|
Liber Rasielis
''Sefer Raziel HaMalakh'', (Hebrew:, "the book of Raziel the angel''"''), is a grimoire of Practical Kabbalah from the Middle Ages written primarily in Hebrew and Aramaic. ''Liber Razielis Archangeli'', its 13th-century Latin translation produced under Alfonso X of Castile, survives. Textual history The book cannot be shown to predate the 13th century, but may in parts date back to late antiquity. Like other obscure ancient texts such as the '' Bahir'' and '' Sefer Yetzirah'', the work has been extant in a number of versions. The tradition around the book attributes it to have been revealed to Adam by the angel Raziel. The title itself is mentioned in another magical work of late antiquity, '' The Sword of Moses''. Critical historians regard it as a medieval work, most probably originating among the Ashkenazi Hasidim, as citations from it begin to appear only in the 13th century. Sections of it are no doubt older. The likely compiler of the medieval version is Eleazar of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Raziel Segulot
Sefer may refer to: * Sefer (Hebrew), a term for a book People with the surname *Franjo Šefer (born 1905), Yugoslav tennis player *Bela Šefer, Yugoslav footballer playing in 1924 People with the forename * Sefer Reis, Turkish privateer and Ottoman admiral * Sefer Turan, Turkish journalist and author * Hoca Sefer Hoca Sefer ( 1536–38) was an Ottoman captain in charge of pro-Ottoman forces in Gujarat in the first half of the 16th century. Hoca Sefer, who had been installed by the Ottoman captain Selman Reis, attempted to maintain Ottoman influence in Diu ..., 15th-century Ottoman captain * Sefer Daja (1897-1977), person from Tirana, Albania See also * * {{disambig, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Of Cusa
Nicholas of Cusa (1401 – 11 August 1464), also referred to as Nicholas of Kues and Nicolaus Cusanus (), was a German Catholic cardinal, philosopher, theologian, jurist, mathematician, and astronomer. One of the first German proponents of Renaissance humanism, he made spiritual and political contributions in European history. A notable example of this is his mystical or spiritual writings on "learned ignorance," as well as his participation in power struggles between Rome and the German states of the Holy Roman Empire. As papal legate to Germany from 1446, he was appointed cardinal for his merits by Pope Nicholas V in 1448 and Prince–Bishop of Brixen two years later. In 1459, he became vicar general in the Papal States. Nicholas has remained an influential figure. In 2001, the sixth centennial of his birth was celebrated on four continents and commemorated by publications on his life and work. Life Nicholas was born in Kues ( Latinized as "Cusa") in southwestern German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Hartlieb
Johannes Hartlieb (c. 1410Hartlieb's year of birth is unknown; his existence is first attested as the author of ''Kunst der Gedächtnüß'', written during 1430–32, and an estimate of his year of birth as either "c. 1400" or "c. 1410" can be found in literature. – 18 May 1468) was a physician of Late Medieval Bavaria, probably of a family from Neuburg an der Donau. He was in the employment of Louis VII of Bavaria and Albert VI of Austria in the 1430s, and of Albert III of Bavaria from 1440, and of the latter's son Sigismund from 1456. In 1444, he married Sibilla, possibly the daughter of Albert and Agnes Bernauer. Hartlieb wrote a compendium on herbs in ca. 1440, and in 1456 the ''puch aller verpoten kunst, ungelaubens und der zaubrey'' (book on all forbidden arts, superstition and sorcery) on the artes magicae, containing the oldest known description of witches' flying ointment. Hartlieb also produced German translations of various classical and medieval authors ( T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necromancy
