|
Les Escoumins, Quebec
Les Escoumins is a municipality in La Haute-Côte-Nord Regional County Municipality in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec. It is located on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River. Its economy is mostly based on the service sectors, especially education, health, and tourism. It is accessible via Route 138; a ferry service runs between Les Escoumins and Trois-Pistoles. Etymology Its name has traditionally been recognized to come from the Montagnais ''iskomin'', meaning "where there are many seeds" or "there are fruits or seeds", in turn from the roots ''isko'' or ''ishko'' ("as far as this/that") and ''min'' (red seeds, or wild berries in general). According to more recent theory, it could also be a variation of the Mi'kmaq term ''eskumunaak'', meaning "lookout place". In addition, other sources say that the place is named ''Essipit'' in Montagnais, meaning "river of shells". Several spellings have been used over the centuries such as ''Uscamin, Les Escoumains, Essuie-Mains, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band." Indian reserves are the areas set aside for First Nations, an indigenous Canadian group, after a contract with the Canadian state ("the Crown"), and are not to be confused with land claims areas, which involve all of that First Nations' traditional lands: a much larger territory than any reserve. Demographics A single "band" (First Nations government) may control one reserve or several, while other reserves are shared between multiple bands. In 2003, the Department of Indian and Northern Affairs stated there were 2,300 reserves in Canada, comprising . According to Statistics Canada in 2011, there are more than 600 First Nations/Indian bands in Canada and 3,100 Indian reserves across Canada. Examples include the Driftpile First Nation, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality (Quebec)
The following is a list of the types of local and supralocal territorial units in Quebec, including those used solely for statistical purposes, as defined by the Ministry of Municipal Affairs, Regions and Land Occupancy and compiled by the Institut de la statistique du Québec. Not included are the urban agglomerations in Quebec, which, although they group together multiple municipalities, exercise only what are ordinarily local municipal powers. A list of local municipal units in Quebec by regional county municipality can be found at List of municipalities in Quebec. Local municipalities All municipalities (except cities), whether township, village, parish, or unspecified ones, are functionally and legally identical. The only difference is that the designation might serve to disambiguate between otherwise identically named municipalities, often neighbouring ones. Many such cases have had their names changed, or merged with the identically named nearby municipality since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands, and bays; the region was designated a World Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 1989. Administratively, it comprises the Charlevoix and Charlevoix-Est regional county municipalities within the larger Capitale-Nationale administrative region. History The region was named after Pierre François-Xavier de Charlevoix, a French Jesuit explorer and historian who travelled through the area in the 18th century. The community of La Malbaie was known as the first resort area in Canada. As early as 1760, Scottish noblemen Malcolm Fraser and John Nairn hosted visitors at their manors. For much of its history, Charlevoix was home to a thriving summer colony of wealthy Americans, including President William Howard Taft. Geography From an administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimouski
Rimouski ( ) is a city in Quebec, Canada. Rimouski is located in the Bas-Saint-Laurent region, at the mouth of the Rimouski River. It has a population of 48,935 (as of 2021). Rimouski is the site of Université du Québec à Rimouski (UQAR), the Cégep de Rimouski (which includes the Institut maritime du Québec) and the Music Conservatory. It is also the home of some ocean sciences research centres ( see below). History The city was founded by Sir René Lepage de Ste-Claire in 1696. Originally from Ouanne in the Burgundy region, he exchanged property he owned on the Île d'Orléans with Augustin Rouer de la Cardonnière for the Seigneurie of Rimouski, which extended along the St. Lawrence River from the Hâtée River at Le Bic to the Métis River. De la Cardonnière had been the owner of Rimouski since 1688, but had never lived there. René Lepage moved his family to Rimouski, where it held the seigneurie until 1790, when it was sold to the Quebec City businessman Joseph Drapeau. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs to fine homeware in a small number of sales shops (as opposed to trading posts) acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque People
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous to, and primarily inhabit, an area traditionally known as the Basque Country ( eu, Euskal Herria) — a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France. Etymology The English word ''Basque'' may be pronounced or and derives from the French ''Basque'' (), itself derived from Gascon ''Basco'' (pronounced ), cognate with Spanish ''Vasco ''(pronounced ). Those, in turn, come from Latin ''Vascō'' (pronounced ; plural '' Vascōnes''—see history section below). The Latin generally evolved into the bilabials and in Gascon and Spanish, probably under the influence of Basque and the related Aquitani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi'kmaq People
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations in Canada, First Nations people of the Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Miꞌkmaꞌki (or Miꞌgmaꞌgi). There are 170,000 Mi'kmaq people in the region, (including 18,044 members in the recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland.) Nearly 11,000 members speak Miꞌkmaq language, Miꞌkmaq, an Eastern Algonquian languages, Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Miꞌkmaq hieroglyphic writing, Miꞌkmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Passamaquoddy, Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
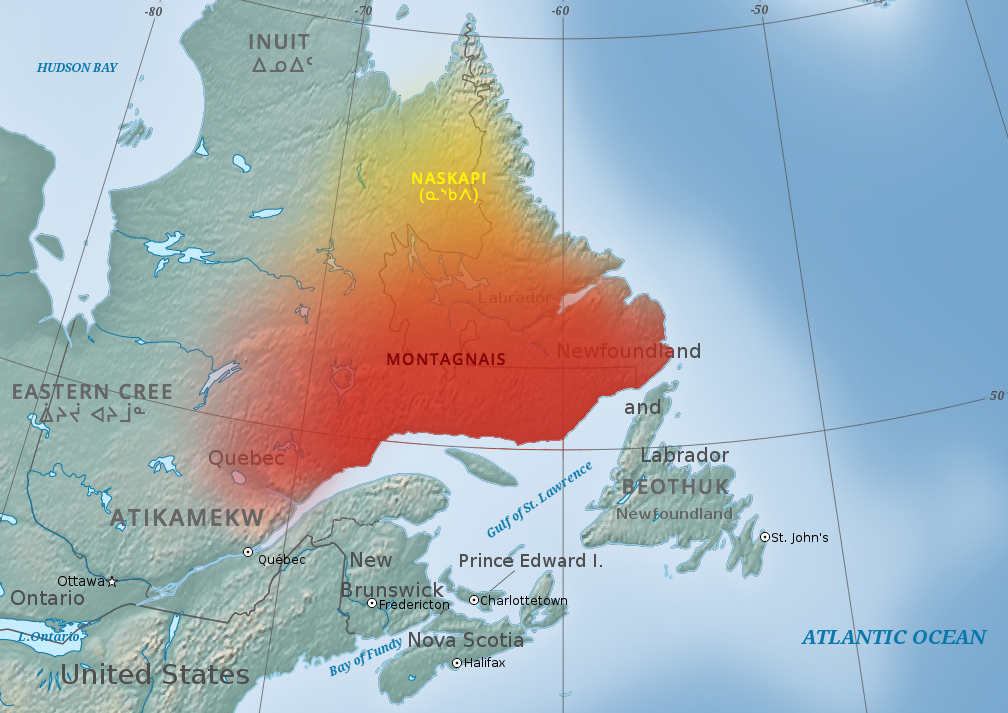
Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi'kmaq Language
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Miꞌkmaꞌki (or Miꞌgmaꞌgi). There are 170,000 Mi'kmaq people in the region, (including 18,044 members in the recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland.) Nearly 11,000 members speak Miꞌkmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Miꞌkmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties with the British Crown throughout the eighteenth century; the first was signed in 1725, and the last in 1779. The Miꞌkmaq maintain that they did not cede or give up their land t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innu-aimun Language
Innu-aimun or Montagnais is an Algonquian language spoken by over 10,000 Innu in Labrador and Quebec in Eastern Canada. It is a member of the Cree–Montagnais–Naskapi dialect continuum and is spoken in various dialects depending on the community. Literature Since the 1980s, Innu-aimun has had considerable exposure in the popular culture of Canada and France due to the success of the rock music band Kashtin and the later solo careers of its founders Claude McKenzie and Florent Vollant. Widely heard hit songs with Innu-language lyrics have included "" ("Girl"), "" ("My Childhood"), "" ("Story") and in particular "" ("Take care of yourself"), which appeared on soundtrack compilations for the television series '' Due South'' and the documentary ''Music for The Native Americans''. The lyrics of Akua Tuta are featured on over 50 websites, making this one of the most broadly accessible pieces of text written in any native North American language. Florent Vollant has also rendered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trois-Pistoles, Quebec
Trois-Pistoles is a city in Les Basques Regional County Municipality in the Bas-Saint-Laurent region of Quebec, Canada. It is also the county seat. The town is located on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River. A ferry crosses the river to Les Escoumins on the north shore. The port facilities are also used by fishing boats and scuba divers. The town is the site of the University of Western Ontario's annual French immersion program, which has existed since 1932. It is the oldest such program in Canada. Just offshore of the town lies Île aux Basques, an island that was used by Basque whalers in the 16th century. The island, part of the surrounding Municipality of Notre-Dame-des-Neiges, is a National Historic Site of Canada and is now a migratory bird sanctuary. The town has hosted the ''Festival Échofête de Trois-Pistoles'', an environmentalism-themed music festival and fair each July since 2002. It is Quebec's largest environmental festival. The town can be reache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
