|
Liberatores
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated by a group of senators on the Ides of March (15 March) of 44 BC during a meeting of the Senate at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey in Rome where the senators stabbed Caesar 23 times. They claimed to be acting over fears that Caesar's unprecedented concentration of power during his dictatorship was undermining the Roman Republic. At least 60 senators were party to the conspiracy, led by Marcus Junius Brutus and Gaius Cassius Longinus. Despite the death of Caesar, the conspirators were unable to restore the institutions of the Republic. The ramifications of the assassination led to the Liberators' civil war and ultimately to the Principate period of the Roman Empire. Causes Caesar had served the Republic for eight years in the Gallic Wars, fully conquering the region of Gaul (roughly equivalent to modern-day France). After the Roman Senate demanded Caesar to disband his army and return home as a civilian, he ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
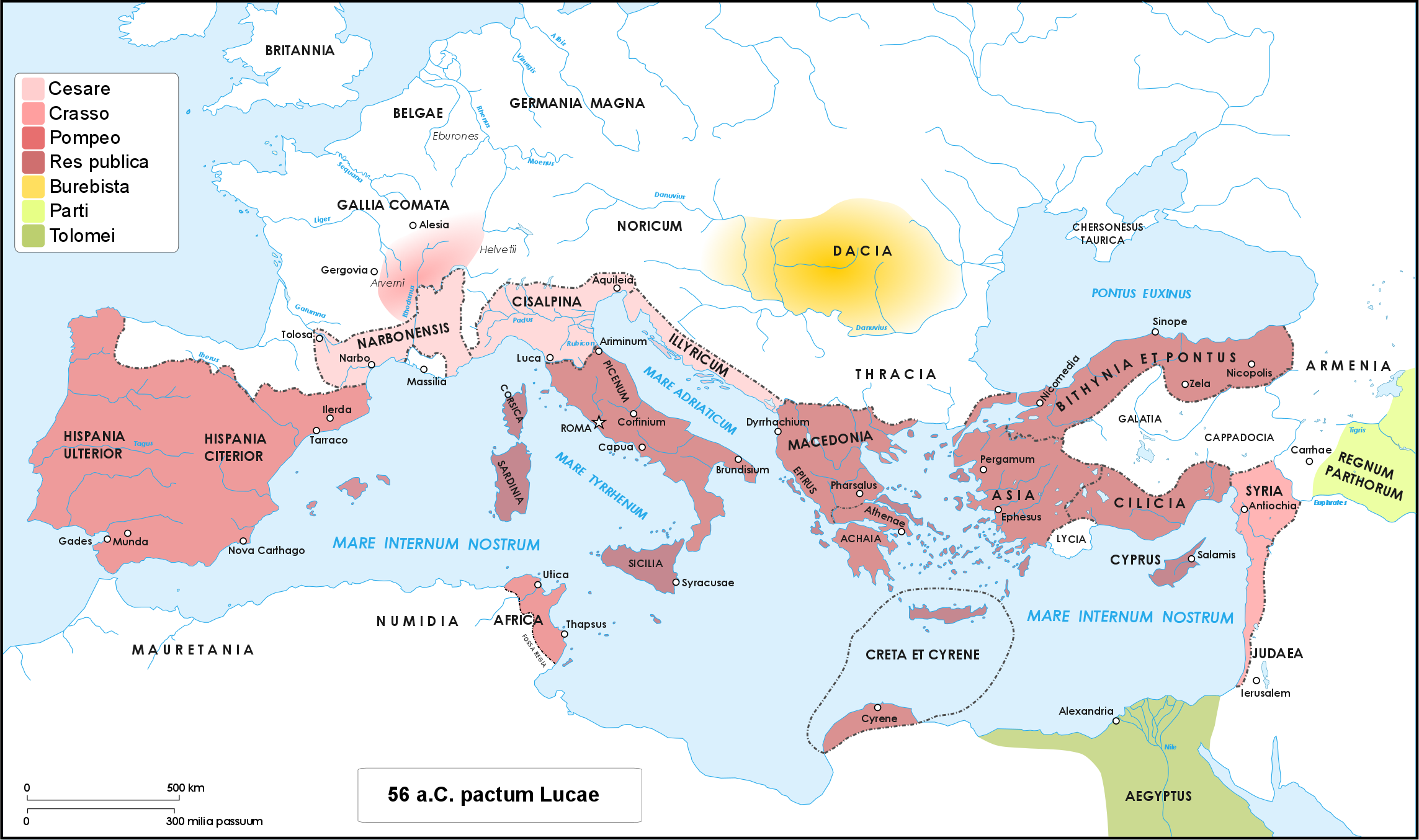
Liberators' Civil War
The Liberators' civil war (43–42 BC) was started by the Second Triumvirate to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination. The war was fought by the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (the Second Triumvirate members) against the forces of Caesar's assassins, led by Marcus Junius Brutus and Gaius Cassius Longinus, also called the ''Liberatores''. The latter were defeated by the Triumvirs at the Battle of Philippi in October 42 BC, and committed suicide. Brutus would also commit suicide after the second part of the battle. Prelude After the murder of Caesar, Brutus and Cassius (the two main conspirators, also known as the Liberatores) had left Italy and taken control of all Eastern provinces (from Greece and Macedonia to Syria) and of the allied Eastern kingdoms. In Rome the three main Caesarian leaders (Antony, Octavian and Marcus Aemilius Lepidus), who controlled almost all the Roman army in the west, had crushed the opposition of the senate and established the second triumvirate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was retained as his legal name. Early in his political career, Brutus opposed Pompey, who was responsible for Brutus' father's death. He also was close to Caesar. However, Caesar's attempts to evade accountability in the law courts put him at greater odds with his opponents in the Roman elite and the senate. Brutus eventually came to oppose Caesar and sided with Pompey against Caesar's forces during the ensuing civil war (49–45 BC). Pompey was defeated at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48, after which Brutus surrendered to Caesar, who granted him amnesty. With Caesar's increasingly monarchical and autocratic behaviour after the civil war, several senators who later called themselves ''liberatores'' (Liberators), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Junius Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was retained as his legal name. Early in his political career, Brutus opposed Pompey, who was responsible for Brutus' father's death. He also was close to Caesar. However, Caesar's attempts to evade accountability in the law courts put him at greater odds with his opponents in the Roman elite and the senate. Brutus eventually came to oppose Caesar and sided with Pompey against Caesar's forces during the ensuing civil war (49–45 BC). Pompey was defeated at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48, after which Brutus surrendered to Caesar, who granted him amnesty. With Caesar's increasingly monarchical and autocratic behaviour after the civil war, several senators who later called themselves ''liberatores'' (Liberators), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus
Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus (27 April 81 BC – September 43 BC) was a Roman general and politician of the late republican period and one of the leading instigators of Julius Caesar's assassination. He had previously been an important supporter of Caesar in the Gallic Wars and in the civil war against Pompey. Decimus Brutus is often confused with his distant cousin and fellow conspirator, Marcus Junius Brutus. Biography Early life Decimus was probably son of the Roman senator Decimus Junius Brutus and his notorious wife Sempronia, one of the participants in the conspiracy of Catilina in 63 BC. His birthday seems to have been 27 April, and he was probably born in the year 81 BC, perhaps slightly earlier. Decimus was of distinguished ancestry: his father, grandfather and great-grandfather had all been consuls, and his mother was likely descended from Gaius Gracchus, the ill-fated popular reformer. He was also adopted by a patrician named Postumius Albinus, one of the last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Of The Roman Republic
The crisis of the Roman Republic refers to an extended period of political instability and social unrest from about 134 BC to 44 BC that culminated in the demise of the Roman Republic and the advent of the Roman Empire. The causes and attributes of the crisis changed throughout the decades, including the forms of slavery, brigandage, wars internal and external, overwhelming corruption, land reform, the invention of excruciating new punishments, the expansion of Roman citizenship, and even the changing composition of the Roman army. Modern scholars also disagree about the nature of the crisis. Traditionally, the expansion of citizenship (with all its rights, privileges, and duties) was looked upon negatively by Sallust, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Gibbon, and others of their schools, because it caused internal dissension, disputes with Rome's Italian allies, slave revolts, and riots.Fields, p. 41, citing Sallust, ''Iugurthinum'' 86.2. However, other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictator Perpetuo
''Dictator perpetuo'' (English: "dictator in perpetuity"), also called ''dictator in perpetuum'', was the office held by Julius Caesar from between 26 January and 15 February during the year 44 BCE until his death on 15 March. By abandoning the time restrictions usually applied in the case of the Roman dictatorship, it elevated Caesar's dictatorship into the monarchical sphere. History Julius Caesar held the dictator position for only eleven days in 49 BCE (holding elections either as ''dictator Comit. habend.'' or as ''dictator rei gerundae causa'') and again for the year 48/47 BCE. In 46 BCE, he was elected dictator for the next ten years. At some point between January and February 44 BCE he was appointed ''dictator perpetuo'', but was assassinated less than two months later (on the Ides of March). Weinstock has argued that the perpetual dictatorship was part of the senatorial decrees regarding Caesar's divine honors, as well as his planned apotheosis as ''Divus Iulius'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubicon
The Rubicon ( la, Rubico; it, Rubicone ; rgn, Rubicôn ) is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, just north of Rimini. It was known as Fiumicino until 1933, when it was identified with the ancient river Rubicon, famously crossed by Julius Caesar in 49 BC. The river flows for around from the Apennine Mountains to the Adriatic Sea through the south of the Emilia-Romagna region, between the towns of Rimini and Cesena. History The Latin word comes from the adjective , meaning "red". The river was so named because its waters are colored red by iron deposits in the riverbed. During the Roman Republic, the Rubicon marked the boundary between the Roman province of Cisalpine Gaul and Italy proper, controlled directly by Rome and its (allies), to the south. On the north-western side, the border was marked by the river Arno, a much wider and more important waterway, which flows westward from the Apennine Mountains (the Arno and the Rubicon rise not far from each other) into the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
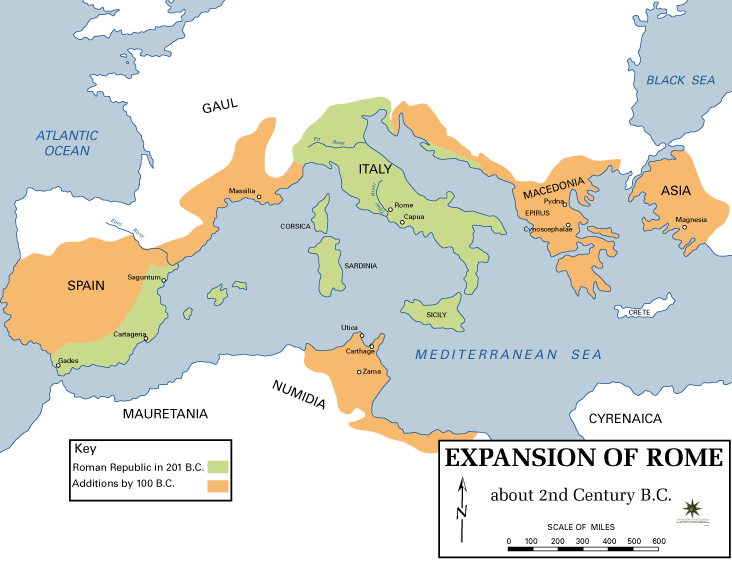
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homelands against an aggressive Roman campaign. The Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul. Though the Gallic military was as strong as the Romans, the Gallic tribes' internal divisions eased victory for Caesar. Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix's attempt to unite the Gauls under a single banner came too late. Caesar portrayed the invasion as being a preemptive and defensive action, but historians agree that he fought the Wars primarily to boost his political career and to pay off his debts. Still, Gaul was of significant military importance to the Romans. Native tribes in the region, both Gallic and Germanic, had attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Brutus%2C_denarius%2C_54_BC%2C_RRC_433-2.jpg)