Necromancy () is the practice of magic or black magic involving communication with the dead by summoning their spirits as apparitions or visions, or by resurrection for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future events; discovery of hidden knowledge; returning a person to life, or to use the dead as a weapon. Sometimes referred to as "death magic," the term is used in a more general sense to refer to black magic or witchcraft. The word ''necromancy'' is adapted from Late Latin : a loan word from the post-Classical Greek (), a compound of Ancient Greek (, or 'dead body') and (, or 'divination'). The Koine Greek compound form was first documented in the writings of Origen of Alexandria in the 3rd century AD. The Classical Greek term was (), from the episode of the ''Odyssey'' in which Odysseus visits the realm of the dead souls, and in Hellenistic Greek; in Latin, and ''necromancy'' in 17th-century English. Antiquity Early necromancy was relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picatrix
''Picatrix'' is the Latin name used today for a 400-page book of magic and astrology originally written in Arabic under the title ''Ghāyat al-Ḥakīm'' ( ar, غاية الحكيم), which most scholars assume was originally written in the middle of the 11th century, though an argument for composition in the first half of the 10th century has been made. The Arabic title translates as ''The Aim of the Sage'' or ''The Goal of The Wise''. The Arabic work was translated into Spanish and then into Latin during the 13th century, at which time it got the Latin title ''Picatrix''. The book's title ''Picatrix'' is also sometimes used to refer to the book's author. ''Picatrix'' is a composite work that synthesizes older works on magic and astrology. One of the most influential interpretations suggests it is to be regarded as a "handbook of talismanic magic". Another researcher summarizes it as "the most thorough exposition of celestial magic in Arabic", indicating the sources for the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Magic
Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of the magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. These magical arts (called '' artes magicae'') were divided into seven types. There was great uncertainty in distinguishing practices of superstition, occultism, and perfectly sound scholarly knowledge or pious ritual. The intellectual and spiritual tensions erupted in the Early Modern witch craze, further reinforced by the turmoil of the Protestant Reformation, especially in Germany, England, and Scotland. Artes magicae The seven ''artes magicae'' or ''artes prohibitae'', arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456, their sevenfold partition reflecting that of the artes liberales and artes mechanicae, were: # nigromancy ('black magic', demonolatry) # geomancy # hydromancy # aeromancy # pyromancy # chiromancy # scapulimancy The division between the four "elemental" disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Adam
Sefer may refer to: * Sefer (Hebrew), a term for a book People with the surname *Franjo Šefer (born 1905), Yugoslav tennis player *Bela Šefer, Yugoslav footballer playing in 1924 People with the forename * Sefer Reis, Turkish privateer and Ottoman admiral * Sefer Turan, Turkish journalist and author * Hoca Sefer Hoca Sefer ( 1536–38) was an Ottoman captain in charge of pro-Ottoman forces in Gujarat in the first half of the 16th century. Hoca Sefer, who had been installed by the Ottoman captain Selman Reis, attempted to maintain Ottoman influence in Diu ..., 15th-century Ottoman captain * Sefer Daja (1897-1977), person from Tirana, Albania See also * * {{disambig, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of God In Judaism
Judaism considers some names of God so holy that, once written, they should not be erased: YHWH, Adonai, El ("God"), Elohim ("God," a plural noun), Shaddai ("Almighty"), and Tzevaot (" fHosts"); some also include Ehyeh ("I Will Be").This is the formulation of Joseph Karo (SA YD 276:9). Maimonides (MT Yesodei haTorah 6:2), Jacob b. Asher (AT YD 276), and Isaac Alfasi (HK Menachot 3b) also included Ehyeh, as do many later authorities, including Moses Isserles (SA YD 276:9). The original lists are found in y. Megillah 1:9 and b. Shavuot 35a, with some MSS agreeing with each authority. Maimonides and followers give the number of names as seven; however, manuscript inconsistency makes it difficult to judge which are included. Early authorities considered other Hebrew names mere epithets or descriptions of God and wrote that they and names in other languages may be written and erased freely. However, some moderns advise special care even in these cases, and many Orthodox Jews h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gematria
Gematria (; he, גמטריא or gimatria , plural or , ''gimatriot'') is the practice of assigning a numerical value to a name, word or phrase according to an alphanumerical cipher. A single word can yield several values depending on the cipher which is used. Hebrew alphanumeric ciphers were probably used in biblical times, and were later adopted by other cultures. Gematria is still widely used in Jewish culture. Similar systems have been used in other languages and cultures: the Greeks isopsephy, and later, derived from or inspired by Hebrew gematria, Arabic abjad numerals, and English gematria. Although a type of gematria system ('Aru') was employed by the ancient Babylonian culture, their writing script was logographic, and the numerical assignations they made were to whole words. The value of these words were assigned in an entirely arbitrary manner and correspondences were made through tables, and so cannot be considered a true form of gematria. Aru was very different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
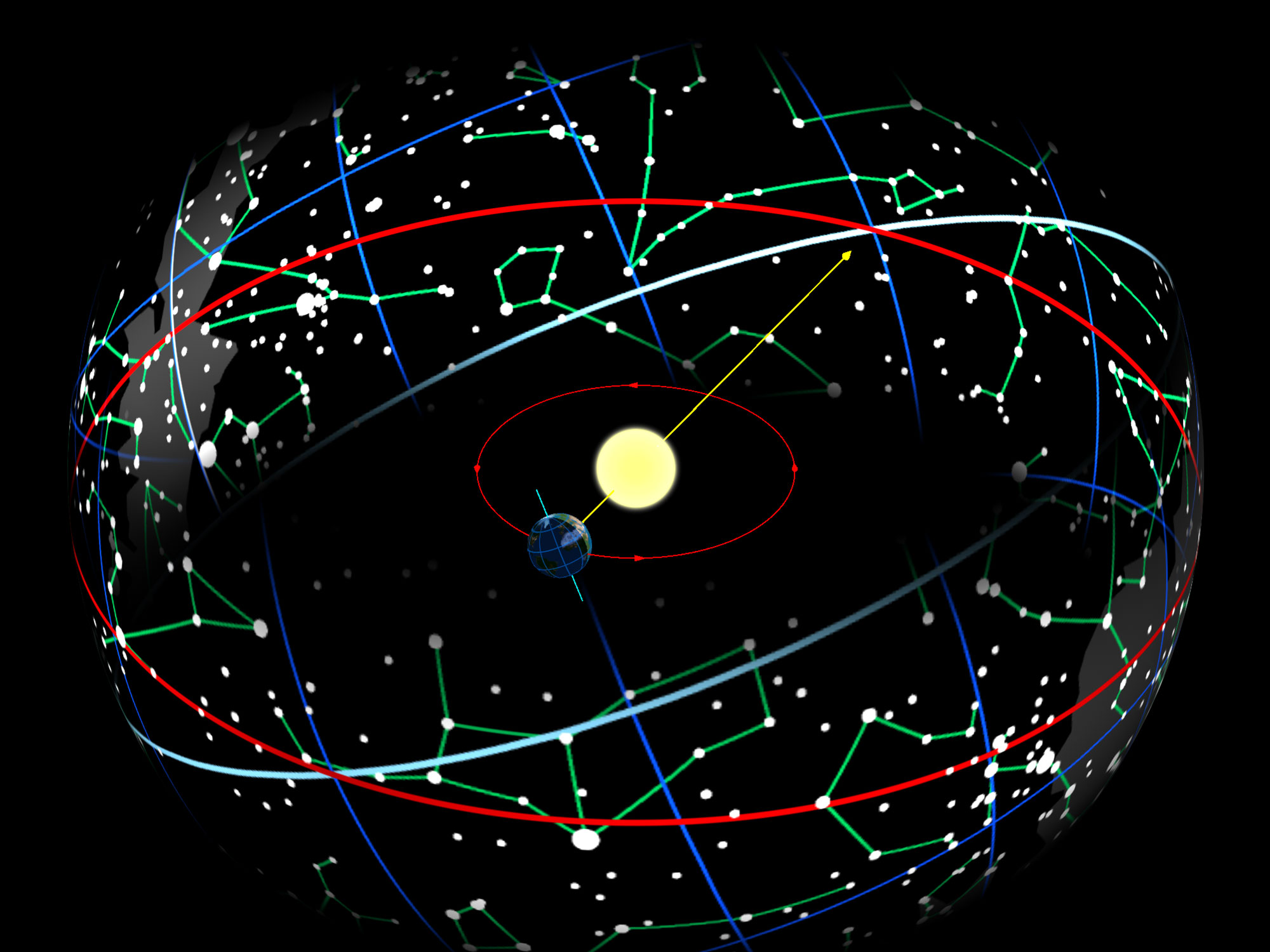
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate system, which takes the ecliptic as the origin of latitude and the Sun's position at vernal equinox as the origin of longitude. Name The English word ' derives from , the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ( ), meaning "cycle or circle of little anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy Of Angels
In the angelology of different religions, a hierarchy of angels is a ranking system of angels. Higher ranks have more power or authority over lower ranks, and with different ranks having differences in appearance, such as varying numbers of wings or faces. Abrahamic religions Judaism The Jewish angelic hierarchy is established in the Hebrew Bible, Talmud, Rabbinic literature, and traditional Jewish prayer, Jewish liturgy. They are categorized in different hierarchies proposed by various theologians. For example, Maimonides, in his ''Mishneh Torah'' or ''Yad ha-Chazakah: Yesodei ha-Torah'', counts ten ranks of angel In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God. Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles inc ...s. Christianity The most influential Christian angelology, Christian angelic hierarchy was that put forward by P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |