|
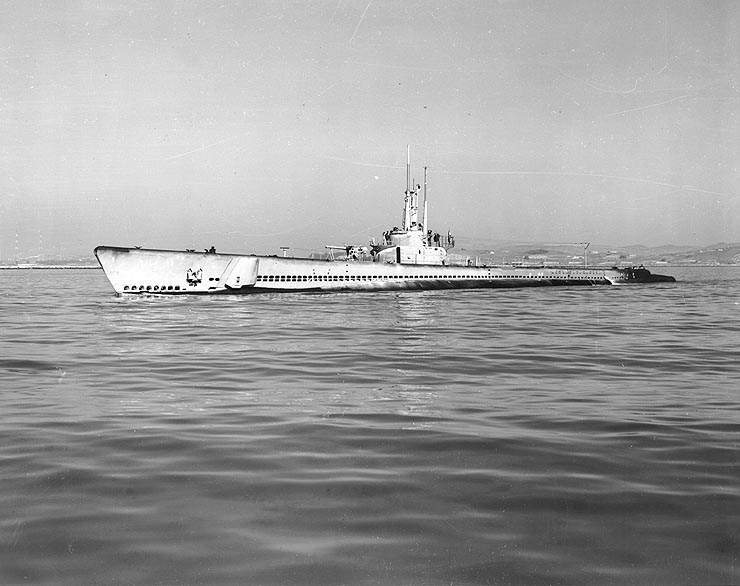
Lawson P. Ramage
Lawson Paterson "Red" Ramage (19 January 1909 – 15 April 1990) was a Vice admiral (United States), vice admiral in the United States Navy and a noted submarine commander during World War II. Ramage was decorated with the Medal of Honor and several other combat Military decorations, decorations during the war. He also served during the Korean War and the Vietnam War. Early life and career Taking his nickname from his hair color, Ramage was born on 19 January 1909, in Monroe, Massachusetts. He graduated from the United States Naval Academy, U.S. Naval Academy in 1931, having injured his right eye while wrestling, and was subsequently commissioned as an ensign in the U.S. Navy. From 1931 to 1935, he served aboard several surface ships. He was the navigator of , the engineering officer of , and the radio officer of . Ramage was unable to pass the submarine physical examination because of his eye injury, and is quoted by Stephen Moore as having said, "I took the opportunity to memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monroe, Massachusetts
Monroe is a town in Franklin County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 118 at the 2020 census. By area, population, and population density, it is the smallest town in the county; and is the second-smallest town by population in the Commonwealth, with only Gosnold having fewer residents. Monroe is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Monroe was first settled in 1800 and was officially incorporated in 1822. The town was named for President James Monroe, who was in office at the time of incorporation. The town was mostly rural, with dairy farming taking up much of the town's economic activity. During the mid-19th century, the town did get some business from the building of the Hoosac Tunnel, just south of town in Florida. In 1885, however, a railroad line was built between neighboring Readsboro, Vermont, and Holyoke to haul wood pulp to a paper factory. This, in turn, enticed the Ramage family to establish the James Ramage Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin D
Franklin may refer to: People * Franklin (given name) * Franklin (surname) * Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class Places Australia * Franklin, Tasmania, a township * Division of Franklin, federal electoral division in Tasmania * Division of Franklin (state), state electoral division in Tasmania * Franklin, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb in the Canberra district of Gungahlin * Franklin River, river of Tasmania * Franklin Sound, waterway of Tasmania Canada * District of Franklin, a former district of the Northwest Territories * Franklin, Quebec, a municipality in the Montérégie region * Rural Municipality of Franklin, Manitoba * Franklin, Manitoba, an unincorporated community in the Rural Municipality of Rosedale, Manitoba * Franklin Glacier Complex, a volcano in southwestern British Columbia * Franklin Range, a mountain range on Vancouver Island, British Columbia * Franklin River (Vancouver Island), British Columbia * Franklin Strai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Breault
Henry Breault (14 October 1900 – 5 December 1941) was a United States Navy submarine sailor who received the Medal of Honor for his actions while serving aboard the submarine . He was the first submariner and he remains the only enlisted submariner to be awarded the Medal of Honor for actions aboard a United States submarine. Biography Henry Breault was born in Putnam, Connecticut, Putnam, Connecticut, on 14 October 1900. During World War I he enlisted in the British Royal Navy at sixteen years of age and, after serving under the White Ensign for four years, joined the U.S. Navy. On 28 October 1923, Torpedoman Second Class Breault was a member of the crew of when that submarine was sunk in a collision in the Panama Canal. Though he could have escaped, Breault chose to assist a shipmate and remained inside the sunken submarine until both were rescued more than a day later. For his "heroism and devotion to duty" on this occasion, Henry Breault was awarded the Medal of Honor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfpack (naval Tactic)
The wolfpack was a convoy attack tactic employed in the Second World War. It was used principally by the U-boats of the during the Battle of the Atlantic, and by the submarines of the United States Navy in the Pacific War. The idea of a co-ordinated submarine attack on convoys had been proposed during the First World War but had no success. In the Atlantic during the Second World War the Germans had considerable successes with their wolfpack attacks but were ultimately defeated by the Allies. In the Pacific the American submarine force was able to devastate Japan’s merchant marine, though this was not solely due to the wolfpack tactic. Wolfpacks fell out of use during the Cold War as the role of the submarine changed and as convoys became rare. World War I During the (German war on trade) Allied ships travelled independently prior to the introduction of the convoy system and were vulnerable to attacks by U-boats operating as 'lone wolves'. By gathering up merchant ships into con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balao Class Submarine
The ''Balao'' class was a successful design of United States Navy submarine used during World War II, and with 120 boats completed, the largest class of submarines in the United States Navy. An improvement on the earlier , the boats had slight internal differences. The most significant improvement was the use of thicker, higher yield strength steel in the pressure hull skins and frames, which increased their test depth to . ''Tang'' actually achieved a depth of during a test dive, and exceeded that test depth when taking on water in the forward torpedo room while evading a destroyer. Design The ''Balao''s were similar to the ''Gato''s, except they were modified to increase test depth from to . In late 1941, two of the Navy's leading submarine designers, Captain Andrew McKee and Commander Armand Morgan, met to explore increasing diving depth in a redesigned ''Gato''. A switch to a new High-Tensile Steel (HTS) alloy, combined with an increase in hull thickness from to , wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Waldo Christie
Ralph Waldo Christie (30 August 1893 – 19 December 1987) was an admiral in the United States Navy who played a pivotal role in the development of torpedo technologies. During World War II, he commanded submarine operations out of the Australian ports of Brisbane and Fremantle. A 1915 graduate of the United States Naval Academy, Christie served on a variety of warships beginning with the battleship in 1915. He was trained in torpedo design and implementation and became one of the first members of the Submarine School at New London. In 1923 Christie graduated from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology with a Master's degree in Mechanical Engineering, specializing in torpedoes. During the 1920s, he was involved with project G-53, a highly secret program to develop a magnetic influence exploder for torpedoes. The result of this was the development of the Mark 6 exploder and the Mark 14 torpedo. Christie also developed a design for an oxygen torpedo, designated project G-49 or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 14 Torpedo
The Mark 14 torpedo was the United States Navy's standard submarine-launched anti-ship torpedo of World War II. This weapon was plagued with many problems which crippled its performance early in the war. It was supplemented by the Mark 18 electric torpedo in the last two years of the war. From December 1941 to November 1943 the Mark 14 and the destroyer-launched Mark 15 torpedo had numerous technical problems that took almost two years to fix. After the fixes the Mark 14 played a major role in the devastating blow U.S. Navy submarines dealt to the Japanese naval and merchant marine forces during the Pacific War. By the end of World War II, the Mark 14 torpedo was a reliable weapon ultimately remaining in service for almost 40 years in the U.S. Navy, and even longer with other navies. Development The design of the Mark 14 started in January 1931; the Navy allocated $143,000 for its development. The Mark 14 was to serve in the new "fleet" submarines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Kirishima
was a warship of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War I and World War II. Designed by British naval engineer George Thurston, she was the third launched of the four s. Laid down in 1912 at the Mitsubishi, Mitsubishi Shipyards in Nagasaki, Nagasaki, Nagasaki, ''Kirishima'' was formally ship commissioning, commissioned in 1915 on the same day as her sister ship, . ''Kirishima'' patrolled on occasion off the Chinese coast during World War I, and helped with rescue efforts following the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake. Starting in 1927, ''Kirishima''s first reconstruction rebuilt her as a battleship, strengthening her armor and improving her speed. From 1934, a second reconstruction completely rebuilt her superstructure, upgraded her engine plant, and equipped her with Aircraft catapult, launch catapults for floatplanes. Now fast enough to accompany Japan's growing aircraft carrier, carrier fleet, she was reclassified as a fast battleship. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Taiyo
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Midway
The Battle of Midway was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II that took place on 4–7 June 1942, six months after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor and one month after the Battle of the Coral Sea. The U.S. Navy under Admirals Chester W. Nimitz, Frank J. Fletcher, and Raymond A. Spruance defeated an attacking fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy under Admirals Isoroku Yamamoto, Chūichi Nagumo, and Nobutake Kondō north of Midway Atoll, inflicting devastating damage on the Japanese fleet. Military historian John Keegan called it "the most stunning and decisive blow in the history of naval warfare", while naval historian Craig Symonds called it "one of the most consequential naval engagements in world history, ranking alongside Salamis, Trafalgar, and Tsushima Strait, as both tactically decisive and strategically influential". Hoping to lure the American aircraft carriers into a trap and occupying Midway was part of an overall "barrier" strategy to extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |