|
Leeuwin Current
The Leeuwin Current is a warm ocean current which flows southwards near the western coast of Australia. It rounds Cape Leeuwin to enter the waters south of Australia where its influence extends as far as Tasmania. Discovery The existence of the current was first suggested by William Saville-Kent in 1897. Saville-Kent noted the presence of warm tropical water offshore in the Houtman Abrolhos, making the water there in winter much warmer than inshore at the adjacent coast. The existence of the current was confirmed over the years, but not characterised and named until Cresswell and Golding did so in the 1980s. Track The West Australian Current and Southern Australian Countercurrent, which are produced by the West Wind Drift on the southern Indian Ocean and at Tasmania, respectively, flow in the opposite direction, producing one of the most interesting oceanic current systems in the world. The ‘core’ of the Leeuwin Current can generally be detected as a peak in the surface te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeuwin Current 2
Leeuwin (Dutch for "lioness") may refer to: Places * Cape Leeuwin, the most south-westerly point of Australia * Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park, the national park in which Cape Leeuwin is located * Leeuwin Barracks, formerly HMAS ''Leeuwin'' (naval base), a Royal Australian Navy shore base in North Fremantle Ships * ''Leeuwin'' (galleon), Dutch galleon that encountered south-west Australia in 1622 * HMAS ''Leeuwin'' (A 245), a hydrographic survey ship ** ''Leeuwin'' class survey vessel, the class of HMAS ''Leeuwin'' * STS ''Leeuwin II'', a Western Australian sail training ship Other uses * Leeuwin Current, a warm ocean current flowing down the west coast of Australia * Leeuwin triplefin (''Norfolkia leeuwin''), a species of small fish of the family Tripterygiidae * ''Leeuwin'' (journal), a short-lived literary journal published in Western Australia by Willem Siebenhaar in 1910 * Leeuwin Estate Leeuwin Estate is an Australian winery and restaurant based in the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of . It is the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha Republic. the state has 2.76 million inhabitants percent of the national total. The vast majority (92 percent) live in the south-west corner; 79 percent of the population lives in the Perth area, leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated. The first Europeans to visit Western Australia belonged to the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first permanent European colony of Western Australia occurred following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters. Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanography. Physical oceanography may be subdivided into ''descriptive'' and ''dynamical'' physical oceanography. Descriptive physical oceanography seeks to research the ocean through observations and complex numerical models, which describe the fluid motions as precisely as possible. Dynamical physical oceanography focuses primarily upon the processes that govern the motion of fluids with emphasis upon theoretical research and numerical models. These are part of the large field of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (GFD) that is shared together with meteorology. GFD is a sub field of Fluid dynamics describing flows occurring on spatial and temporal scales that are greatly influenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Gyres
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the ''wind stress curl'' (torque). ''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex in an atmosphere or a sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems. Major gyres The following are the five most notable ocean gyres:The five most notable gyres PowerPoint Presentation * * |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other areas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canary Current
The Canary Current is a wind-driven surface current that is part of the North Atlantic Gyre. This eastern boundary current branches south from the North Atlantic Current and flows southwest about as far as Senegal where it turns west and later joins the Atlantic North Equatorial Current. The current is named after the Canary Islands. The archipelago partially blocks the flow of the Canary Current (Gyory, 2007). This wide and slow moving current is thought to have been exploited in the early Phoenician navigation and settlement along the coast of western Morocco. The ancient Phoenicians not only exploited numerous fisheries within this current zone, but also established a factory at Iles Purpuraires off present day Essaouira for extracting a Tyrian purple dye from a marine gastropod murex species. Upwelling A prominent feature of Eastern Boundary Currents is the presence of upwelling. Ekman drift causes offshore transport of surface waters, which are then replaced with deep wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
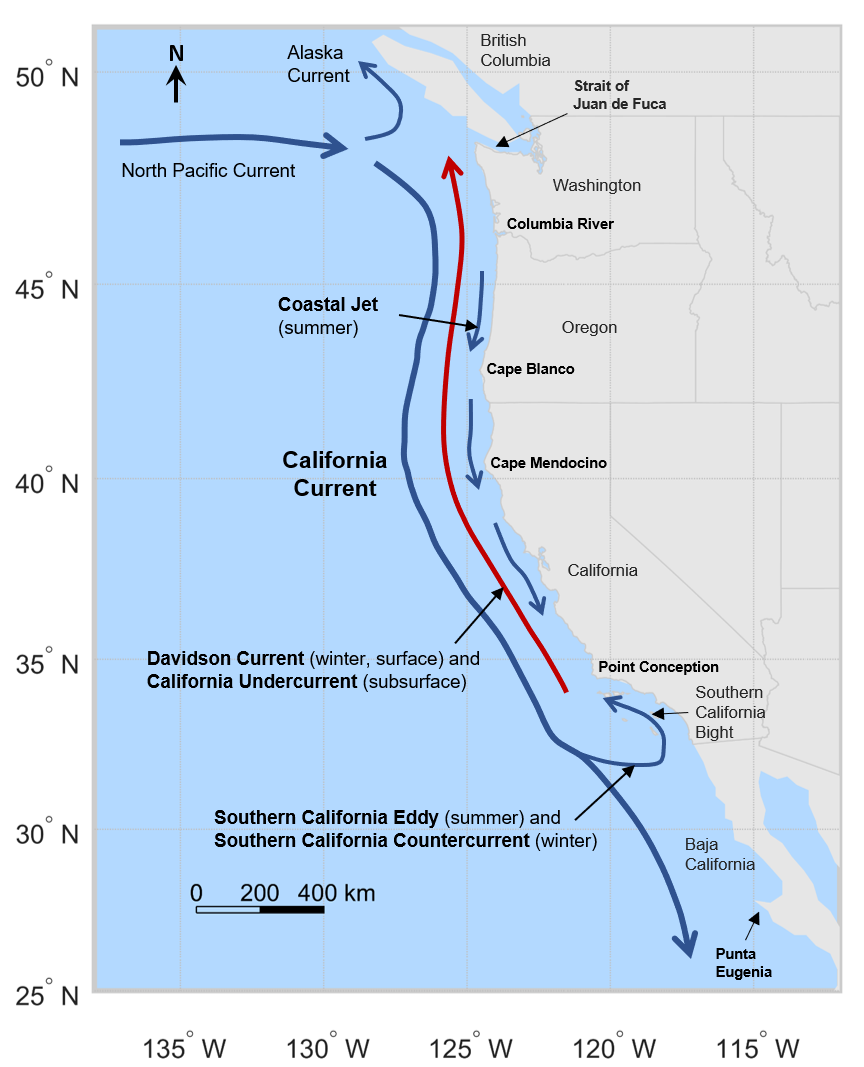
California Current
The California Current is a cold water Pacific Ocean current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern boundary current due to the influence of the North American coastline on its course. It is also one of five major coastal currents affiliated with strong upwelling zones, the others being the Humboldt Current, the Canary Current, the Benguela Current, and the Somali Current. The California Current is part of the North Pacific Gyre, a large swirling current that occupies the northern basin of the Pacific. Physical properties The movement of Alaskan and northern ocean currents southward down the west coast results in much cooler ocean temperatures than at comparable latitudes on the east coast of the United States, where ocean currents come from the Caribbean and tropical Atlantic. The cooler ocean current along the west coast also makes summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low- salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America.Montecino, Vivian, and Carina B. Lange. "The Humboldt Current System: Ecosystem components and processes, fisheries, and sediment studies." ''Progress in Oceanography'' 83.1 (2009): 65-79. DOI10.1016/j.pocean.2009.07.041/ref> It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book ''Cosmos''. The current extends from southern Chile (~ 45th parallel south) to northern Peru (~ 4th parallel south) where cold, upwelled, waters intersect warm tropical waters to form the Equatorial Front. Sea surface temperatures off the coast of Peru, around 5th parallel sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño
El Niño (; ; ) is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific (approximately between the International Date Line and 120°W), including the area off the Pacific coast of South America. The ENSO is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to last close to four years; however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September–November. The cool phase of ENSO is es, La Niña, translation=The Girl, with SSTs in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle, including bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an ''insular shelf''. The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores of a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |