|
Lianghu (town)
Huguang was a Provinces of China, province of History of China, China during the Yuan dynasty, Yuan and Ming dynasty, Ming list of Chinese dynasties, dynasties. It was founded by the Yuan dynasty in 1274. During the Yuan dynasty it included the areas of modern Hubei south of the Yangtze river, Hunan, Guizhou, and Guangxi. During the Ming dynasty it came to include just the modern provinces of Hubei and Hunan, in the process adding areas north of the Yangtze. It was partitioned in 1644 by the newly established Qing dynasty, becoming the provinces of Hubei and Hunan, which were administered by the viceroy of Lianghu ("The Two Lake Provinces"). Governors Li Hongzhang was the viceroy of Huguang from 1867 to 1870. Zhang Zhidong became the viceroy of Huguang in 1896, following the First Sino-Japanese War. He was notable for employing foreigners to train and equip the local military to the standards of a contemporary European army. The most elite of Zhang's forces were known as the "Wuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Poyang
Poyang Lake (, Gan: Po-yong U), located in Jiujiang, is the largest freshwater lake in China. The lake is fed by the Gan, Xin, and Xiu rivers, which connect to the Yangtze through a channel. The area of Poyang Lake fluctuates dramatically between the wet and dry seasons, but in recent years the size of the lake has been decreasing overall. In a normal year the area of the lake averages . In early 2012, drought, sand quarrying, and the practice of storing water at the Three Gorges Dam lowered the area of the lake to about . The lake provides a habitat for half a million migratory birds and is a favorite destination for birding. During the winter, the lake becomes home to many migrating Siberian cranes, up to 90% of which spend the winter there. Formation Poyang Lake has also been called Pengli Lake () historically, but they are not the same. Before the Han Dynasty, the Yangtze followed a more northerly course through what is now Longgan Lake whilst Pengli Marsh formed the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Zhidong
Zhang Zhidong () (4 September 18375 October 1909) was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Qing dynasty. Along with Zeng Guofan, Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang, Zhang Zhidong was one of the four most famous officials of the late Qing dynasty. Known for advocating controlled reform and modernization of Chinese troops, he served as the governor of Shanxi Province and viceroy of Huguang, Liangguang and Liangjiang, and also as a member of the Grand Council. He took a leading role in the abolition of the Imperial examination system in 1905. The Red Guards destroyed his tomb in 1966 during the Cultural Revolution. His remains were rediscovered in 2007 and reburied with honors. Other names Zhang Zhidong was also known by other names. An older Wade–Giles form was Chang Chih-tung. His courtesy name was Xiaoda () or Xiangtao (). His pseudonyms were Xiangyan (), Hugong (), Wujing Jushi () and Baobing (). The posthumous name given to him by the Qing government was Wenxiang ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang, Cao Bằng, Lạng Sơn, and Quảng Ninh Provinces) and the Gulf of Tonkin. Formerly a province, Guangxi became an autonomous region in 1958. Its current capital is Nanning. Guangxi's location, in mountainous terrain in the far south of China, has placed it on the frontier of Chinese civilization throughout much of Chinese history. The current name "Guang" means "expanse" and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in 226 AD. It was given provincial level status during the Yuan dynasty, but even into the 20th century, it was considered an open, wild territory. The abbreviation of the region is "" (Hanyu pinyin: ; Zhuang: ), which comes from the name of the city of Guilin, the provincial capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the south, Yunnan to the west, Sichuan to the northwest, the municipality of Chongqing to the north, and Hunan to the east. The population of Guizhou stands at 38.5 million, ranking 18th among the provinces in China. The Dian Kingdom, which inhabited the present-day area of Guizhou, was annexed by the Han dynasty in 106 BC. Guizhou was formally made a province in 1413 during the Ming dynasty. After the overthrow of the Qing in 1911 and following the Chinese Civil War, the Chinese Communist Party took refuge in Guizhou during the Long March between 1934 and 1935. After the establishment of the People's Republic of China, Mao Zedong promoted the relocation of heavy industry into inland provinces such as Guizhou, to better protect them from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of –771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 – 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to