projects, while the word ''Ubuntu'' means "humanity towards others" in the Zulu and Xhosa languages. Lubuntu received official recognition as a formal member of the Ubuntu family on 11 May 2011, commencing with Lubuntu 11.10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArchBang
ArchBang Linux is a simple lightweight rolling release Linux distribution based on a minimal Arch Linux operating system with the I3 (window manager), i3 window manager, but was previously using the Openbox Window manager, windows manager. ArchBang is especially suitable for high performance on old or low-end hardware with limited resources. ArchBang's aim is to provide a simple out-of-the-box Arch-based Linux distribution with a pre-configured i3 desktop suite, adhering to Arch principles. ArchBang has also been recommended as a fast installation method for people who have experience installing Arch Linux but want to avoid the more demanding default installation of Arch Linux when reinstalling it on another PC. History Inspired by CrunchBang Linux (which was derived from Debian), ArchBang was originally conceived and founded in a forum thread posted on the CrunchBang Forums by Willensky Aristide (a.k.a. Will X TrEmE). Aristide wanted a rolling release with the Openbox setup that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
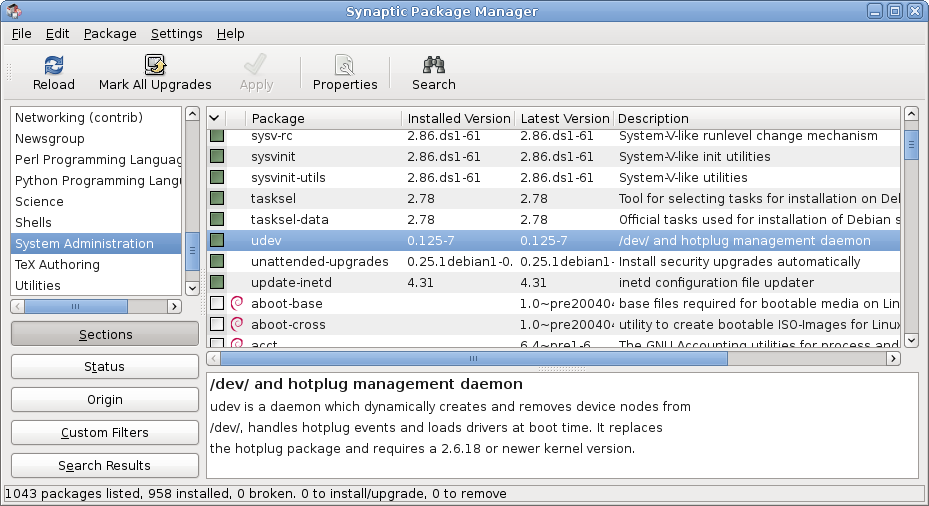
Package Manager
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zorin OS
Zorin may refer to: People * Andrei Zorin (born 1997), Russian footballer * Leonid Zorin, (1924–2020), Russian playwright * Sergey Zorin (1891–1937), Soviet politician * Simcha Zorin (1902–1974), Soviet Jewish partisan in World War II * Valentin Zorin (1925–2016), Russian author * Valerian Zorin (1902–1986), Soviet diplomat * Yuriy Zorin (born 1947), Russian athlete Other uses * Max Zorin, a fictional James Bond character * Zorin Blitz, a fictional Nazi vampire from Hellsing, a manga by Kouta Hirano * Zorin OS, a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu See also * Vera Zorina (1917–2003), Norwegian ballerina and actress * Zorino, Astrakhan Oblast {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SparkyLinux
SparkyLinux is a desktop-oriented operating system based on the Debian operating system. The project offers a ready to use operating system with a set of various customised lightweight desktops to choose from. SparkyLinux is released 3-4 times per year to provide the latest versions of all applications. History The project was born on October, 2011 as an Ubuntu remix with Enlightenment as the default desktop having the name ue17r (Ubuntu Enlightenment17 Remix). After a few months of testing, the base system was changed to Debian and it was renamed to SparkyLinux. Features SparkyLinux is based on "stable" and "testing" branches of Debian and uses a 'rolling-release-cycle' (testing based only). It includes a collection of tools and scripts to help users with easy administration of the system. The default desktop environments are LXQt (former LXDE), MATE, Xfce and KDE, but users can install other desktops via 'Sparky APTus'. As Sparky ISO image features a few proprietary pack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PostmarketOS
postmarketOS (abbreviated as pmOS) is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution. postmarketOS was launched on 26 May 2017 with the source code available on GitHub before migrating to GitLab in 2018. It is capable of running different X and Wayland based user interfaces, such as Plasma Mobile, MATE, GNOME 3, and XFCE; later updates added support for Unity8 and Phosh. It is also capable of running Docker, if the device specific kernel has cgroups and relevant configs enabled. The project aims to provide a ten-year lifecycle for smartphones. Architecture Unlike many other projects porting conventional Linux distributions to Android phones, postmarketOS does not use the Android build system or userspace. Each phone has only one unique package, and flashable installation images are generated using the pmbootstrap tool. The project intends to support the mainline Linux kernel on all phones in the future, instead of the often outdated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)#501(c)(3), 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft ("share alike") terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, US, where it is also based. From its founding until the mid-1990s, FSF's funds were mostly used to employ software developers to write free software for the GNU Project. Since the mid-1990s, the FSF's employees and volunteers have mostly worked on legal and structural issues for the free software movement and the free software community. Consistent with its goals, the FSF aims to use only free software on its own computers. History The Free Software Foundation was founded in 1985 as a Nonprofit corporation, non-profit corporation supporting free software development. It continued existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola GNU/Linux-libre
Parabola GNU/Linux-libre is an operating system for the i686, x86-64 and ARMv7 architectures. It is based on many of the packages from Arch Linux and Arch Linux ARM, but distinguishes from the former by offering only free software. It includes the GNU operating system components common to many Linux distributions and the Linux-libre kernel instead of the generic Linux kernel. Parabola is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a completely free operating system, true to their Free System Distribution Guidelines. Parabola uses a rolling release model like Arch, such that a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest software. Development focuses on system simplicity, community involvement and use of the latest free software packages. History Parabola was originally proposed by members of the gNewSense IRC channel in 2009. Members of different Arch Linux communities, especially Spanish-speaking members, started the development and maintenance of the proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LinuxConsole
LinuxConsole is a Linux-based operating system independently developed by Yann Le Doaré. The distro is built from scratch by developers from France, and has support for multiple languages. It is not based on any other Linux distribution and primarily focuses on being lightweight and easily accessible. LinuxConsole can function as a Live CD and Live USB. It can also be installed as a complete modern operating system. History The earliest known verifiable release is documented as version 0.4 in 2004 on Distrowatch, and was based on Mandrake Linux. Version 0.4 expanded upon the previous release by adding many applications, and tools making it useful for more than just games and multimedia. The list of added software included programs used for working with documents, playing music as well as other server utilities, firewall security, and printer/scanner tools. The first release confirmed to be independently developed was version 1.0.2007 released in 2007. It added full capabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IceWM
IceWM is a stacking window manager for the X Window System, originally written by Marko Maček. It was written from scratch in C++ and is released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License. It is customizable, relatively lightweight in terms of memory and CPU usage, and comes with themes that allow it to imitate the GUI of Windows 95, Windows XP, Windows 7, OS/2, Motif, and other graphical user interfaces. IceWM can be configured from plain text files stored in a user's home directory, making it easy to customize and copy settings. IceWM has an optional, built-in taskbar with a dynamic start menu, tasks display, system tray, network and CPU meters, mail check and configurable clock. It features a task list window and an Alt+Tab task switcher. Official support for GNOME and KDE menus used to be available as a separate package. In recent IceWM versions, support for them is built-in as well. External graphical programs for editing the configuration and the menu a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
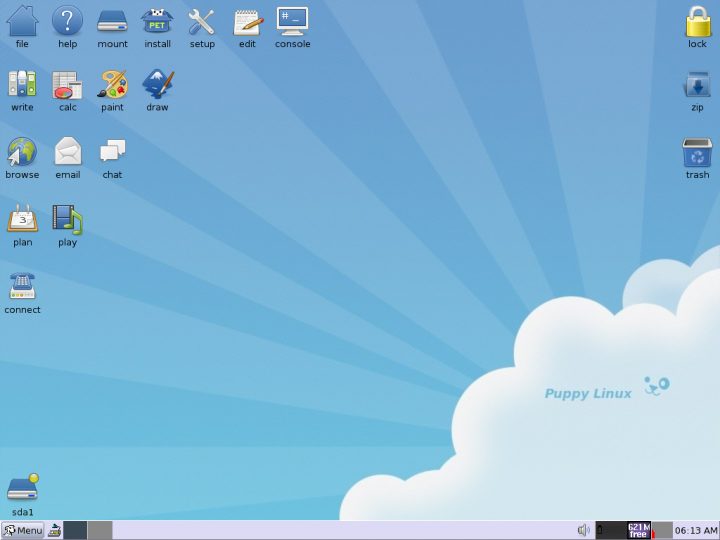
Puppy Linux
Puppy Linux is an operating system and family of light-weight Linux distributions that focus on ease of use and minimal memory footprint. The entire system can be run from random-access memory (RAM) with current versions generally taking up about 600 MB (64-bit), 300 MB (32-bit), allowing the boot medium to be removed after the operating system has started. Applications such as AbiWord, Gnumeric and MPlayer are included, along with a choice of lightweight web browsers and a utility for downloading other packages. The distribution was originally developed by Barry Kauler and other members of the community, until Kauler retired in 2013. The tool Woof can build a Puppy Linux distribution from the binary packages of other Linux distributions. History Barry Kauler started Puppy Linux in response to a trend of other distributions becoming stricter on system requirements over time. His own distribution, with an emphasis on speed and efficiency and being lightweight, started from "Boot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |