|
Le Prieur Rocket
''Le Prieur'' rockets (French ''Fusées Le Prieur'') were a type of incendiary air-to-air rocket used in World War I against observation balloons and airships. They were invented by the French lieutenant Yves Le Prieur and were first used in the Battle of Verdun in April 1916. Due to great inaccuracy their range was limited to about . Development The Le Prieur rocket was essentially a cardboard tube filled with 200 grams of black powder with a wooden conical head attached (by doped paper or linen tape) and had a triangular knife blade inserted in a slot across its apex forming a spear point. A square-section wooden stick (usually pine) was taped to the fish with about extending back from the base of the rocket and fitted snugly into a launch tube attached to the aircraft inter-plane struts. As top French military officers had expressed concerns about fire hazard for the attacking aircraft, Yves Le Prieur first experimented with his weapon by fitting one on a short section of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
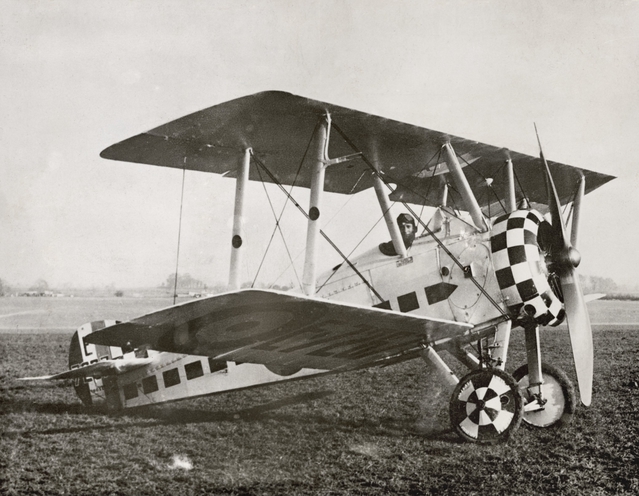
Nieuport W Le Prieur Rockets
Nieuport, later Nieuport-Delage, was a French aeroplane company that primarily built racing aircraft before World War I and fighter aircraft during World War I and between the wars. History Beginnings Originally formed as Nieuport-Duplex in 1902 for the manufacture of engine components the company was reformed in 1909 as the Société Générale d'Aéro-locomotion, and its products were marketed to the aviation industry, including ignition components. During this time they built their first aircraft, a small single-seat pod and boom monoplane. This was destroyed shortly after having been flown successfully, during the Great Flood of Paris in 1909 . A second design flew before the end of 1909 and had the essential form of modern aircraft, including an enclosed fuselage with the pilot protected from the slipstream and a horizontal tail whose aerodynamic force acted downwards, balancing the weight of the engine ahead of the centre of gravity, as opposed to upwards as on contempo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incendiary Bullet
Incendiary ammunition is a type of ammunition that contains a chemical that, upon hitting a hard obstacle, has the characteristic of causing fire/setting flammable materials in the vincinity of the impact on fire. World War I The first time incendiary ammunition was widely used was in World War I, more specifically in 1916. At the time, phosphorus was the primary ingredient in the incendiary charge and ignited upon firing, leaving a trail of blue smoke. These early forms were also known as "smoke tracers" because of this. Though deadly, the effective range of these bullets was only 350 yards (320 m), as the phosphorus charge burned quickly. Incendiary bullets called "Buckingham" ammunition were supplied to early British night fighters for use against military zeppelins threatening the British Isles. The flammable hydrogen gas of the zeppelins made incendiary bullets much more deadly than standard ones which would pass through the outer skin without igniting the gas. Similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftstreitkräfte
The ''Deutsche Luftstreitkräfte'' (, German Air Force)—known before October 1916 as (Flyer Troops)—was the air arm of the Imperial German Army. In English-language sources it is usually referred to as the Imperial German Air Service, although that is not a literal translation of either name. German naval aviators of the were an integral part of the Imperial German Navy (). Both military branches operated aeroplanes, observation balloons and airships. Founding The Imperial German Army created an experimental balloon company inspired by the American balloon corps they had seen while observing the American Civil War, with varying forms of organisation from 1884 to 1901 until a Balloon Battalion was finally formed. The rapid development of aeronautics led to trials of airships and the choice of rigid types built by Zeppelin and Schutte-Lanz. The first military aircraft to be acquired by the German Army entered service in 1910 and the first five aviation battalions were est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halberstadt D