the east, Guangdong and Guangxi to the south, Guizhou to the west and Chongqing to the northwest. Its capital and largest city is Changsha, which also abuts the Xiang River. Hengyang, Zhuzhou, and Yueyang are among its most populous urban cities. With a population of just over 66 million residing in an area of approximately , it is China's 7th most populous province, the fourth most populous among landlocked provinces, the second most populous in South Central China after Guangdong and the most populous province in Central China. It is the largest province in South-Central China and the fourth largest among landlocked provinces and the 10th most extensive province by area. Hunan's nominal GDP was US$ 724 billion (CNY 4.6 trillion) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Ancient China
Administration may refer to: Management of organizations * Management, the act of directing people towards accomplishing a goal ** Administrative Assistant, traditionally known as a Secretary, or also known as an administrative officer, administrative support specialist, or management assistant is a person whose work consists of supporting management, including executives, using a variety of project management, communication, or organizational skills, while in some cases, in addition, may require specialized knowledge acquired through higher education. ** Administration (government), management in or of government *** Administrative division ** Academic administration, a branch of an academic institution responsible for the maintenance and supervision of the institution ** Arts administration, a field that concerns business operations around an art organization ** Business administration, the performance or management of business operations *** Bachelor of Business Administratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Ming Dynasty
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Yuan Dynasty
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy, Italy. The term ''province'' has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city". While some provinces were produced artificially by Colonialism, colonial powers, others were formed around local groups with their own ethnic identities. Many have their own powers independent of central or Federation, federal authority, especially Provinces of Canada, in Canada and Pakistan. In other countries, like Provinces of China, China or Administrative divisions of France, France, provinces are the creation of central government, with very little autonomy. Etymology The English langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingzhou (ancient China)
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in Chinese historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally "chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was from Chu. Chu was conquered by Qin in 223 BCE in the final stages of the Qi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
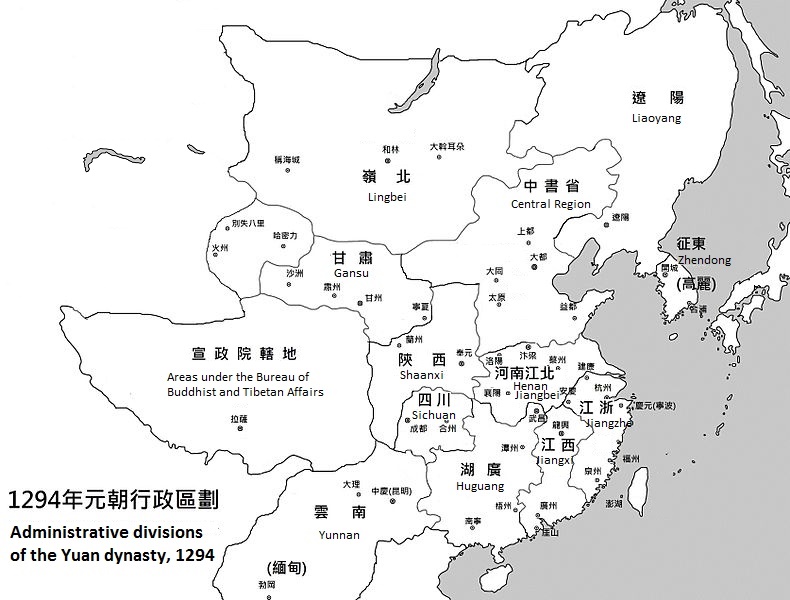
Administrative Divisions Of The Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng) and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (Xuanzheng Yuan). In addition, the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire. Overview The most important part of the Yuan Empire was the Central Region, which covered the region of the Yuan capital Khanbaliq (Dadu, modern Beijing). The Central Region consisted of present-day Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, the south-eastern part of present-day Inner Mongolia and the Henan areas to the north of the Yellow River. Since it was considered the most important region of the dynasty, it was directly governe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YUAN(South China)
Yuan may refer to: Currency * Yuan (currency), the basic unit of currency in historic and contemporary mainland China and Taiwan **Renminbi, the current currency used in mainland China, whose basic unit is yuan ** New Taiwan dollar, the current currency used in Taiwan, whose basic unit is yuán in Mandarin ** Manchukuo yuan, the unit of currency that was used in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo Governmental organ * "Government branch" or "Court" (), the Chinese name for a kind of executive institution. Government of Taiwan * Control Yuan * Examination Yuan * Executive Yuan * Judicial Yuan * Legislative Yuan Government of Imperial China * Xuanzheng Yuan, or Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs during the Yuan dynasty * Lifan Yuan during the Qing dynasty Dynasties * Yuan dynasty (元朝), a dynasty of China ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan ** Northern Yuan dynasty (北元), the Yuan dynasty's successor state in northern China and the Mongolian Plateau People and languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)