|
Leukoaraiosis
Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) in T2 FLAIR images. On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions. The term "leukoaraiosis" was coined in 1986 by Hachinski, Potter, and Merskey as a descriptive term for rarefaction ("araiosis") of the white matter, showing up as decreased density on CT and increased signal intensity on T2/FLAIR sequences (white matter hyperintensities) performed as part of MRI brain scans. These white matter changes are also commonly referred to as periventricular white matter disease, or white matter hyperintensities (WMH), due to their bright white appearance on T2 MRI scans. Many patients can have leukoaraiosis without any associated clinical abnormality. However, underlying vascular mechanisms are susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukoaraiosis
Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) in T2 FLAIR images. On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions. The term "leukoaraiosis" was coined in 1986 by Hachinski, Potter, and Merskey as a descriptive term for rarefaction ("araiosis") of the white matter, showing up as decreased density on CT and increased signal intensity on T2/FLAIR sequences (white matter hyperintensities) performed as part of MRI brain scans. These white matter changes are also commonly referred to as periventricular white matter disease, or white matter hyperintensities (WMH), due to their bright white appearance on T2 MRI scans. Many patients can have leukoaraiosis without any associated clinical abnormality. However, underlying vascular mechanisms are susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukoaraiosis 1
Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) in T2 FLAIR images. On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions. The term "leukoaraiosis" was coined in 1986 by Hachinski, Potter, and Merskey as a descriptive term for rarefaction ("araiosis") of the white matter, showing up as decreased density on CT and increased signal intensity on T2/FLAIR sequences (white matter hyperintensities) performed as part of MRI brain scans. These white matter changes are also commonly referred to as periventricular white matter disease, or white matter hyperintensities (WMH), due to their bright white appearance on T2 MRI scans. Many patients can have leukoaraiosis without any associated clinical abnormality. However, underlying vascular mechanisms are suspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
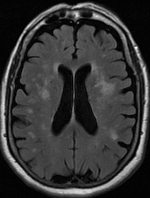
Periventricular White Matter Lesions (annotated)
Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities (WMHs) in T2 FLAIR images. On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions. The term "leukoaraiosis" was coined in 1986 by Hachinski, Potter, and Merskey as a descriptive term for rarefaction ("araiosis") of the white matter, showing up as decreased density on CT and increased signal intensity on T2/FLAIR sequences (white matter hyperintensities) performed as part of MRI brain scans. These white matter changes are also commonly referred to as periventricular white matter disease, or white matter hyperintensities (WMH), due to their bright white appearance on T2 MRI scans. Many patients can have leukoaraiosis without any associated clinical abnormality. However, underlying vascular mechanisms are suspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipohyalinosis
Lipohyalinosis is a cerebral small vessel disease affecting the small arteries, arterioles or capillaries in the brain. Originally defined by C. Miller Fisher as 'segmental arteriolar wall disorganisation', it is characterized by vessel wall thickening and a resultant reduction in luminal diameter. Fisher considered this small vessel disease to be the result of hypertension, induced in the acute stage by fibrinoid necrosis that would lead to occlusion and hence lacunar stroke. However, recent evidence suggests that endothelial dysfunction as a result of inflammation is a more likely cause for it. This may occur subsequent to blood–brain barrier failure, and lead to extravasation of serum components into the brain that are potentially toxic. Lacunar infarction could thus occur in this way, and the narrowing – the hallmark feature of lipohyalinosis – may merely be a feature of the swelling occurring around it that squeezes on the structure. Misuse of the term C. Miller Fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperintensities
A hyperintensity or T2 hyperintensity is an area of high intensity on types of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the brain of a human or of another mammal that reflect lesions produced largely by demyelination and axonal loss. These small regions of high intensity are observed on T2 weighted MRI images (typically created using 3D FLAIR) within cerebral white matter (white matter lesions, white matter hyperintensities or WMH) or subcortical gray matter (gray matter hyperintensities or GMH). The volume and frequency is strongly associated with increasing age. They are also seen in a number of neurological disorders and psychiatric illnesses. For example, deep white matter hyperintensites are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to occur in bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder than control subjects. WMH volume, calculated as a potential diagnostic measure, has been shown to correlate to certain cognitive factors. Hyperintensities appear as "bright signals" (bright areas) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperintense
A hyperintensity or T2 hyperintensity is an area of high intensity on types of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the brain of a human or of another mammal that reflect lesions produced largely by demyelination and axonal loss. These small regions of high intensity are observed on T2 weighted MRI images (typically created using 3D FLAIR) within cerebral white matter (white matter lesions, white matter hyperintensities or WMH) or subcortical gray matter (gray matter hyperintensities or GMH). The volume and frequency is strongly associated with increasing age. They are also seen in a number of neurological disorders and psychiatric illnesses. For example, deep white matter hyperintensites are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to occur in bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder than control subjects. WMH volume, calculated as a potential diagnostic measure, has been shown to correlate to certain cognitive factors. Hyperintensities appear as "bright signals" (bright areas) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binswanger's Disease
Binswanger's disease, also known as subcortical leukoencephalopathy and subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, is a form of small-vessel vascular dementia caused by damage to the white brain matter. White matter atrophy can be caused by many circumstances including chronic hypertension as well as old age.Giovannetti, T. Personal Interview. 16 October 2009 This disease is characterized by loss of memory and intellectual function and by changes in mood. These changes encompass what are known as executive functions of the brain. It usually presents between 54 and 66 years of age, and the first symptoms are usually mental deterioration or stroke. It was described by Otto Binswanger in 1894, and Alois Alzheimer first used the phrase "Binswanger's disease" in 1902. However, Jerzy Olszewski is credited with much of the modern-day investigation of this disease which began in 1962. Signs and symptoms Symptoms include mental deterioration, language disorder, transient ischemic attack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potentials, acting as a relay and coordinating communication between different brain regions. White matter is named for its relatively light appearance resulting from the lipid content of myelin. However, the tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish-white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color in prepared specimens is due to its usual preservation in formaldehyde. Structure White matter White matter is composed of bundles, which connect various grey matter areas (the locations of nerve cell bodies) of the brain to each other, and carry nerve impulses between neurons. Myelin acts as an insulator, which allows electrical signals to jump, rather than c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliosis
Gliosis is a nonspecific reactive change of glial cells in response to damage to the central nervous system (CNS). In most cases, gliosis involves the proliferation or hypertrophy of several different types of glial cells, including astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes. In its most extreme form, the proliferation associated with gliosis leads to the formation of a glial scar. The process of gliosis involves a series of cellular and molecular events that occur over several days. Typically, the first response to injury is the migration of macrophages and local microglia to the injury site. This process, which constitutes a form of gliosis known as microgliosis, begins within hours of the initial CNS injury. Later, after 3–5 days, oligodendrocyte precursor cells are also recruited to the site and may contribute to remyelination. The final component of gliosis is astrogliosis, the proliferation of surrounding astrocytes, which are the main constituents of the glial scar. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CADASIL
CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder, and is thought to be caused by mutations of the ''Notch 3'' gene on chromosome 19. The disease belongs to a family of disorders called the leukodystrophies. The most common clinical manifestations are migraine headaches and transient ischemic attacks or strokes, which usually occur between 40 and 50 years of age, although MRI is able to detect signs of the disease years prior to clinical manifestation of disease. The condition was identified and named by French researchers Marie-Germaine Bousser and Elisabeth Tournier-Lasserve in the 1990s. Together with two other researchers, Hugues Chabriat and Anne Joutel, they received the 2019 Brain Prize for their research into the condition. Signs and symptoms CADASIL may start with attacks of migraine with aura or subcortical transient ischemic attacks or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


