|
Liang Bua
Liang Bua is a limestone cave on the island of Flores, Indonesia, slightly north of the town of Ruteng in Manggarai Regency, East Nusa Tenggara. The cave demonstrated archaeological and paleontological potential in the 1950s and 1960s as described by the Dutch missionary and archaeologist Theodor L. Verhoeven. In September 2003, an Indonesian field team and its coordinator of the excavation team, Thomas Sutikna, uncovered the first indications of a skull. Initially, the archeologists only analyzed the top of the cranium and due to the small size believed that the skull belonged to a small child. However, Sutikna and his colleagues soon discovered that its teeth were permanent and mature, revealing that it actually belonged to a fully grown adult. After a few weeks, the team had discovered most of this particular hominid's skeleton and later was coded LB1, LB2, etc., after the name of the cave. This skeleton later became the holotype specimen of ''Homo floresiensis,'' also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and the population was 1,878,875 in the 2020 Census (including various offshore islands); the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 1,897,550. The largest towns are Maumere and Ende. The name ''Flores'' is the Portuguese and Spanish word for "Flowers". Flores is located east of Sumbawa and the Komodo islands, and west of the Solor Islands and the Alor Archipelago. To the southeast is Timor. To the south, across the Sumba Strait, is Sumba island and to the north, beyond the Flores Sea, is Sulawesi. Among all islands containing Indonesian territory, Flores is the 10th most populous after Java, Sumatra, Borneo ( Kalimantan), Sulawesi, New Guinea, Bali, Madura, Lombok, and Timor and also the 10th biggest island of Indonesia. Until the arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
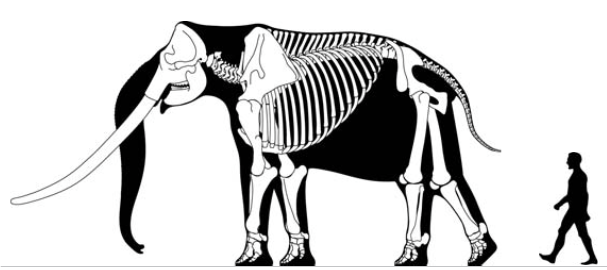
Stegodon Florensis Insularis
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the Ancient Greek words , , 'to cover', + , , 'tooth' because of the distinctive ridges on the animal's molars) is an extinct genus of proboscidean, related to elephants. It was originally assigned to the family Elephantidae along with modern elephants but is now placed in the extinct family Stegodontidae. Like elephants, ''Stegodon'' had teeth with plate-like lophs that are different from those of more primitive proboscideans like gomphotheres and mastodons. The oldest fossils of the genus are found in Late Miocene strata in Asia, likely originating from the more archaic ''Stegolophodon,'' shortly afterwards migrating into Africa. While the genus became extinct in Africa during the Pliocene, ''Stegodon'' remained widespread in Asia until the end of the Pleistocene. Morphology Size Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the Yellow River that is tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoanthropological Sites
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship lines within the family Hominidae, working from biological evidence (such as petrified skeletal remains, bone fragments, footprints) and cultural evidence (such as stone tools, artifacts, and settlement localities). The field draws from and combines primatology, paleontology, biological anthropology, and cultural anthropology. As technologies and methods advance, genetics plays an ever-increasing role, in particular to examine and compare DNA structure as a vital tool of research of the evolutionary kinship lines of related species and genera. Etymology The term paleoanthropology derives from Greek palaiós (παλαιός) "old, ancient", ánthrōpos (ἄνθρωπος) "man, human" and the suffix -logía (-λογία) "study of". Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Indonesia
