|
Lennox–Gastaut Syndrome
Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a complex, rare, and severe childhood-onset epilepsy. It is characterized by multiple and concurrent seizure types, cognitive dysfunction, and slow spike waves on electroencephalogram (EEG). Typically, it presents in children aged 3–5 years and can persist into adulthood. It has been associated with several gene mutations, perinatal injuries, congenital infections, brain tumors/malformations, and genetic disorders such as tuberous sclerosis and West syndrome. The prognosis for LGS is poor with a 5% mortality in childhood and persistent seizures into adulthood (80%–90%). LGS was named for neurologists William G. Lennox (Boston, USA) and Henri Gastaut (Marseille, France), who independently described the condition. The international LGS Awareness Day is on November 1. Signs and symptoms The symptoms vary and progress with age and are characterized by a triad of seizures, cognitive dysfunction, and EEG findings. The triad may not fully emerge u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spike-and-wave
Spike-and-wave is a pattern of the electroencephalogram (EEG) typically observed during epileptic seizures. A spike-and-wave discharge is a regular, symmetrical, generalized EEG pattern seen particularly during absence epilepsy, also known as ‘petit mal’ epilepsy. The basic mechanisms underlying these patterns are complex and involve part of the cerebral cortex, the thalamocortical network, and intrinsic neuronal mechanisms. The first spike-and-wave pattern was recorded in the early twentieth century by Hans Berger. Many aspects of the pattern are still being researched and discovered, and still many aspects are uncertain. The spike-and-wave pattern is most commonly researched in absence epilepsy, but is common in several epilepsies such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Ohtahara syndrome. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to treat epileptic seizures, and new ones are being discovered with fewer adverse effects. Today, most of the research is focused on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABRB3
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GABRB3'' gene. It is located within the 15q12 region in the human genome and spans 250kb. This gene includes 10 exons within its coding region. Due to alternative splicing, the gene codes for many protein isoforms, all being subunits in the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel. The beta-3 subunit is expressed at different levels within the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, thalamus, olivary body and piriform cortex of the brain at different points of development and maturity. GABRB3 deficiencies are implicated in many human neurodevelopmental disorders and syndromes such as Angelman syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, nonsyndromic orofacial clefts, epilepsy and autism. The effects of methaqualone and etomidate are mediated through GABBR3 positive allosteric modulation. Gene The GABRB3 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 15, within the q12 region in the human genom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHD2
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CHD2'' gene. Function The CHD family of proteins is characterized by the presence of chromo (chromatin organization modifier) domains and SNF2-related helicase/ATPase domains. CHD genes alter gene expression possibly by modification of chromatin structure thus altering access of the transcriptional apparatus to its chromosomal DNA template. CHD2 catalyzes the assembly of chromatin into periodic arrays; and the N-terminal region of CHD2, which contains tandem chromodomains, serves an auto-inhibitory role in both the DNA-binding and ATPase activities of CHD2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. Clinical significance De novo mutations and deletions in this gene have been associated with cases of epileptic encephalopathies. CHD2 epilepsy is increasingly being identified as a subpopulation of Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome. CHD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Mutation
A de novo mutation is any mutation/alteration in the genome of any organism (humans, animals, plant, microbes, etc.) that wasn't present or transmitted by their parents. This type of mutation (like any other) occurs spontaneously during the process of DNA replication during cell division in a fetus whose close, biological relatives don't have the mutation. Often, these kind of mutations have very little to no effect on the affected organism, but in rare cases they have a notable and/or serious effect on overall health, physical appearance, etc. Rate The average number of spontaneous mutations (not present in the parents) an infant has in its genome is approximately 43.86 DNMs. A study done in September of 2019 by the University of Utah Health revealed that certain families have a higher spontaneous mutation rate than average, meaning that their newborns had more spontaneous mutations (not present in their parents) than the average newborn, this tendency was found to be hereditar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
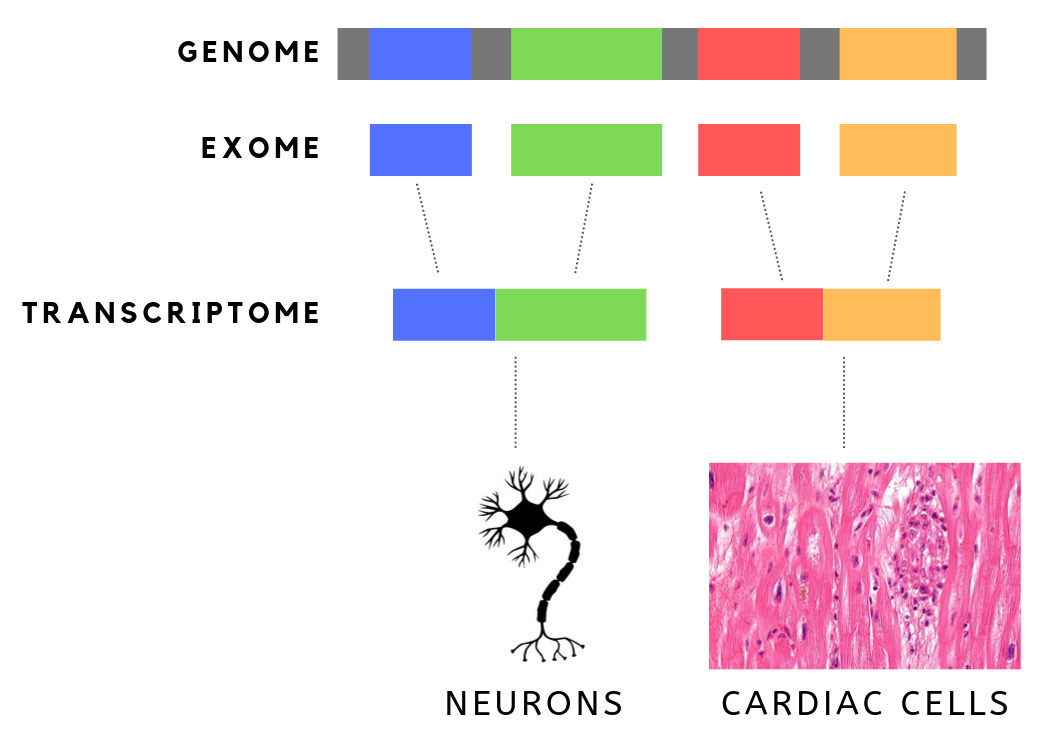
Exome
The exome is composed of all of the exons within the genome, the sequences which, when transcribed, remain within the mature RNA after introns are removed by RNA splicing. This includes untranslated regions of messenger RNA (mRNA), and coding regions. Exome sequencing has proven to be an efficient method of determining the genetic basis of more than two dozen Mendelian or single gene disorders. Statistics The human exome consists of roughly 233,785 exons, about 80% of which are less than 200 base pairs in length, constituting a total of about 1.1% of the total genome, or about 30 megabases of DNA. Though composing a very small fraction of the genome, mutations in the exome are thought to harbor 85% of mutations that have a large effect on disease. Definition It is important to note that the exome is distinct from the transcriptome, which is all of the transcribed RNA within a cell type. While the exome is constant from cell-type to cell-type, the transcriptome changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase
Methylenetetrahydrofolatereductase (MTHFR) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the methyl cycle, and it is encoded by the ''MTHFR'' gene. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a cosubstrate for homocysteine remethylation to methionine. Natural variation in this gene is common in otherwise healthy people. Although some variants have been reported to influence susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, colon cancer, and acute leukemia, findings from small early studies have not been reproduced. Some mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency. Complex I deficiency with recessive spastic paraparesis has also been linked to ''MTHFR'' variants. In addition, the aberrant promoter hypermethylation of this gene is associated with male infertility and recurrent spontaneous abortion. Bioche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (N5,N10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-CH2-THF) is cofactor in several biochemical reactions. It exists in nature as the diastereoisomer R5,10-methylene-THF. As an intermediate in one-carbon metabolism, 5,10-CH2-THF interconverts to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, 5-formyltetrahydrofolate, and methenyltetrahydrofolate. It is substrate for the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) It is mainly produced by the reaction of tetrahydrofolate with serine, catalyzed by the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Selected functions Formaldehyde detoxification Methylenetetrahydrofolate is an intermediate in the detoxification of formaldehyde. Pyrimidine biosynthesis It is the one-carbon donor for thymidylate synthase, for methylation of 2-deoxy-uridine-5-monophosphate ( dUMP) to 2-deoxy-thymidine-5-monophosphate (dTMP). The coenzyme is necessary for the biosynthesis of thymidine and is the C1-donor in the reactions catalyzed by TS and thymidyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumbar puncture, in which a needle is inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, trouble speaking, memory problems, and problems with hearing. Causes of encephalitis include viruses such as herpes simplex virus and rabies virus as well as bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and certain medications. In many cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include a weak immune system. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by blood tests, medical imaging, and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Certain types are preventable with vaccines. Treatment may include antiviral medications (such as acyclovir), anticonvulsants, and corticosteroids. Treatment generally takes place in hospital. Some people require artificial respiration. Once the immediate problem is under co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically included under the umbrella term retinopathy but is often discussed as a separate entity. Retinopathy, or retinal vascular disease, can be broadly categorized into proliferative and non-proliferative types. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease as seen in diabetes or hypertension. Diabetes is the most common cause of retinopathy in the U.S. as of 2008. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-aged people. It accounts for about 5% of blindness worldwide and is designated a priority eye disease by the World Health Organization. Signs and symptoms Many people often do not have symptoms until very late in their disease course. Patients often become symptomatic when there is irreversible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |