|
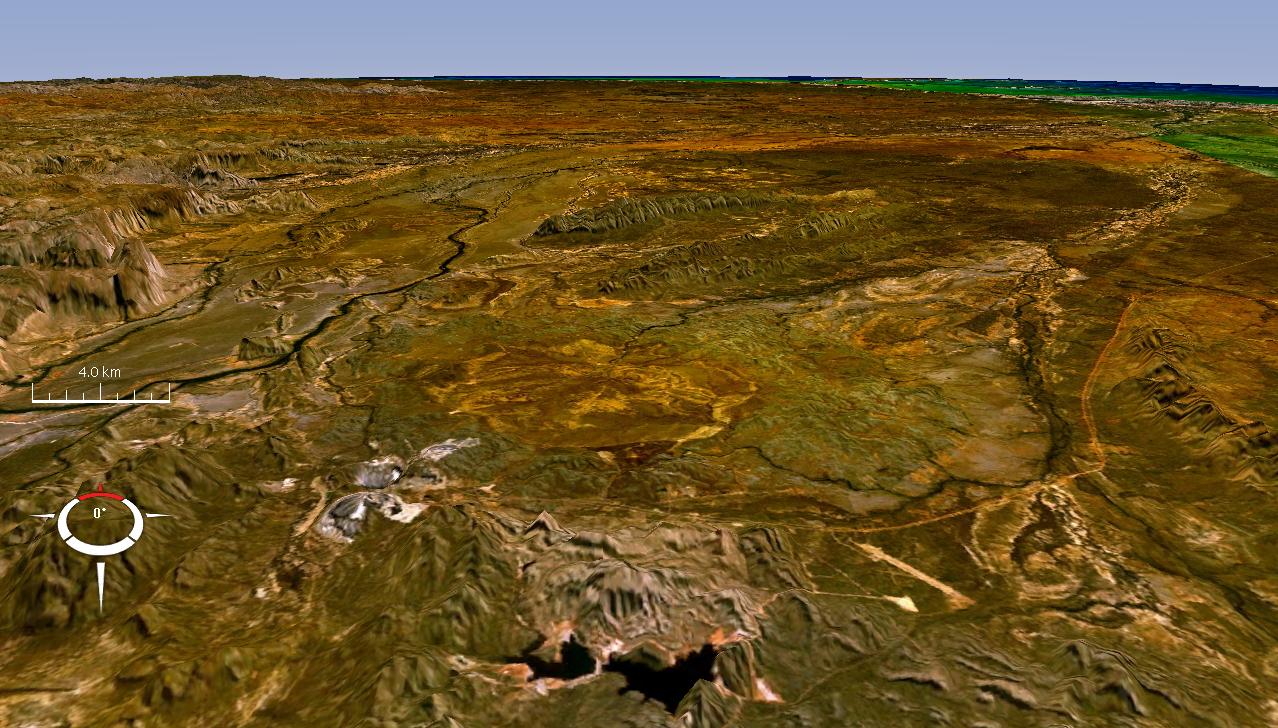
Lawn Hill Crater
Lawn Hill ‘crater’ refers to an Ordovician impact structure, the eroded remnant of a former impact crater, situated approximately 220 km north-north-west of Mount Isa in northwestern Queensland, Australia. The site is marked by an 18 km diameter ring of dolomite hills. The origin of this circular feature was uncertain until the discovery of shatter cones and shocked quartz from uplifted rocks at the centre was reported in 1987. Description The site is eroded and it has been suggested that the original crater was slightly larger, at around 20 km diameter. In the past it has been debated whether the limestones, which are of Middle Cambrian age (ca. 510 Ma) based on comparisons with nearby outcrops of marine limestone in the Georgina Basin, were simply deposited in the crater after its formation, or were actually deformed by the impact event. Those differing points of view suggest that the crater may be of earlier Cambrian or Proterozoic age, or it could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021. The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. Landsat 7 data has eight spectral bands with spatial resolutions ranging from ; the temporal resolution is 16 days. Landsat images are usually divided into scenes for easy downloading. Each Landsat scene is about 115 miles long and 115 miles wide (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawn Hill Oblique
A lawn is an area of soil-covered land planted with grasses and other durable plants such as clover which are maintained at a short height with a lawnmower (or sometimes grazing animals) and used for aesthetic and recreational purposes. Lawns are usually composed only of grass species, subject to weed and pest control, maintained in a green color (e.g., by watering), and are regularly mowed to ensure an acceptable length. Lawns are used around houses, apartments, commercial buildings and offices. Many city parks also have large lawn areas. In recreational contexts, the specialised names turf, pitch, field or green may be used, depending on the sport and the continent. The term "lawn", referring to a managed grass space, dates to at least than the 16th century. With suburban expansion, the lawn has become culturally ingrained in some areas of the world as part of the desired household aesthetic.Robbins, PaulLawn People: How Grasses, Weeds, and Chemicals Make Us Who We A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Impact Craters
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Craters Of Queensland
Impact may refer to: * Impact (mechanics), a high force or shock (mechanics) over a short time period * Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US Science and technology * Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event * Impact event, the collision of a meteoroid, asteroid or comet with Earth * Impact factor, a measure of the citations to a science or social science journal Books and magazines * ''Impact'' (novel), a 2010 novel by Douglas Preston *'' Impact Press'', a former Orlando, Florida-based magazine * Impact Magazines, a former UK magazine publisher * ''Impact'' (conservative magazine), a British political magazine * ''Impact'' (British magazine), a British action film magazine * ''Impact'', a French action film magazine spun off from '' Mad Movies'' * ''Impact'' (UNESCO magazine), a former UNESCO quarterly titled ''IMPACT of science on society'' * ''Impact'' (student magazine), a student magazine for the University of Nottingham, England * ''Bath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic. The Proterozoic covers the time from the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life (such as trilobites or corals) on the Earth. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two forms of ultimately Greek origin: meaning 'former, earlier', and , 'of life'. The well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes; several glaciations, which produced the hypothesized Snowball Earth during the Cryogenian Period in the late Neoproterozoic Era; and the Ediacaran Period (635 to 538.8 Ma) which is characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgina Basin
The Georgina Basin is a large (c. 330,000 km2) intracratonic sedimentary basin in central and northern Australia, lying mostly within the Northern Territory and partly within Queensland.Smith, KG (1972). "Stratigraphy of the Georgina Basin." Bureau of Mineral Resources, Australia, Bulletin 111. It is named after the Georgina River which drains part of the basin. Deposition of locally up to c. 4 km of marine and non-marine sedimentary rocks took place from the Neoproterozoic to the late Paleozoic (c. 850-350 Ma). Along with other nearby sedimentary basins of similar age (Amadeus Basin, Officer Basin), the Georgina Basin is believed to have once been part of the hypothetical Centralian Superbasin, that was fragmented during episodes of tectonic activity. See also *Ngalia Basin *Alice Springs Orogeny The Alice Springs Orogeny was a major intraplate tectonic (mountain building) episode in central Australia responsible for the formation of a series of large mountain ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annum
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shocked Quartz
Shocked quartz is a form of quartz that has a microscopic structure that is different from normal quartz. Under intense pressure (but limited temperature), the crystalline structure of quartz is deformed along planes inside the crystal. These planes, which show up as lines under a microscope, are called planar deformation features (PDFs), or shock lamellae. Discovery Shocked quartz was discovered following underground nuclear weapons testing, which generated the intense pressures required to alter the quartz lattice. Eugene Shoemaker showed that shocked quartz is also found inside craters created by meteor impact, such as the Barringer Crater and Chicxulub crater. The presence of shocked quartz supports that such craters were formed by impact, because a volcanic eruption would not generate the required pressure. Lightning is now known to contribute to the surface record of shocked quartz grains, complicating identification of hypervelocity impact features. Formation Shocked q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA World Wind
NASA WorldWind is an open-source (released under the NOSA license and the Apache 2.0 license) virtual globe. According to the website (https://worldwind.arc.nasa.gov/), "WorldWind is an open source virtual globe API. WorldWind allows developers to quickly and easily create interactive visualizations of 3D globe, map and geographical information. Organizations around the world use WorldWind to monitor weather patterns, visualize cities and terrain, track vehicle movement, analyze geospatial data and educate humanity about the Earth." It was first developed by NASA in 2003 for use on personal computers and then further developed in concert with the open source community since 2004. As of 2017, a web-based version of WorldWind is available online. An Android version is also available. The original version relied on .NET Framework, which ran only on Microsoft Windows. The more recent Java version, WorldWind Java, is cross platform, a software development kit (SDK) aime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shatter Cone
Shatter cones are rare geological features that are only known to form in the bedrock beneath meteorite impact craters or underground nuclear explosions. They are evidence that the rock has been subjected to a shock with pressures in the range of . Morphology Shatter cones have a distinctively conical shape that radiates from the top (''apex'') of the cones repeating cone-on-cone in large and small scales in the same sample. Sometimes they have more of a spoon shape on the side of a larger cone. In finer-grained rocks such as limestone, they form an easily recognizable "horsetail" pattern with thin grooves (''striae''). However, the word "striae" should not be used to describe shatter cones, as that is considered misleading. Coarser grained rocks tend to yield less well developed shatter cones, which may be difficult to distinguish from other geological formations such as slickensides. Geologists have various theories of what causes shatter cones to form, including compress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |