|
Leishmania Major
''Leishmania major'' is a species of parasite found in the genus ''Leishmania'', and is associated with the disease zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis (also known as Aleppo boil, Baghdad boil, Bay sore, Biskra button, Chiclero ulcer, Delhi boil, Kandahar sore, Lahore sore, Oriental sore, Pian bois, and Uta). ''L. major'' is an intracellular pathogen which infects the macrophages and dendritic cells of the immune system. Though ''Leishmania'' species are found on every continent aside from Antarctica, ''Leishmania major'' is found only in the Eastern Hemisphere, specifically in Northern Africa, the Middle East, Northwestern China, and Northwestern India. Biology Life cycle As a trypanosomatid, ''L. major'' begins its lifecycle in amastigote form in the midgut of the main vector, female sand flies ('' Phlebotomus spp.''). Once in the gut of the sand fly, the parasites change from aflagelated amastigotes into flagellated promastigotes for 1–2 weeks until they are fully develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
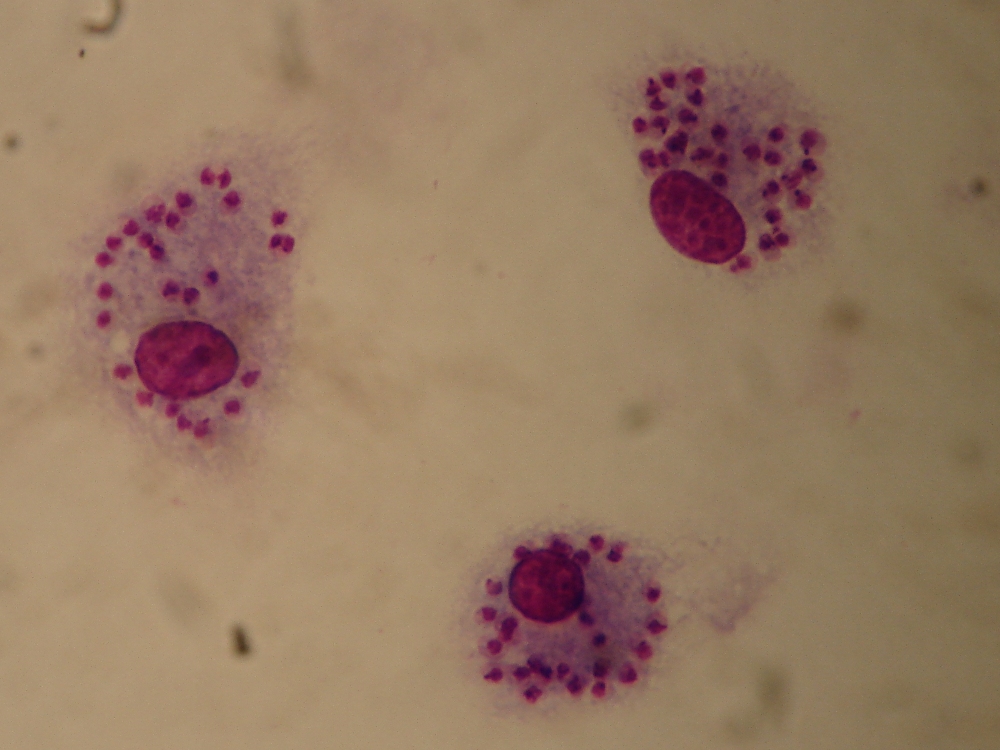
Amastigote
An amastigote is a protist cell that does not have visible external flagella or cilia. The term is used mainly to describe an intracellular phase in the life-cycle of trypanosomes that replicates. It is also called the leishmanial stage, since in ''Leishmania ''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...'' it is the form the parasite takes in the vertebrate host, but occurs in all trypanosome genera. References Kinetoplastids {{Protist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amastigotes
An amastigote is a protist cell that does not have visible external flagella or cilia. The term is used mainly to describe an intracellular phase in the life-cycle of trypanosomes that replicates. It is also called the leishmanial stage, since in ''Leishmania ''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...'' it is the form the parasite takes in the vertebrate host, but occurs in all trypanosome genera. References Kinetoplastids {{Protist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloodstream
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host (biology)
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasite, parasitic, a mutualism (biology), mutualistic, or a commensalism, commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cell (biology), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a Fabaceae, bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) Rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies nutrient, food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala or thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms are characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promastigote
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid excavates distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of Trypanosoma brucei. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by '' T. cruzi'' and transmitted by triatomine bugs), and leishmaniasis (a set of trypanosomal diseases caused by various species of ''Leishmania'' trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmaniasis Life Cycle Diagram En
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, '' Phlebotomus'' and '' Lutzomyia'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver. Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty, malnutrition, deforestation, and urbanization. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Additionally, visceral disease can be diagnosed by blood tests. Leishmaniasis can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amastigotes
An amastigote is a protist cell that does not have visible external flagella or cilia. The term is used mainly to describe an intracellular phase in the life-cycle of trypanosomes that replicates. It is also called the leishmanial stage, since in ''Leishmania ''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...'' it is the form the parasite takes in the vertebrate host, but occurs in all trypanosome genera. References Kinetoplastids {{Protist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebotomus
''Phlebotomus'' is a genus of " sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance. Epidemiology In the Old World, ''Phlebotomus'' sand flies are primarily responsible for the transmission of leishmaniasis, an important parasitic disease, while transmission in the New World, is generally via sand flies of the genus ''Lutzomyia''. The protozoan parasite itself is a species of the genus ''Leishmania''. Leishmaniasis normally finds a mammalian reservoir in rodents and other small animals such as canids ( canine leishmaniasis) and hyraxes. The female sand fly carries the ''Leishmania'' protozoa from infected animals after feeding, thus transmitting the disease, while the male feeds on plant nectar. The parasite ''Leishmania donovani'' is the main causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_2.jpg)
_Trypanosoma_equiperdum.jpg)
