|
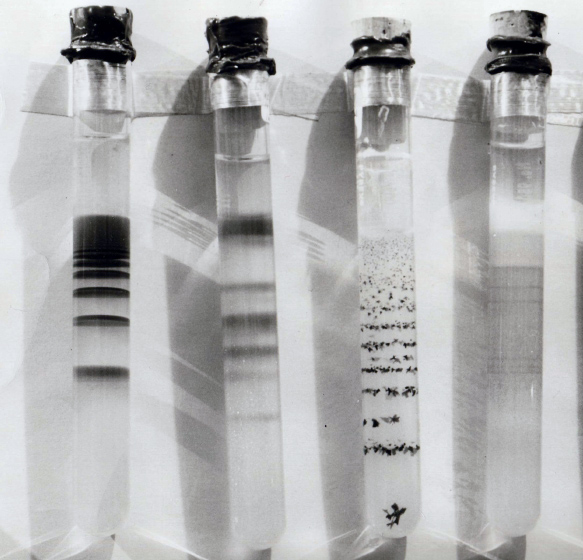
Liesegang Rings
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and " Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liesegang Rings
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and " Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
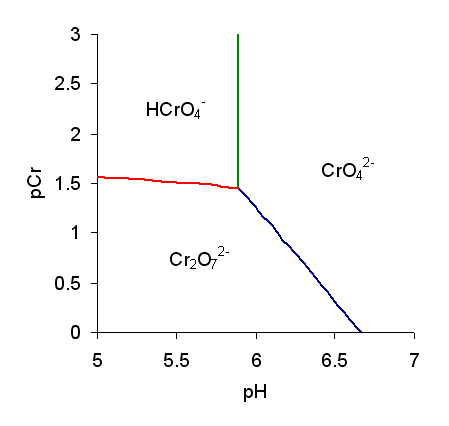
Chromates
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, CrO(O2)2, is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex CrO(O2)2py. Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. :2 + 2 H+ + H2O The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ostwald
Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald (; 4 April 1932) was a Baltic German chemist and German philosophy, philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst, and Svante Arrhenius. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909 for his scientific contributions to the fields of catalysis, chemical equilibria and Reaction velocity, reaction velocities. Following his 1906 retirement from academic life, Ostwald became much involved in philosophy, art, and politics. He made significant contributions to each of these fields. He has been described as a polymath. Early life and education Ostwald was born ethnically Baltic German in Riga, Russian Empire (now Latvia) to cooper (profession), master-cooper Gottfried Wilhelm Ostwald (1824–1903) and Elisabeth Leuckel (1824–1903). He was the middle child of three, born after Eugen (1851–1932) and before Gottfried (1855–1918). Ostwald developed an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liesegang Rings Of Magnesium Hydroxide In Agar Gel - (4)
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and " Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride
Hydroxylammonium chloride is the hydrochloric acid salt of hydroxylamine. Hydroxylamine is a biological intermediate in nitrification (biological oxidation of ammonia with oxygen into nitrite) and in anammox (biological oxidation of nitrite and ammonium into dinitrogen gas) which are important in the nitrogen cycle in soil and in wastewater treatment plants. Applications Hydroxylammonium chloride is used in organic synthesis for preparation of oximes and hydroxamic acids from carboxylic acids, N- and O- substituted hydroxylamines, and addition reactions of carbon-carbon double bond. During the acetyl bromide method of extracting lignin from lignocellulosic biomass, hydroxylammonium chloride can be used to remove bromine and polybromide from the solution. In surface treatments, it is used in the preparation of anti-skinning agents, corrosion inhibitors, and cleaner additives. It is also a starting material for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals manufacturing. In the rubber and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sulfate
Copper sulfate may refer to: * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, a common compound used as a fungicide and herbicide * Copper(I) sulfate Copper(I) sulfate, also known as cuprous sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2 SO4. It is a white solid that has attracted little attention, in contrast to copper(II) sulfate. It is an unusual example of a copper(I) ..., Cu2SO4, which is uncommonly used * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4 is greenish blue Copper compounds {{Chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Glass
Sodium silicate is a generic name for chemical compounds with the formula or ·, such as sodium metasilicate , sodium orthosilicate , and sodium pyrosilicate . The anions are often polymeric. These compounds are generally colorless transparent solids or white powders, and soluble in water in various amounts. Sodium silicate is also the technical and common name for a mixture of such compounds, chiefly the metasilicate, also called waterglass, water glass, or liquid glass. The product has a wide variety of uses, including the formulation of cements, passive fire protection, textile and lumber processing, manufacture of refractory ceramics, as adhesives, and in the production of silica gel. The commercial product, available in water solution or in solid form, is often greenish or blue owing to the presence of iron-containing impurities. In industry, the various grades of sodium silicate are characterized by their SiO2:Na2O weight ratio (which can be converted to molar ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicic Acid
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar
Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is a mixture of two components, the linear polysaccharide agarose and a heterogeneous mixture of smaller molecules called agaropectin. It forms the supporting structure in the cell walls of certain species of algae and is released on boiling. These algae are known as agarophytes, belonging to the Rhodophyta (red algae) phylum. The processing of food-grade agar removes the agaropectin, and the commercial product is essentially pure agarose. Agar has been used as an ingredient in desserts throughout Asia and also as a solid substrate to contain culture media for microbiological work. Agar can be used as a laxative; an appetite suppressant; a vegan substitute for gelatin; a thickener for soups; in fruit preserves, ice cream, and other desser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics. Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein fibrils into smaller peptides; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin desserts, most gummy candy and marshmallows, ice creams, dips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