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic Paleontological Sites Of Asia
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Indonesia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marabou Stork
The marabou stork (''Leptoptilos crumenifer'') is a large wading bird in the stork family Ciconiidae native to sub-Saharan Africa. It breeds in both wet and arid habitats, often near human habitation, especially landfill sites. It is sometimes called the "undertaker bird" due to its shape from behind: cloak-like wings and back, skinny white legs, and sometimes a large white mass of "hair". Taxonomy The marabou stork was formally described in 1831 by the French naturalist René Lesson. He placed it in the stork genus '' Ciconia'' and coined the binomial name ''Ciconia crumenifera''. He specified that locality as Senegal. The species is now placed with the lesser adjutant and the greater adjutant in the genus ''Leptoptilos'' that Lesson had introduced at the same time he described the marabou stork. The species is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised. The common name marabou is thought to be derived from the Arabic word '' murābit'' meaning quiet or hermit-like. The spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptoptilos Robustus
''Leptoptilos robustus'' (from reek: thin, slender+ reek: soft featherand atin: strong is an extinct species of large-bodied stork belonging to the genus ''Leptoptilos'' that lived on the island of Flores in Indonesia during the Pleistocene epoch. It stood at about tall and weighed up to an estimated . The majority of the discoveries are concentrated in Liang Bua cave located slightly north of Ruteng in the East Nusa Tenggara province. Taxonomy The genus name ''Leptotilos'' is derived from the Greek word meaning "thin or slender", which refers to the storks slim build and the Greek word meaning "down or soft feather", referring to the soft feather down covering the frame of the members of ''Leptotilos'' stork. The species name, "robustus" is derived from Latin word, meaning "hardness or strength". The species name ''robustus'' is a reference to the notably large size of the tibiotarsus and the thickness of its cortex. Debate over the relation between the Liang Bua speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
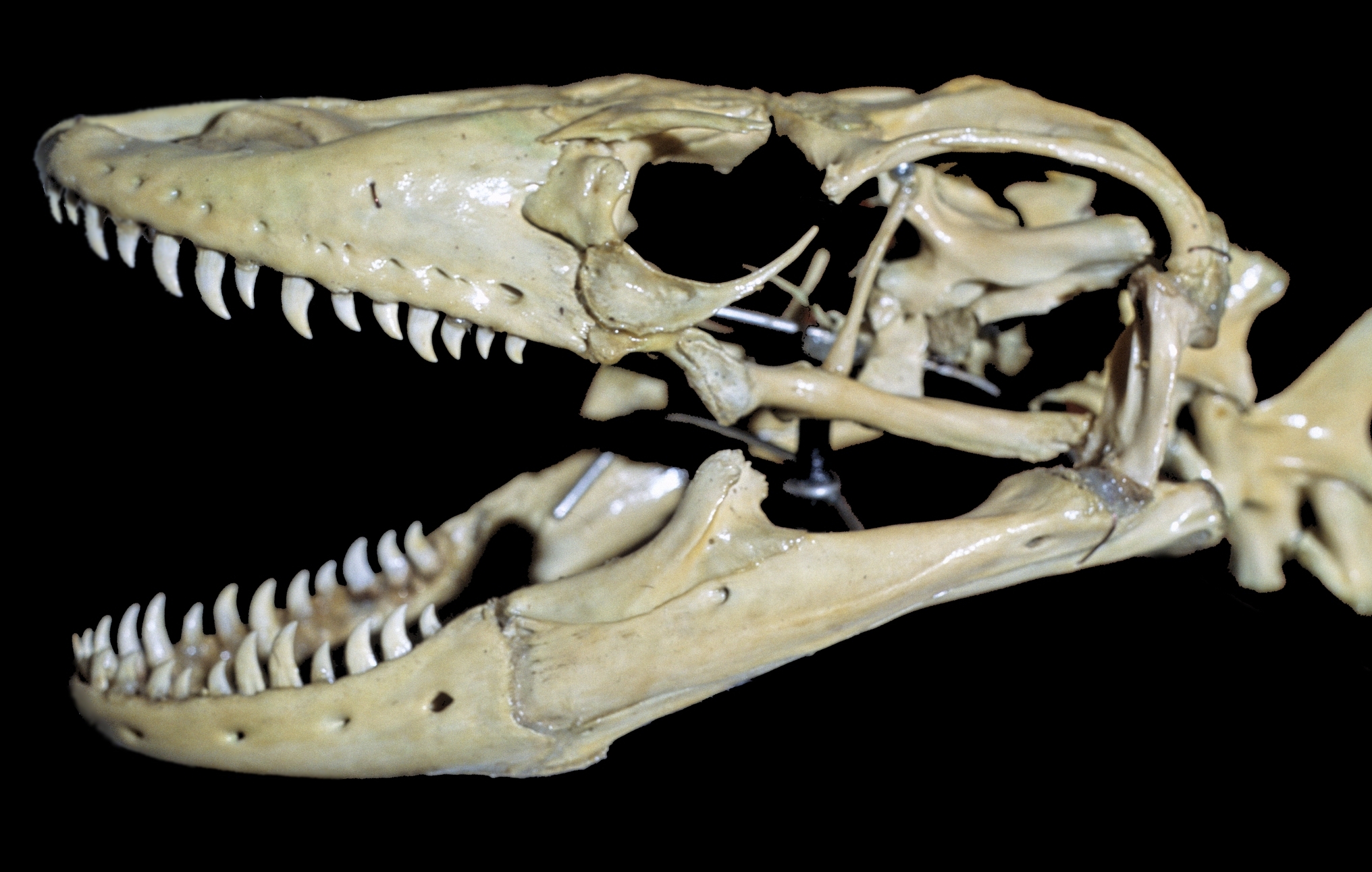
Varanidae
The Varanidae are a family of lizards in the superfamily Varanoidea within the Anguimorpha group. The family, a group of carnivorous and frugivorous lizards, includes the living genus '' Varanus'' and a number of extinct genera more closely related to ''Varanus'' than to the earless monitor lizard (''Lanthanotus''). ''Varanus'' includes the Komodo dragon (the largest living lizard), crocodile monitor, savannah monitor, the goannas of Australia and Southeast Asia, and various other species with a similarly distinctive appearance. Their closest living relatives are the earless monitor lizard and chinese crocodile lizard. The oldest members of the family are known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Taxonomy The Varanidae were defined (using morphological characteristics) by Estes, de Queiroz and Gauthier (1988) as the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of ''Lanthanotus'' and ''Varanus'' and all of its descendants. A similar definition was formulated by Conrad ''et al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanus Komodoensis
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo (island), Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the List of largest extant lizards, largest extant species of lizard, growing to a maximum length of , and weighing up to . As a result of their size, Komodo dragons are apex predators, and dominate the ecosystems in which they live. Komodo dragons hunt and ambush prey including invertebrates, birds, and mammals. It has been claimed that they have a venomous bite; there are two glands in the lower jaw that secrete several toxic proteins. The biological significance of these proteins is disputed, but the glands have been shown to secrete an anticoagulant. Komodo dragons' group behavior in hunting is exceptional in the reptile world. The diet of Komodo dragons mainly consists of Javan rusa (''Rusa timorensis''), though they also eat considerable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papagomys Armandvillei
The Flores giant rat (''Papagomys armandvillei'') is a rodent of the family Muridae that occurs on the island of Flores in Indonesia. It has been recorded in Rutong Protection Forest. The species is found in primary, secondary and disturbed forest over a wide range of elevations. Head and body length is and tail length is . These dimensions are about twice as large as those of a typical brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus''), which suggests about eight times the body mass. ''Papagomys armandvillei'' is the only extant species in the genus ''Papagomys''. The specific epithet, armandvillei, honours the Dutch Jesuit missionary Cornelis J. F. le Cocq d'Armandville (1846-1896) who was stationed in the Dutch East Indies, and later in New Guinea. Guy Musser describes the Flores giant rat as having small, round ears, a chunky body, and a small tail, and as appearing to be adapted for life on the ground with refuge in burrows. It has dense dark hair (pelage). Analysis of the teeth suggests a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papagomys Theodorverhoeveni
Verhoeven's giant tree rat (''Papagomys theodorverhoeveni'') is an extinct rat of subfamily Murinae that lived on Flores in Indonesia. It was judged to be extinct in 1996. However, experts believe that it died out before 1500 AD. The species is known only from several subfossil fragments. It was named after Dutch priest Theodor Verhoeven Theodorus (Theo) Lambertus Verhoeven, SVD, (17 September 1907, Uden, The Netherlands – 3 June 1990, Antwerp, Belgium) was a Dutch missionary and archaeologist who has become famous by his discovery of stone tools on the Indonesian island of .... A 1974 report of a recent specimen has been judged to represent '' P. armandvillei'' instead. References Further reading * Papagomys Rats of Asia Extinct rodents Flores Island (Indonesia) Rodents of Indonesia Extinct animals of Indonesia Extinct mammals of Asia Holocene extinctions Mammals described in 1981 Taxobox binomials not recognized by IUCN [Baidu] |





.jpg)
_head.jpg)


