|
Legacy Of The Qing Dynasty
As a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the legacy of the Qing dynasty has been significant and enduring. It is generally agreed that the Qing dynasty had major impact in China, laying the foundation for the modern Chinese state as a geographic and ethnic entity. Additionally, it had varying degrees of influence in surrounding countries (such as Russia and Mongolia) and other parts of the world. Overview The Qing dynasty (1644–1912) was the largest political entity ever to center itself on China as known today. Succeeding the Ming dynasty, the Qing dynasty more than doubled the geographical extent of the Ming dynasty, which it displayed in 1644, and also tripled the Ming population, reaching a size of about half a billion people in its last years. The vast majority of its large territory, together with its immense and expanding population as well as the associated problems, would be bequeathed to its successor states, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchu People
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Qing (1636–1912) dynasties of China were established and ruled by the Manchus, who are descended from the Jurchen people who earlier established the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) in northern China. Manchus form the largest branch of the Tungusic peoples and are distributed throughout China, forming the fourth largest ethnic group in the country. They can be found in 31 Chinese provincial regions. Among them, Liaoning has the largest population and Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia and Beijing have over 100,000 Manchu residents. About half of the population live in Liaoning and one-fifth in Hebei. There are a number of Manchu autonomous counties in China, such as Xinbin, Xiuyan, Qinglong, Fengning, Yitong, Qingyuan, Weichang, Kua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
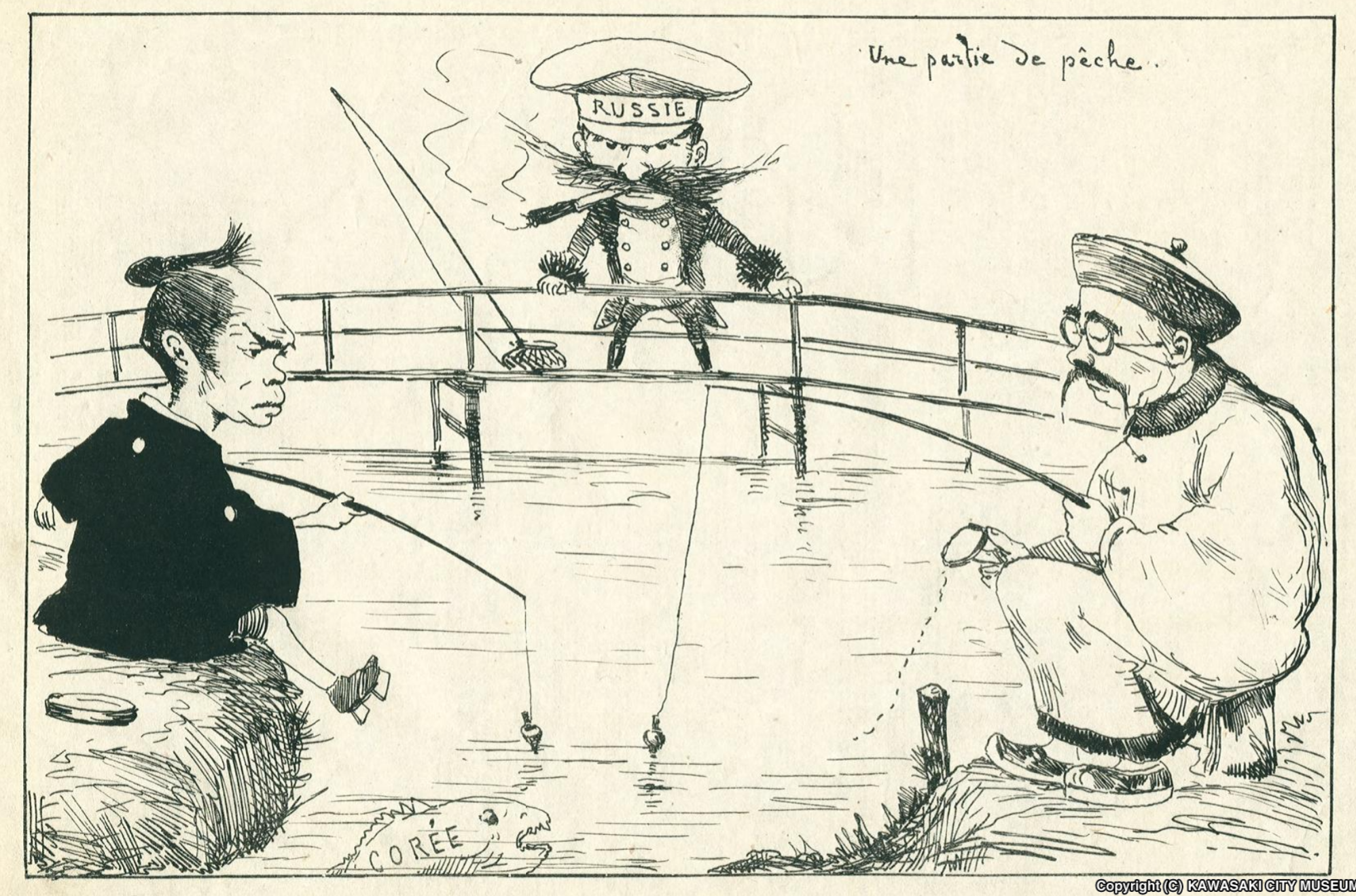
Treaty Of Kyakhta
The Treaty of Kyakhta (or Kiakhta),, ; , Xiao'erjing: بُلِيًاصِٿِ\ٿِاكْتُ تِيَوْيُؤ; mn, Хиагтын гэрээ, Hiagtiin geree, along with the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689), regulated the relations between Imperial Russia and the Qing Empire of China until the mid-19th century. It was signed by Tulišen and Count Sava Lukich Raguzinskii-Vladislavich at the border city of Kyakhta on 23 August 1727. Results *Diplomatic and trade relations were established that lasted until the mid-19 century. *It established the northern border of Mongolia (what was then part of the Qing-Russian border). *The caravan trade from Kyakhta opened up (Russian furs for Chinese tea). *Agreement with Russia helped China expand westward and annex Xinjiang. Qing subjects are referred to as those from "Dulimbai gurun" in Manchu in the Treaty. Background By the 1640s Russian adventurers had taken control of the forested area north of Mongolia and Manchuria. From 1644, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto'' independence from Qing China during the Xinhai Revolution. While the administrative region of Outer Mongolia during the Qing dynasty only consisted of the four Khalkha aimags (Setsen Khan Aimag, Tüsheet Khan Aimag, Sain Noyon Khan Aimag, and Zasagt Khan Aimag), in the late Qing period "Outer Mongolia" was also used to refer to the combined Khalkha and Oirat regions, as well as the directly-ruled Tannu Uriankhai. The region was subsequently claimed by the Republic of China, which had acquired the legal right to inherit all Qing territories through the Imperial Edict of the Abdication of the Qing Emperor, as an integral part of the state. Most of Outer Mongolia, however, was under the ''de facto'' control of the Bogd Khanate, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Races Under One Union
Description This principle emphasized harmony between what were considered the five major ethnic groups in China, as represented by the colored stripes of the Flag of the Republic of China, Five-Colored Flag of the Republic: the Han Chinese, Han (red); the Manchu people, Manchus (yellow); the Mongols in China, Mongols (blue); the Hui (white); and the Tibetan people, Tibetans (black).Fitzgerald, John. [1998] (1998). Awakening China: Politics, Culture, and Class in the Nationalist Revolution. Stanford University Press publishing. , . pg 180. The term , , primarily referred in this context to Muslims, as a whole, and as such for a certain period of time (before the 1911 Revolution, Xinhai Revolution) the term also referred to the Uyghurs in Western China, since the term "Muslim Territory" (; ) was an older name for Xinjiang during the Qing dynasty. The meaning of the term "Hui people" gradually shifted to Hui people, its current sense—a group distinguished from Han Chinese by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of 2,132 years of imperial rule in China and 276 years of the Qing dynasty, and the beginning of China's early republican era.Li, Xiaobing. 007(2007). ''A History of the Modern Chinese Army''. University Press of Kentucky. , . pp. 13, 26–27. The Qing dynasty had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the War of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opium Wars
The Opium Wars () were two conflicts waged between China and Western powers during the mid-19th century. The First Opium War was fought from 1839 to 1842 between China and the United Kingdom, and was triggered by the Chinese government's campaign to enforce its prohibition against opium trafficking by British merchants. The Second Opium War was waged by Britain and France against China from 1856 to 1860. In each war, the superior military advantages enjoyed by European forces led to several easy victories over the Chinese military, with the consequence that China was compelled to sign unequal treaties to grant favourable tariffs, trade concessions, reparations and territory to Western powers. The two conflicts, along with the various treaties imposed during the " century of humiliation", weakened the Chinese government's authority and forced China to open specified treaty ports (including Shanghai) to Western merchants. In addition, China ceded sovereignty over Hong Kong to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country located in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, formerly known in the Western political circles, press and literature as Formosa, makes up 99% of the land area of the territories under ROC control. The main island measures and lies some across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The East China Sea lies to the north of the island, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south and the South China Sea to its southwest. The ROC also controls a number of smaller islands, including the Penghu archipelago in the Taiwan Strait, the Kinmen and Matsu Islands near the PRC's coast, and some of the South China Sea Islands. Geologically, the main island comprises a tilted fault block, characterized by the contrast between the eastern two-thirds, consisting mostly of five rugged mountain ranges running parallel to the east coast, and the flat to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Manchuria
Outer Manchuria (russian: Приаму́рье, translit=Priamurye; zh, s=外满洲, t=外滿洲, p=Wài Mǎnzhōu), or Outer Northeast China ( zh, s=外东北, t=外東北, p=Wài Dōngběi), refers to a territory in Northeast Asia that is now part of Russia but used to belong to a series of Chinese dynasties, including the Tang, Liao, Jin, Eastern Xia, Yuan, Northern Yuan, Ming, Later Jin, and Qing dynasties. The Russian Empire annexed this territory through a series of unequal treaties forced upon Qing China, most notably the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Peking in 1860. It is a part of the larger region of Manchuria, with the term "Outer Manchuria" only arising because of the Russian annexation. Outer Manchuria comprises the modern-day Russian areas of Primorsky Krai, southern Khabarovsk Krai, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the Amur Oblast and the island of Sakhalin. The northern part of the area was disputed by Qing China and the Russian Empire, in the midst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |