|
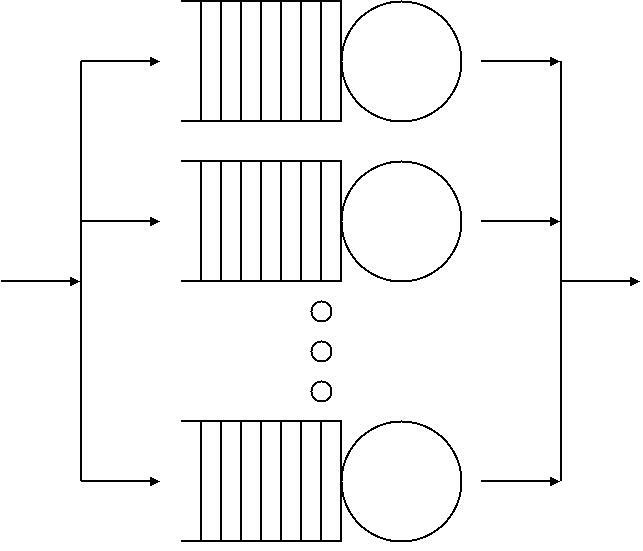
Layered Queueing Network
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, a layered queueing network (or rendezvous network) is a queueing network model where the service time for each job at each service node is given by the response time of a queueing network (and those service times in turn may also be determined by further nested networks). Resources can be nested and queues form along the nodes of the nesting structure. The nesting structure thus defines "layers" within the queueing model. Layered queueing has applications in a wide range of distributed systems which involve different master/slave, replicated services and client-server components, allowing each local node to be represented by a specific queue, then orchestrating the evaluation of these queues. For large population of jobs, a fluid limit has been shown in PEPA Performance Evaluation Process Algebra (PEPA) is a stochastic process algebra designed for modelling computer and communication systems intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Transactions On Software Engineering
The ''IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the IEEE Computer Society. It was established in 1975 and covers the area of software engineering. It is considered the leading journal in this field. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Science Citation Index Expanded and Current Contents/Engineering, Computing & Technology. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 6.226. Past editors-in-chief See also * ''IEEE Software'' * ''IET Software ''IET Software'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on software engineering and related issues, published by the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET) in the United Kingdom. The journal was previously published under the following t ...'' References External links * Transactions on Software Engineering Computer science journals Software engineering publications Monthly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queueing Network
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecture Notes In Computer Science
''Lecture Notes in Computer Science'' is a series of computer science books published by Springer Science+Business Media since 1973. Overview The series contains proceedings, post-proceedings, monographs, and Festschrifts. In addition, tutorials, state-of-the-art surveys, and "hot topics" are increasingly being included. The series is indexed by DBLP. See also *''Monographiae Biologicae'', another monograph series published by Springer Science+Business Media *''Lecture Notes in Physics'' *''Lecture Notes in Mathematics'' *''Electronic Workshops in Computing ''Electronic Workshops in Computing'' (eWiC) is a publication series by the British Computer Society. The series provides free online access for conferences and workshops in the area of computing. For example, the EVA London Conference proceeding ...'', published by the British Computer Society References External links * Publications established in 1973 Computer science books Series of non-fiction books Springer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queueing Model
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is '' Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing nod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different computer network, networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by message passing, passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the clock synchronization, lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from service-oriented architecture, SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer, peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master/slave (technology)
Master/slave is a model of asymmetric communication or control where one device or process (the "master") controls one or more other devices or processes (the "slaves") and serves as their communication hub. In some systems, a master is selected from a group of eligible devices, with the other devices acting in the role of slaves. The ''master/slave'' terminology was first used in 1904. Since the early 21st century, the terms have become a subject of controversy from their association with slavery and some organizations have opted to replace them with alternative terms. Examples * In electronics, master/slave relationships are used to describe some of the following scenarios: ** In parallel ATA hard drive arrangements, the terms master and slave are used to describe drives on the same cable, but neither drive has control or priority over the other. ** A master clock that provides time signals used to synchronize one or more slave clocks as part of a clock network. ** In AXI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Limit
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, a fluid limit, fluid approximation or fluid analysis of a stochastic model is a deterministic real-valued process which approximates the evolution of a given stochastic process, usually subject to some scaling or limiting criteria. Fluid limits were first introduced by Thomas G. Kurtz publishing a law of large numbers and central limit theorem In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) establishes that, in many situations, when independent random variables are summed up, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themsel ... for Markov chains. It is known that a queueing network can be stable, but have an unstable fluid limit. References Queueing theory {{probability-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEPA
Performance Evaluation Process Algebra (PEPA) is a stochastic process algebra designed for modelling computer and communication systems introduced by Jane Hillston in the 1990s. The language extends classical process algebras such as Milner's CCS and Hoare's CSP by introducing probabilistic branching and timing of transitions. Rates are drawn from the exponential distribution and PEPA models are finite-state and so give rise to a stochastic process, specifically a continuous-time Markov process (CTMC). Thus the language can be used to study quantitative properties of models of computer and communication systems such as throughput, utilisation and response time as well as qualitative properties such as freedom from deadlock. The language is formally defined using a structured operational semantics in the style invented by Gordon Plotkin. As with most process algebras, PEPA is a parsimonious language. It has only four combinators, ''prefix'', ''choice'', ''co-operation'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |