|
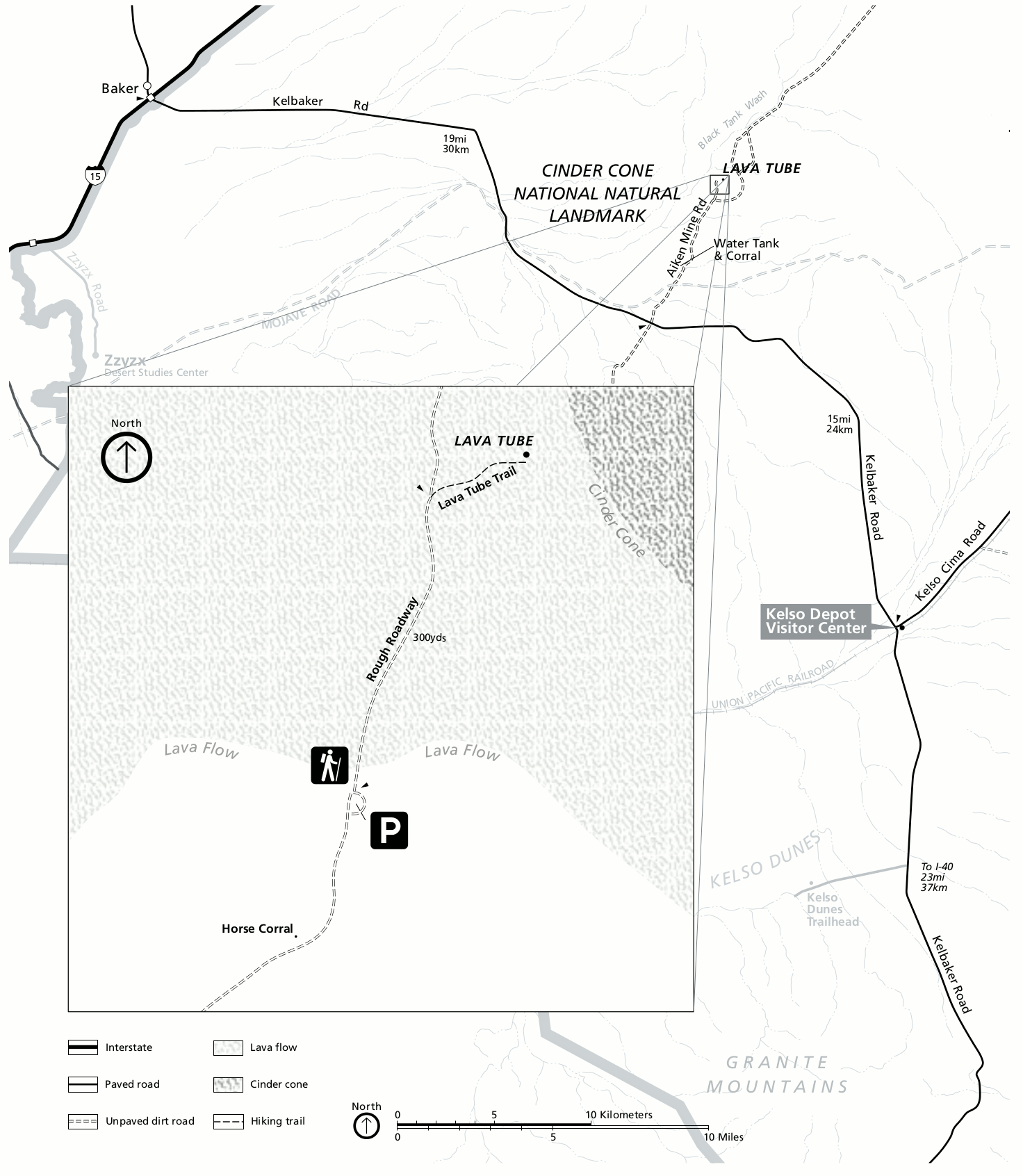
Lavic Lake Volcanic Field
The Lavic Lake volcanic field is a volcanic field with extinct cinder cones in the Mojave Desert, in San Bernardino County, California, United States, at elevation. Its cones lie directly alongside historic Route 66 and modern Interstate 40, between Barstow to the west and Ludlow to the east.Global Volcanism Program, 2013. Lavic Lake (323190) in Volcanoes of the World, v. 4.6.7. Venzke, E (ed.). Smithsonian Institution. Downloaded 15 May 2018 (http://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=323190). https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.VOTW4-2013 Description The Lavic Lake volcanic field is a basaltic pahoehoe lava plain and has four Holocene (approximately 10,000 years ago) cinder cone type volcanos, three in the Lavic Dry Lake area, and a fourth located southwest in the Rodman Mountains. The oldest cinder cone, Pisgah Crater may be pre-Holocene, erupting around 25,000 years ago. Of the four cinder cones, Pisgah Crater stands as the most accessible and prominent volcano in the volcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Fields Of California
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Of The Mojave Desert
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coso Volcanic Field
The Coso Volcanic Field is located in Inyo County, California, at the western edge of the Basin and Range geologic province and northern region of the Mojave Desert. The Fossil Falls are part of the Coso Field, created by the prehistoric Owens River. They are within the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake and northeast of Little Lake and U.S. Route 395. Geology Initiation of volcanism at Coso preceded the onset of Basin and Range crustal extension there, as expressed by normal faulting. The earlier of the two principal periods of volcanism began with the emplacement of basalt flows over a surface of little relief. Then, during the ensuing period of approximately 1.5 million years, eruptive activity included chemically more evolved rocks erupted upon a faulted terrain of substantial relief. Following a 1.5-million-year hiatus with few eruptions, a bimodal volcanic field of basalt lava flows and rhyolite lava domes and flows developed on Basin and Range terrain of essentiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchell Caverns
The Mitchell Caverns, within the Mitchell Caverns Natural Preserve, are three solution limestone caves, only two of which are open to the public, located on the east side of the Providence Mountains at an elevation of , within the Providence Mountains State Recreation Area. The caverns are located in the Mojave Desert, in San Bernardino County, California. Geology The caves lie within a thick sequence of marine Permian limestone. They were formed before the Pleistocene epoch, when ground water with a high carbonic acid content ate into the surrounding sedimentary limestone. Stalactites, stalagmites, and other cave formations were formed from calcium carbonate left by dripping mineral water. History Numerous paleontological and archaeological finds have been made in and around the caverns. Scientists have found the remains of several prehistoric animals, including a Shasta ground sloth. The caverns were a special place for the Chemehuevi Indians, and a number of tools and mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Providence Mountains State Recreation Area
The Providence Mountains State Recreation Area is located in the Providence Mountains, within the Mojave National Preserve in San Bernardino County, California. It is also home to the Mitchell Caverns Natural Preserve. Geography The Recreation Area is located on the east side of the Providence Mountain range and has dramatic views of the surrounding Mojave Desert. On approaching the Providence Mountains State Recreation Area one can see layers of tilted grey rock that are ancient limestone formed during the Paleozoic Era. The base elevation of the park is 4,300 feet with the Providence Mountains reaching to 7000 feet. Flora Vegetation on the lower parts of the mountains is xeric shrublands scrub habitat, composed of creosote bush (''Larrea tridentata''), California barrel cactus (''Ferocactus cylindraceus''), and Mojave yucca (''Yucca schidigera''). The habitat dramatically shifts with elevations above 4000 feet to a sky island where numerous animals and plants flourish in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojave National Preserve
Mojave National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California, USA, between Interstate 15 in California, Interstate 15 and Interstate 40. The preserve was established October 31, 1994, with the passage of the California Desert Protection Act by the US Congress, which also established Joshua Tree National Park and Death Valley National Park as National park, National Parks. Previously, some lands contained within the Preserve were the East Mojave National Scenic Area, under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Land Management. At , within the contiguous United States it is the third largest unit of the National Park System and the first largest National preserve, National Preserve. The preserve was created within the Pacific West Region of the National Park Service and remains within that jurisdiction today. Natural features include the Kelso Dunes, the Marl Mountains and the Cima Dome & Volcanic Field National Natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cima Volcanic Field
Cima volcanic field is a volcanic field in San Bernardino County, California, close to the border with Nevada. The volcanic field covers a surface area of within the Mojave National Preserve west of the Cima Dome and consists of about 40 volcanic cones with about 60 lava flows. The volcanic cones range from simple cones over multi-cratered mountains to eroded hills, and lava flows are up to long. At least one lava tube exists in the field and can be visited. Volcanic activity in the field commenced in the Late Miocene and after a pause between 3 and 1 million years ago continued into the latest Pleistocene. The youngest cone is known as the Black Tank cone and formed about 15,000 years before present, although it is possible that it was formed through two separate eruption events; formerly it was considered to be of historical age. Geography and geology The Cima volcanic field lies in the eastern Mojave Desert of California, between the Shadow Valley in the northeast, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amboy Crater
Amboy Crater is a dormant cinder cone volcano that rises above a lava field in the eastern Mojave Desert of southern California, within Mojave Trails National Monument. It is about equidistant from Barstow to the west and Needles to the east, and south of historic U.S. Route 66, near the town of Amboy in San Bernardino County. In 1973, Amboy Crater was designated the Amboy Crater National Natural Landmark. Location The crater's location is southwest of the town of Amboy and the Route 66- National Trails Highway. The Bullion Mountains are to the west, and the Bristol Mountains to the northeast. Description This cinder cone is estimated to be 79,000 years old (+/- 5,000 years)http://alliance.la.asu.edu/rockart/vmltest/PhillipsMojaveTest.pdf . accessed 3/25/2013 and was formed in layers of mostly vesicular pahoehoe during the Pleistocene geological period. The interior has a lava lake. Lava flows as old as Amboy Crater itself blanket the surrounding area. The most rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration, or electromagnetism. Settling is the falling of suspended particles through the liquid, whereas sedimentation is the final result of the settling process. In geology, sedimentation is the deposition of sediments which results in the formation of sedimentary rock. The term is broadly applied to the entire range of processes that result in the formation of sedimentary rock, from initial erosion through sediment transport and settling to the lithification of the sediments. However, the strict geological definition of sedimentation is the mechanical deposition of sediment particles from an initial suspension in air or water. Sedimentation may pertain to ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)