|
Leta Hollingworth
Leta Stetter Hollingworth (25 May 1886 – 27 November 1939) was an American psychologist, educator, and feminist. Hollingworth also made contributions in psychology of women; clinical psychology; and educational psychology. She is best known for her work with gifted children.Hochman, S. K. "Leta Stetter Hollingworth." Webster University. Retrieved from . Early life On May 25, 1886, Leta Anna Stetter was born in Dawes County, Nebraska near the town of Chadron. She was the first of three children born to Margaret Elinor Danley (1862–1890) and John George Stetter (1856–1943). Her childhood consisted of multiple hardships. At three years old, her mother died after giving birth to her third child, and her father deserted the family. Leta and her sisters were then raised by their maternal grandparents — Samuel Thomas Danley (1833–1898) and Mary (1838–1904) — on their farm. After ten years of absence, Leta's father remarried and forced the children to leave their grandpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadron, Nebraska
Chadron ( ) is a city and the county seat of Dawes County, in the state of Nebraska in the Great Plains region of the United States. The population was 5,851 at the 2010 census. This city is the location of Chadron State College. Chadron also is the United States Forest Service headquarters of the Nebraska and Samuel R. McKelvie National Forests, and the Buffalo Gap, Fort Pierre, and Oglala National Grasslands. The Museum of the Fur Trade is located near Chadron, at the site of the American Fur Company's former Bordeaux Trading Post. History Succeeding cultures of indigenous peoples lived in the area for thousands of years. In historic times, tribes such as the Oglala Lakota (Oglala Sioux Tribe), Cheyenne and others lived in the area. The Sioux used this territory as a hunting ground after pushing other tribes to the west. Chadron is named for Louis Chartran, a French-Indian (Métis) fur trapper who ran a trading post on Chadron Creek in 1841. He was married to a Native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States, and the most prestigious, due in part to its long history and academic selectivity. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal arts and sciences, and to induct the most outstanding students of arts and sciences at only select American colleges and universities. It was founded at the College of William and Mary on December 5, 1776, as the first collegiate Greek-letter fraternity and was among the earliest collegiate fraternal societies. Since its inception, 17 U.S. Presidents, 40 U.S. Supreme Court Justices, and 136 Nobel Laureates have been inducted members. Phi Beta Kappa () stands for ('), which means "Wisdom it. love of knowledgeis the guide it. helmsmanof life". Membership Phi Beta Kappa has chapters in only about 10% of American higher learning institutions, and only about 10% of these schools' Arts and Sciences graduates are invited to join the society. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
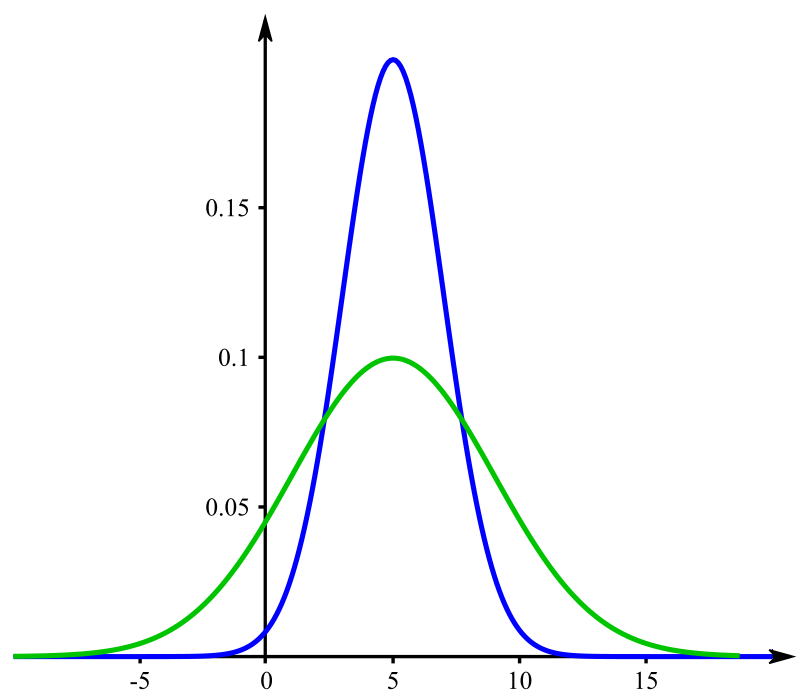
Variability Hypothesis
The variability hypothesis, also known as the greater male variability hypothesis, is the hypothesis that males generally display greater variability in traits than females do. It has often been discussed in relation to human cognitive ability, where some studies appear to show that males are more likely than females to have either very high or very low IQ test scores. In this context, there is controversy over whether such sex-based differences in the variability of intelligence exist, and if so, whether they are caused by genetic differences, environmental conditioning, or a mixture of both. Sex-differences in variability have been observed in many abilities and traits –– including physical, psychological and genetic ones –– across a wide range of sexually dimorphic species. History The notion of greater male variability — at least in respect to physical characteristics — can be traced back to the writings of Charles Darwin. When he expounded his theory of sexual s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Periodicity
Functional periodicity is a term that emerged around the late 19th century around the belief, later to be found invalid, that women suffered from physical and mental impairment during their menstrual cycle. Men held a higher status and were regarded as superior to women at this period in time. Many prominent male psychologists promoted the idea of functional periodicity. Women were not seen as being fit for certain types of work, responsibilities, and roles because of this idea.Stetter-Hollingworth, L. (1914). Functional periodicity: An experimental study of the mental and motor abilities of women during menstruation. ''Contributions to Education,'' 69. The idea of functional periodicity stems from ancient taboos and rituals that were passed on from generation to generation. It then developed into an actual theory in the twentieth century. Functional periodicity was investigated by a female psychologist named Leta Hollingworth. She made key contributions in the research of function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Rogers
Carl Ransom Rogers (January 8, 1902 – February 4, 1987) was an American psychologist and among the founders of the humanistic approach (and client-centered approach) in psychology. Rogers is widely considered one of the founding fathers of psychotherapy research and was honored for his pioneering research with the Award for Distinguished Scientific Contributions by the American Psychological Association (APA) in 1956. The person-centered approach, Rogers's unique approach to understanding personality and human relationships, found wide application in various domains, such as psychotherapy and counseling (client-centered therapy), education (student-centered learning), organizations, and other group settings. For his professional work he received the Award for Distinguished Professional Contributions to Psychology from the APA in 1972. In a study by Steven J. Haggbloom and colleagues using six criteria such as citations and recognition, Rogers was found to be the sixth most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales
The Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales (or more commonly the Stanford–Binet) is an individually-administered intelligence test that was revised from the original Binet–Simon Scale by Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon. The Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scale is now in its fifth edition (SB5), which was released in 2003. It is a cognitive ability and intelligence test that is used to diagnose developmental or intellectual deficiencies in young children. The test measures five weighted factors and consists of both verbal and nonverbal subtests. The five factors being tested are knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual-spatial processing, working memory, and fluid reasoning. The development of the Stanford–Binet initiated the modern field of intelligence testing and was one of the first examples of an adaptive test. The test originated in France, then was revised in the United States. It was initially created by the French psychologist Alfred Binet, who, following the introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speyer School
''Note: this article is about two distinct but related schools for gifted education in New York City, USA: the Speyer Legacy School (founded 2009, ongoing), and the Speyer School (1935-1941). The present-day school is named after the earlier one, and takes its inspiration from the approach to gifted education that was developed there.'' The Speyer School (1935-1941) The Speyer School (1935-1941) was started in a building at Columbia's Teachers College and named after financier James Speyer. It became well known between 1935-39 when it was used a "laboratory" to study how children perform when separated by educational ability. There were seven classrooms with 175 students, who had an IQ range on the Stanford Binet test of between 75-90 and two classrooms with students that tested at the level of 130+ on the same IQ test. The experiment was led by Leta Stetter Hollingworth, an American psychologist who specialized in education and who is credited with writing the first textbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Testing
An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term ''Intelligenzquotient'', his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book. Historically, IQ was a score obtained by dividing a person's mental age score, obtained by administering an intelligence test, by the person's chronological age, both expressed in terms of years and months. The resulting fraction (quotient) was multiplied by 100 to obtain the IQ score. For modern IQ tests, the raw score is transformed to a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 15. This results in approximately two-thirds of the population scoring between IQ 85 and IQ 115 and about 2.5 percent each above 130 and below 70. Scores from intelligence tests are estimates of intelligence. Unlike, for example, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Madison Terman
Lewis Madison Terman (January 15, 1877 – December 21, 1956) was an American psychologist and author. He was noted as a pioneer in educational psychology in the early 20th century at the Stanford Graduate School of Education. He is best known for his revision of the Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales and for initiating the longitudinal study of children with high IQs called the Genetic Studies of Genius. He was a prominent eugenicist and was a member of the Human Betterment Foundation. He also served as president of the American Psychological Association. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Terman as the 72nd most cited psychologist of the 20th century, in a tie with G. Stanley Hall. Background Terman was born in Johnson County, Indiana, the son of Martha P. (Cutsinger) and James William Terman. He received a BS, BPd (Bachelor of Pedagogy), and BA from Central Normal College in 1894 and 1898, and a BA and MA from the Indiana University B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Teacher's College
Teachers College, Columbia University (TC), is the graduate school of education, health, and psychology of Columbia University, a private research university in New York City. Founded in 1887, it has served as one of the official faculties and the Department of Education of Columbia University since 1898 and is consistently ranked among the top 10 graduate schools of education in the United States (currently 7th as of 2022). It is the oldest and largest graduate school of education in the United States. Although it was founded as an independent institution and retains some independence, it has been associated with Columbia University since shortly after its founding and merger with the university. Teachers College alumni and faculty have held prominent positions in academia, government, music, non-profit, healthcare, and social science research just to name a few. Overall, Teachers College has over 90,000 alumni in more than 30 countries. Notable alumni and former faculty inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellevue Hospital Center
Bellevue Hospital (officially NYC Health + Hospitals/Bellevue and formerly known as Bellevue Hospital Center) is a hospital in New York City and the oldest public hospital in the United States. One of the largest hospitals in the United States by number of beds, it is located at 462 First Avenue in the Kips Bay neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Bellevue is also home to FDNY EMS Station 08, formerly NYC EMS Station 13. Historically, Bellevue was popularly associated with its treatment of mentally ill patients such that "Bellevue" became a local pejorative slang term for a psychiatric hospital. This is long past the case as the hospital since developed into a comprehensive major medical center over the years, including outpatient, specialty, and skilled nursing care, as well as emergency and inpatient services. The hospital contains a 25-story patient care facility and has an attending physician staff of 1,200 and an in-house staff of about 5,500. Bellevue is a safety n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feminist Alliance
The Feminist Alliance was a progressive era organization founded in 1914 by feminist activist Henrietta Rodman and her husband, Herman de Fremery, a professor at Columbia University. Creation of the Feminist Alliance Henrietta Rodman and Herman de Fremery created the Feminist Alliance in 1914. Leta Hollingworth served on the board and the organization had more than fifty members. The group frequently worked with women from the feminist group Heterodoxy. Political campaigns Co-operative living The Feminist Alliance worked to create an apartment house where families could live together and share the workload. According to Marie Dille of the ''Fall River Globe'' who reported on this movement, the apartment was for "...married professional women who have achieved such success as to desire continuing their work after marriage." Equality in the workplace The Feminist Alliance was an important organization in the campaign for equal rights for women in the workforce. In Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