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bombings in late stages of World War II after local Nazi leaders refused to surrender. The town was rebuilt in the following decades. In World War I, Halberstadt was the site of a German military airbase and aircraft manufacturing facilities. In World War II, Halberstadt was a regional production center for Junkers aircraft, which also housed an SS forced labor camp. Halberstadt now encompasses the area where the Langenstein-Zwieberge concentration camp existed. Geography Halberstadt is situated between the Harz in the south and the Huy hills in the north on the Holtemme and Goldbach rivers, both left tributaries of the Bode. Halberstadt is the base of the Department of Public Management of the Hochschule Harz University of Applied Studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria and was also known as the Quadruple Alliance.german: Vierbund, tr, Dörtlü İttifak, hu, Központi hatalmak, bg, Четворен съюз, translit=Chetvoren sūyuz Colonies of these countries also fought on the Central Powers' side such as German New Guinea and German East Africa, until almost all of their colonies were occupied by the Allies. The Central Powers faced and were defeated by the Allied Powers that had formed around the Triple Entente. The Central Powers' origin was the alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary in 1879. Despite having nominally joined the Triple Alliance before, Italy d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Nebel
Rudolf Nebel (21 March 1894 – 18 September 1978) was a spaceflight advocate active in Germany's amateur rocket group, the ''Verein für Raumschiffahrt'' (VfR – "Spaceflight Society") in the 1930s and in rebuilding German rocketry following World War II. Early life and involvement in World War I Nebel was born in Weißenburg. During the First World War he served in the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' as a fighter pilot with Jagdstaffel 5, pioneering the use of unguided air-launched signal rockets as offensive armament from a German fighter aircraft in the Luftstreitkräfte while flying the Halberstadt D.II in early 1916, even forcing down two British aircraft with the improvised rocket armament. Following the war, the former ''Leutnant'' Nebel earned a degree in engineering.Neufeld, M.J. ''Von Braun: Dreamer of Space, Engineer of War''. New York: Knopf, 2007. p 38. Activities in civilian rocketry and politics before the Second World War He was an early member of the German Society fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farman HF
Farman Aviation Works (french: Avions Farman) was a French aircraft company founded and run by the brothers Richard, Henri, and Maurice Farman. They designed and constructed aircraft and engines from 1908 until 1936; during the French nationalization and rationalization of its aeronautical industry, Farman's assets were assigned to the ''Société Nationale de Constructions Aéronautiques du Centre'' (SNCAC). In 1941 the Farman brothers reestablished the firm as the "''Société Anonyme des Usines Farman''" (SAUF), but only three years later it was absorbed by Sud-Ouest. Maurice's son, Marcel Farman, reestablished the SAUF in 1952, but his effort proved unsuccessful and the firm was dissolved in 1956. The Farman brothers designed and built more than 200 types of aircraft between 1908 and 1941. They also built cars until 1931 and boats until 1930. Background In 1907, Henri Farman bought his first aircraft from Gabriel Voisin and soon began to improve the design of the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPAD S
SPAD may refer to: In aircraft manufacture * Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés, also Société Provisoire des Aéroplanes Deperdussin and Blériot-SPAD, French aircraft manufacturer (1912–1921) * SPAD VII, SPAD S.XII and SPAD S.XIII, French fighter planes of World War I produced by Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés * A-1 Skyraider, nicknamed ''Spad'', an attack aircraft (1950s and 1960s) * Simple Plastic Airplane Design, a type of radio-controlled model airplane In science * Single Pass Albumin Dialysis, liver dialysis * Single-photon avalanche diode, a photodetector Other uses * Special adviser (UK), a government post * Self-propelled air defence, weapons * Signal passed at danger by a train * ''Suruhanjaya Pengangkutan Awam Darat'', the Land Public Transport Commission of Malaysia See also * Spade (other) A spade is a digging and gardening tool. Spade or Spades may also refer to: Cards * Spades (card game), a trick-taking card game *Spades (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
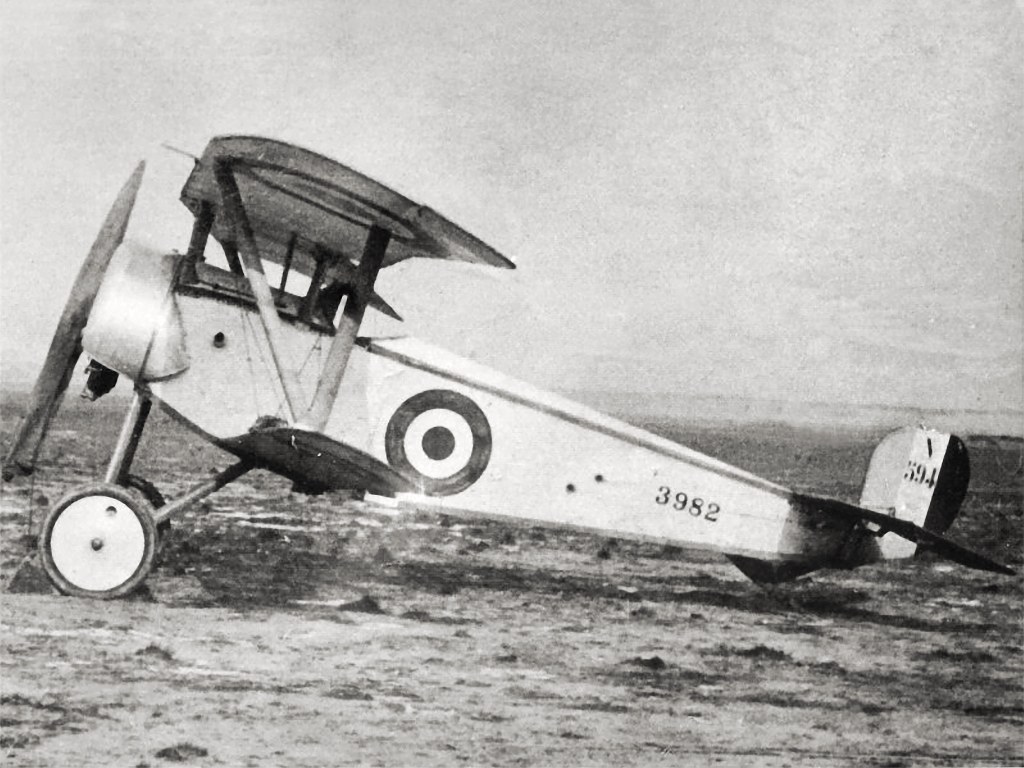
Nieuport 17
The Nieuport 17 C.1 (or Nieuport XVII C.1 in contemporary sources) was a French sesquiplane fighter designed and manufactured by the Nieuport company during World War I. An improvement over the Nieuport 11, it was a little larger than earlier Nieuports and better adapted to the more powerful engine than the interim Nieuport 16. Aside from early examples, it had the new Alkan-Hamy synchronization gear, permitting the use of a fuselage-mounted synchronised Vickers gun firing through the propeller disc. At the time of its introduction in March 1916, the type's outstanding manoeuvrability and excellent rate of climb gave it a significant advantage over fighters on both sides and was described as "the best pursuit plane of the day". It was used by many operators and entered service with every Allied power and copies were also operated by the (German Air Service). Mass-produced by several French firms, the Nieuport 17 and its derivatives were built under licence in Italy by Nieupo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport 16
The Nieuport 16 C.1 (or Nieuport XVI C.1 in contemporary sources)The C in the designation indicates that it is a ''chasseur'' or fighter, and the 1 indicates the number of crew members. was a French World War I single-seat sesquiplane fighter aircraft, designed by Gustave Delage as a development of the Nieuport 11 with a more powerful engine. The Nieuport 16's service life coincided with the period when the first air-to-air rockets, the Le Prieur rocket, were used most frequently, and the type has a closer association with them than any other aircraft. Development The Nieuport 16 was an improved Nieuport 11 developed in 1916, with a strengthened airframe powered by a more powerful Le Rhône 9J rotary engine.Durkota, 1995, p.353 Visible differences included a headrest for the pilot and a larger aperture in front of the "horseshoe" cowling. The Nieuport 16 was an interim type pending the delivery of the slightly larger Nieuport 17 C.1, whose design was begun in parallel with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport 11
The Nieuport 11 (or Nieuport XI C.1 in contemporary sources), nicknamed the ''Bébé'', was a French World War I single seat sesquiplane fighter aircraft, designed by Gustave Delage. It was the primary aircraft that ended the Fokker Scourge in 1916.Chant & Taylor 2007, p. 14. The type saw service with several of France's allies, and gave rise to the series of "vee-strut" Nieuport fighters that remained in service (latterly as trainers) into the 1920s. Design and development The Nieuport 11 was a scaled down development of the Nieuport 10, designed specifically as a single-seat fighter. Like the "10" the "11" was a sesquiplane, a biplane with a full-sized top wing with two spars, and a lower wing of much narrower chord and a single spar. Interplane struts in the form of a "Vee" joined the upper and lower wings. The sesquiplane layout reduced drag and improved the rate of climb, as well as offering a better view from the cockpit than either biplane or monoplane, while being su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Camel
The Sopwith Camel is a British First World War single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that was introduced on the Western Front in 1917. It was developed by the Sopwith Aviation Company as a successor to the Sopwith Pup and became one of the best known fighter aircraft of the Great War. The Camel was powered by a single rotary engine and was armed with twin synchronized Vickers machine guns. Though difficult to handle, it was highly manoeuvrable in the hands of an experienced pilot, a vital attribute in the relatively low-speed, low-altitude dogfights of the era. In total, Camel pilots have been credited with downing 1,294 enemy aircraft, more than any other Allied fighter of the conflict. Towards the end of the First World War, the type also saw use as a ground-attack aircraft, partly because the capabilities of fighter aircraft on both sides had advanced rapidly and left the Camel somewhat outclassed. The main variant of the Camel was designated as the F.1. Other variants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_Rudolf_Nebel.jpg)