|
Leiden Plate
The Leyden plaque, sometime called Leiden plate or Leiden plaque, is a jadeite belt plate from the early classic period of the Maya civilization. Although the plate was found on the Caribbean coast, it may have been made in Tikal. The plate is now in the National Museum of Ethnology in Leiden, Netherlands, hence its official name. It is one of the oldest Maya objects using the Mesoamerican Long Count calendar. History The plate was discovered by chance by a Dutch engineer, S.A. van Braam, in 1864. He was part of a team employed by a lumber company to dig a canal near present-day Puerto Barrios, in the lower Motagua Valley, a border area of Guatemala and Honduras. The team transected what looked like an ancient Central-American funeral mound. There, together with copper bells and pottery fragments, the little jade plate was found. The plate was taken to the Netherlands in 1864 and gifted to the National Museum of Ethnology. The first scientific description of the plate was m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jadeite
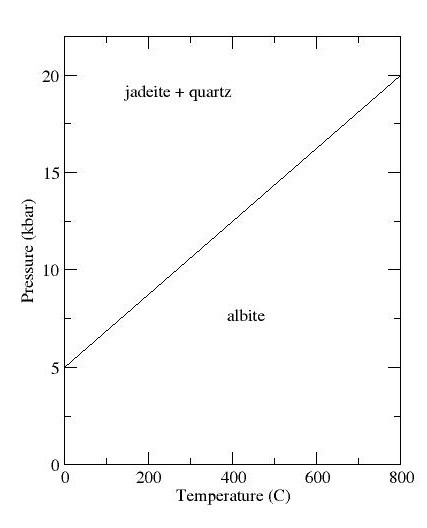
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition sodium, Naaluminium, Alsilicon, Si2oxygen, O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades of green or white. Jadeite is formed only in subduction zones on continental margins, where rock undergoes metamorphism at high pressure but relatively low temperature. Jadeite is the principal mineral making up the most valuable form of jade, a precious stone particularly prized in China. Most gem-quality jadeite jade comes from northern Myanmar. Jade tools and implements have been found at Stone Age sites, showing that the mineral has been prized by humans since before the beginning of written history. Name The name ''jadeite'' is derived (via french: jade and la, ilia) from the Spanish language, Spanish phrase "piedra de ijada" which means "stone of the side". The Latin version of the name, ''lapis neph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimbell Art Museum
The Kimbell Art Museum in Fort Worth, Texas, hosts an art collection as well as traveling art exhibitions, educational programs and an extensive research library. Its initial artwork came from the private collection of Kay and Velma Kimbell, who also provided funds for a new building to house it. The building was designed by architect Louis I. Kahn and is widely recognized as one of the most significant works of architecture of recent times. It is especially noted for the wash of silvery natural light across its vaulted gallery ceilings. History Kay Kimbell was a wealthy Fort Worth businessman who built an empire of over 70 companies in a variety of industries. He married Velma Fuller, who kindled his interest in art collecting by taking him to an art show in Fort Worth in 1931, where he bought a British painting. They set up the Kimbell Art Foundation in 1935 to establish an art institute, and by the time of his death in 1964, the couple had amassed what was considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize God
Like other Mesoamerican peoples, the traditional Maya civilization, Maya recognize in their staple crop, maize, a vital force with which they strongly identify. This is clearly shown by their mythological traditions. According to the 16th-century Popol Vuh, the Hero Twins have maize plants for alter egos and man himself is created from maize. The discovery and opening of the Maize Mountain – the place where the corn seeds are hidden – is still one of the most popular of Maya tales. In the Classic period (200-900 AD), the maize deity shows aspects of a culture hero. Female and male deities In Maya oral tradition, maize is usually personified as a woman — like rice in Southeast Asia, or wheat in ancient Greece and Rome. The acquisition of this woman through bridal capture constitutes one of the basic Maya myths. In contrast to this, the pre-Spanish Maya aristocracy appears to have primarily conceived of maize as male. The classic period distinguished two male forms: a foliated ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodman-Martinez-Thompson Correlation
The Mesoamerican Long Count calendar is a non-repeating vigesimal, base-20 and base-18 calendar used by several pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya civilization, Maya. For this reason, it is often known as the Maya Long Count calendar. Using a modified vigesimal tally, the Long Count calendar identifies a day by counting the number of days passed since a Mesoamerican creation myths, mythical creation date that corresponds to August 11, 3114 Common Era, BCE in the proleptic Gregorian calendar. The Long Count calendar was widely used on monuments. Background The two most widely used calendars in pre-Columbian Mesoamerica were the 260-day Tzolkʼin and the 365-day Haabʼ. The equivalent Aztec calendars are known in Nahuatl as the Tonalpohualli and Xiuhpohualli, respectively. The combination of a Haabʼ and a Tzolkʼin date identifies a day in a combination which does not occur again for 18,980 days (52 Haabʼ cycles of 365 days equals 73 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proleptic Gregorian Calendar
The proleptic Gregorian calendar is produced by extending the Gregorian calendar backward to the dates preceding its official introduction in 1582. In nations that adopted the Gregorian calendar after its official and first introduction, dates occurring in the interim period of 15 October 1582 (the first date of use of Gregorian calendrical dates, being dated 5 October 1582 in the preceding Julian calendar) to the date on which the pertinent nation adopted the Gregorian calendar and abandoned the Julian calendar are sometimes 'Gregorianized' also. For example, the birthday of U.S. President George Washington was originally dated 11 February 1731 (Old Style) because Great Britain, of which he was born a subject, used (until September 1752) the Julian calendar and dated the beginning of English years as 25 March. After Great Britain switched to the Gregorian calendar, Washington's birthday was dated 22 February 1732 proleptically, according to the Gregorian calendar applied backward. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnabar
Cinnabar (), or cinnabarite (), from the grc, κιννάβαρι (), is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and is the historic source for the brilliant red or scarlet pigment termed vermilion and associated red mercury pigments. Cinnabar generally occurs as a vein-filling mineral associated with recent volcanic activity and alkaline hot springs. The mineral resembles quartz in symmetry and in its exhibiting birefringence. Cinnabar has a mean refractive index near 3.2, a mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness between 2.0 and 2.5, and a specific gravity of approximately 8.1. The color and properties derive from a structure that is a hexagonal crystalline bravais lattice, lattice belonging to the trigonal crystal system, crystals that sometimes exhibit Crystal twinning, twinning. Cinnabar has been used for its color since antiquity in the Near East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyph
A glyph () is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A grapheme, or part of a grapheme (such as a diacritic), or sometimes several graphemes in combination (a composed glyph) can be represented by a glyph. Glyphs, graphemes and characters In most languages written in any variety of the Latin alphabet except English, the use of diacritics to signify a sound mutation is common. For example, the grapheme requires two glyphs: the basic and the grave accent . In general, a diacritic is regarded as a glyph, even if it is contiguous with the rest of the character like a cedilla in French, Catalan or Portuguese, the ogonek in several languages, or the stroke on a Polish " Ł". Although these marks originally had no independent meaning, they have since acquired meaning in the field of mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden Plate (Frontal Design Linework)
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes (Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Europe's most prominent scientific centres for more than four centuries. Leiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation Positional notation (or place-value notation, or positional numeral system) usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal system). More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the ... such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by Multiplication, multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usually by 10. As a number, 0 fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and other algebraic structures. Common names for the number 0 in English are ''zero'', ''nought'', ''naught'' (), ''nil''. In contexts where at least one adjacent digit distinguishes it from the O, letter O, the number is sometimes pronounced as ''oh'' or ''o'' (). Informal or slang terms for 0 include ''zilch'' and ''zip''. Historically, ''ought'', ''aught'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |