|
Left-handedness
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to it being stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dextrous or simply less subjectively preferred, is called the non-dominant hand. In a study from 1975 on 7688 children in US grades 1-6, Left handers comprised 9.6% of the sample, with 10.5% of male children and 8.7% of female children being left-handed. Handedness is often defined by one's writing hand, as it is fairly common for people to prefer to do some tasks with each hand. There are examples of true ambidexterity (equal preference of either hand), but it is rare—most people prefer using one hand for most purposes. Most of the current research suggests that left-handedness has an epigenetic marker—a combination of genetics, biology and the environment. Because the vast majority of the population is right-handed, many devices are designed for u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Handedness Inventory
The Edinburgh Handedness Inventory is a measurement scale used to assess the dominance of a person's right or Left-handedness, left hand in everyday activities, sometimes referred to as laterality. The inventory can be used by an observer assessing the person, or by a person self-reporting hand use. The latter method tends to be less reliable due to a person over-attributing tasks to the dominant hand. The Edinburgh Handedness Inventory was published in 1971 by Richard Charles Oldfield and has been used in various scientific studies as well as popular literature. See also * Ambidexterity * Cross-dominance * Dextrocardia * Footedness * Handedness * Laterality * Ocular dominance * Situs inversus References External links An online example of the tool authored by Mark Cohen hosted ahttp://www.brainmapping.org Motor skills Upper limb anatomy Handedness Chirality {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Study
Twin studies are studies conducted on identical or fraternal twins. They aim to reveal the importance of environmental and genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in related fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the broader methodology used in behavior genetics, which uses all data that are genetically informative – siblings studies, adoption studies, pedigree, etc. These studies have been used to track traits ranging from personal behavior to the presentation of severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia. Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of environmental influence and varying genetic makeup: "identical" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share essentially 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) are due to experiences that one tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Asymmetry
In human neuroanatomy, brain asymmetry can refer to at least two quite distinct findings: * Neuroanatomical differences between the left and right sides of the brain * Lateralized functional differences: lateralization of brain function Neuroanatomical differences themselves exist on different scales, from neuronal densities, to the size of regions such as the planum temporale, to—at the largest scale—the torsion or "wind" in the human brain, reflected shape of the skull, which reflects a backward (posterior) protrusion of the left occipital bone and a forward (anterior) protrusion of the right frontal bone. In addition to gross size differences, both neurochemical and structural differences have been found between the hemispheres. Asymmetries appear in the spacing of cortical columns, as well as dendritic structure and complexity. Larger cell sizes are also found in layer III of Broca's area. The human brain has an overall leftward posterior and rightward anterior as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliogenesis
Ciliogenesis is defined as the building of the cell's antenna (primary cilia) or extracellular fluid mediation mechanism (motile cilium). It includes the assembly and disassembly of the cilia during the cell cycle. Cilia are important organelles of cells and are involved in numerous activities such as cell signaling, processing developmental signals, and directing the flow of fluids such as mucus over and around cells. Due to the importance of these cell processes, defects in ciliogenesis can lead to numerous human diseases related to non-functioning cilia. Ciliogenesis may also play a role in the development of left/right handedness in humans. Cilia formation Ciliogenesis occurs through an ordered set of steps.Sorokin, S. Centrioles and the formation of rudimentary cilia by fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. ''J. Cell Biol.'' 15, 363–377 (1962). First, the basal bodies from centrioles must migrate to the surface of the cell and attach to the cortex. Along the way, the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodal Signaling
The Nodal signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway important in regional and cellular differentiation during embryonic development. The Nodal family of proteins, a subset of the transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) superfamily, is responsible for mesoendoderm induction, patterning of the nervous system, and determination of dorsal- ventral axis in vertebrate embryos. Activation of the Nodal pathway involves nodal binding to activin and activin-like receptors which leads to phosphorylation of the Smad2. The P-Smad2/Smad4 complex translocates into the nucleus to interact with transcription factors such as FoxH1, p53 and Mixer (''Xenopus'' mix-like endodermal regulator). This will, in turn, lead to induction of target genes such as NODAL, Lefty, the antagonist of nodal cerberus, and others. The activation of the Nodal pathway induces the transcription of many target genes including of its own, but at the same time, micro-RNAs and other proteins interfere with this pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvia Paracchini
Silvia Paracchini FRSE is a geneticist who researches the contribution of genetic variation to neurodevelopmental traits such as dyslexia and human handedness. Education As an undergraduate, Paracchini studied Biological Sciences at the University of Pavia, Italy. During this time she undertook an ERASMUS scholarship project at the Technical University of Denmark. She obtained her DPhil in Human Genetics from the University of Oxford in 2003. Career and research After obtaining her doctorate, Paracchini held a post-doctoral research position with the Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics from 2003 to 2011. In 2011, she was awarded a Royal Society University Research Fellowship. Her research group at the University of St Andrews School of Medicine explores the genetic underpinnings of human behavioral traits like handedness, and neurodevelopment disorders like dyslexia by combining large genetic screenings for quantitative measures followed by gene function characterizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-right Asymmetry
Left-right asymmetry, (LR asymmetry) is the process in early embryonic development that Homochirality#Symmetry breaking, breaks the normal symmetry in the Symmetry#In biology, bilateral embryo. In vertebrates, left-right asymmetry is established early in development at a structure called the left-right organizer (the name of which varies between species) and leads to activation of different signalling pathways on the left and right of the embryo. This in turn cause several organs in adults to develop LR asymmetry, such as the tilt of the heart, the different number lung lobes on each side of the body and the position of the stomach and spleen on the right side of the body. If this process does not occur correctly in humans it can result in the syndromes heterotaxy or situs inversus. LR asymmetry is pervasive throughout all animals, including invertebrates. Examples of invertebrate LR asymmetry include the large and small claws of the fiddler crab, asymmetrical gut coiling in ''Dros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygenic
A polygene is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance (polygenic inheritance, multigenic inheritance, quantitative inheritance), a type of non-Mendelian inheritance, as opposed to single-gene inheritance, which is the core notion of Mendelian inheritance. The term "monozygous" is usually used to refer to a hypothetical gene as it is often difficult to distinguish the effect of an individual gene from the effects of other genes and the environment on a particular phenotype. Advances in statistical methodology and high throughput sequencing are, however, allowing researchers to locate candidate genes for the trait. In the case that such a gene is identified, it is referred to as a quantitative trait locus (QTL). These genes are generally pleiotropic as well. The genes that contribute to type 2 diabetes are thought to be mostly polygenes. In July 2016, scientists reported identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
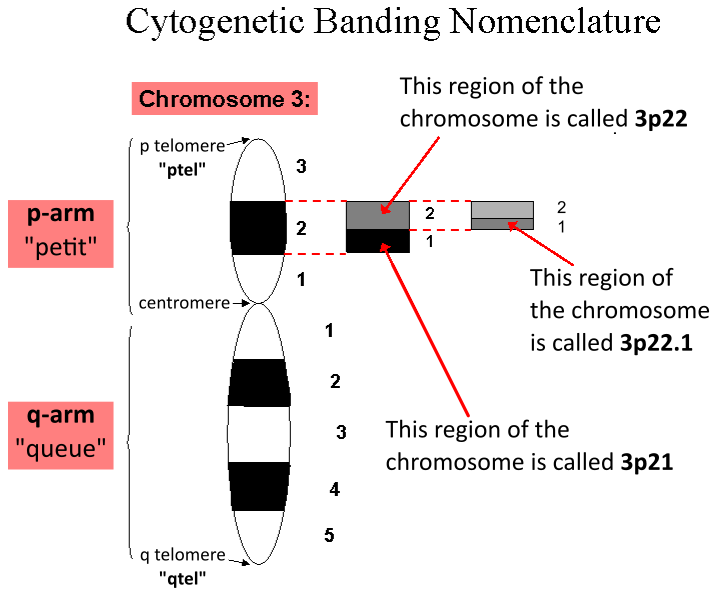
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
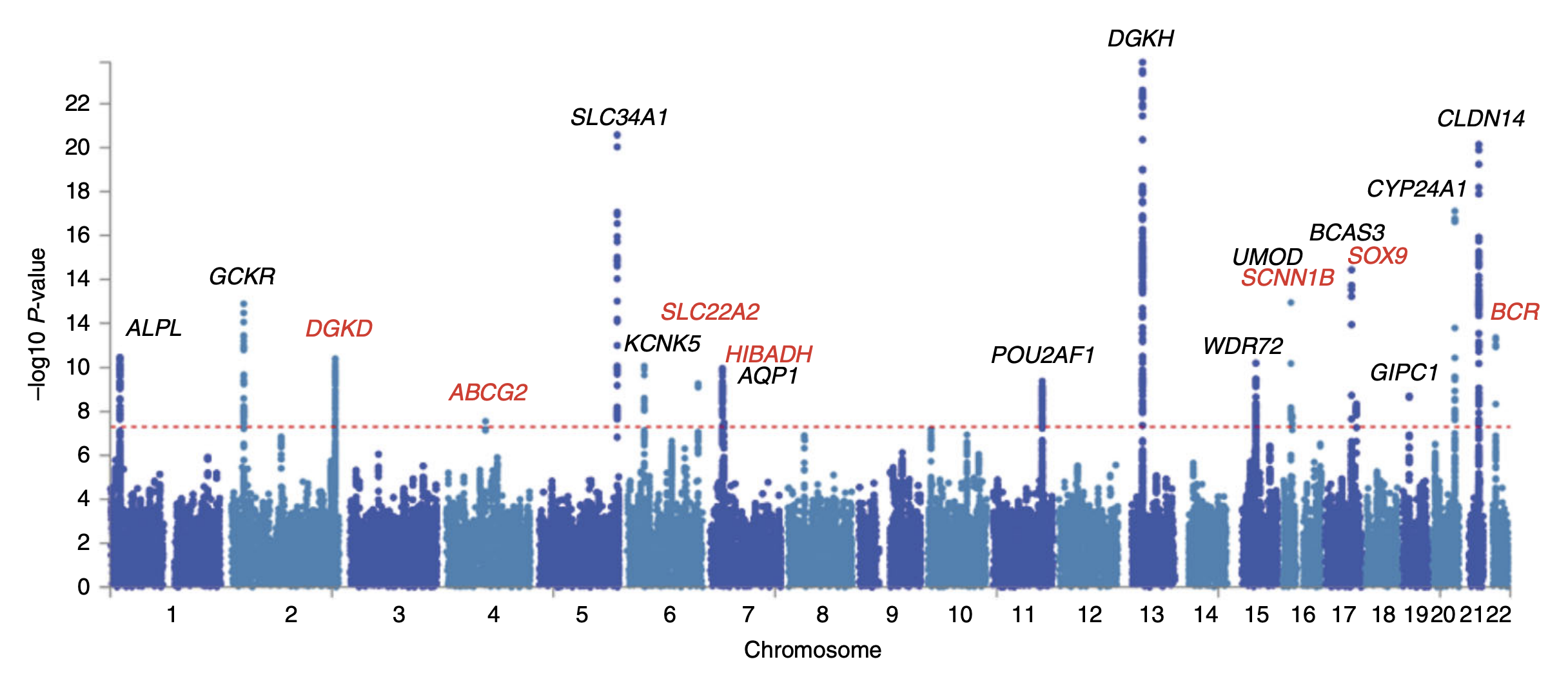
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), also known as whole genome association study (WGA study, or WGAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as oppose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Linkage
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more ''linked'' than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly ''unlinked'', although the penetrance of potentially deleterious alleles may be influenced by the presence of other alleles, and these other alleles may be located on other chromosomes than that on which a particular potentially deleterious allele is located. Genetic linkage is the most prominent exception to Gregor Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. The first experiment to demonstrate li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)