|
Laverda 1000
The Laverda 1000 is a series of air cooled DOHC triple motorcycles produced by the Italian manufacturer Laverda between 1973 and 1988. The high-performance variant, the Jota, was the fastest production motorcycle from 1976 to 1981. Approximately 7,100 triples of the various models were produced. Background In 1969 Laverda announced their intention to produce a 1000 cc triple. General manager Massimo Laverda claimed the triple would be lighter and narrower than the recently introduced Honda CB750. A prototype was shown at the Milan Show later that year. Chief designer Luciano Zen prototype was based on the SOHC 750 twin with an extra cylinder. It retained the 750's layout of starter behind the cylinders and generator in front. The original engine was not producing enough power so a second prototype was built in 1970 with a double overhead cam layout. The cams were driven by a belt on the right side of the engine. Due to casting difficulties, both cams were housed in separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laverda
Laverda (''Moto Laverda S.A.S. – Dottore Francesco Laverda e fratelli'') was an Italian manufacturer of high performance motorcycles. The motorcycles in their day gained a reputation for being robust and innovative. The Laverda brand was absorbed by Piaggio when, in 2004, Piaggio absorbed Aprilia. Piaggio has elected to quietly close all activities related to the Laverda brand and has publicly stated that they would be willing to sell the rights to the brand if an investor should appear. As of 2015, Laverda.com no longer redirects to Aprilia's website. As of 2021, laverda.com shows the history of the company between 1873 and 2004. History Early history The roots of the Laverda Motorcycle company go back to 1873, when Pietro Laverda (1845-1930) decided to start an agricultural engines enterprise – Laverda (harvesters), Laverda S.p.A. – in the small rural village of Breganze in Vicenza province (North-East of Italy). Almost exactly three quarters of a century later, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Brake
A drum brake is a brake that uses friction caused by a set of shoes or pads that press outward against a rotating cylinder-shaped part called a brake drum. The term ''drum brake'' usually means a brake in which shoes press on the inner surface of the drum. When shoes press on the outside of the drum, it is usually called a '' clasp brake''. Where the drum is pinched between two shoes, similar to a conventional disc brake, it is sometimes called a ''pinch drum brake'', though such brakes are relatively rare. A related type called a band brake uses a flexible belt or "band" wrapping around the outside of a drum. History The modern automobile drum brake was first used in a car made by Maybach in 1900, although the principle was only later patented in 1902 by Louis Renault. He used woven asbestos lining for the drum brake lining, as no alternative dissipated heat like the asbestos lining, though Maybach had used a less sophisticated drum brake. In the first drum brakes, levers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roller Bearings
In mechanical engineering, a rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing (mechanical), bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) between two concentric, Groove (engineering), grooved rings called Race (bearing), races. The relative motion of the races causes the rolling elements to rolling, roll with very little rolling resistance and with little sliding (motion), sliding. One of the earliest and best-known rolling-element bearings are sets of logs laid on the ground with a large stone block on top. As the stone is pulled, the logs roll along the ground with little sliding friction. As each log comes out the back, it is moved to the front where the block then rolls on to it. It is possible to imitate such a bearing by placing several pens or pencils on a table and placing an item on top of them. See "bearing (mechanical), bearings" for more on the historical development of bearings. A rolling element rotary bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Bearing
Main may refer to: Geography * Main River (other) **Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany * Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province *"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries *''The Main'', the diverse core running through Montreal, Quebec, Canada, also separating the Two Solitudes *Main (lunar crater), located near the north pole of the Moon *Main (Martian crater) People and organisations * Main (surname), a list of people with this family name *Ma'in, alternate spelling for the Minaeans, an ancient people of modern-day Yemen *Main (band), a British ambient band formed in 1991 * Chas. T. Main, an American engineering and hydroelectric company founded in 1893 *MAIN (Mountain Area Information Network), former operator of WPVM-LP (MAIN-FM) in Asheville, North Carolina, U.S. Ships * ''Main'' (ship), an iron sailing ship launched in 1884 * SS ''Main'', list of steamships with this name * ''Main'' (A515), a moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
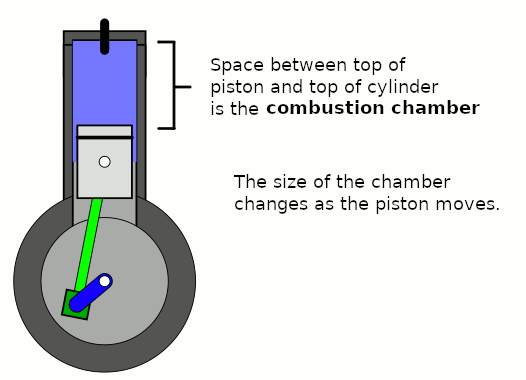
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy Wheel
In the automotive industry, alloy wheels are wheels that are made from an alloy of aluminium or magnesium. Alloys are mixtures of a metal and other elements. They generally provide greater strength over pure metals, which are usually much softer and more ductile. Alloys of aluminium or magnesium are typically lighter for the same strength, provide better heat conduction, and often produce improved cosmetic appearance over steel wheels. Although steel, the most common material used in wheel production, is an alloy of iron and carbon, the term "alloy wheel" is usually reserved for wheels made from nonferrous alloys. The earliest light-alloy wheels were made of magnesium alloys. Although they lost favor on common vehicles, they remained popular through the 1960s, albeit in very limited numbers. In the mid-to-late 1960s, aluminium-casting refinements allowed the manufacture of safer wheels that were not as brittle. Until this time, most aluminium wheels suffered from low ductility, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts downwards through the connecting rod and onto the crankshaft. The connecting rod is att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Brake
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses the calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or a "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hold it stationary. The energy of motion is converted into waste heat which must be dispersed. Hydraulically actuated disc brakes are the most commonly used form of brake for motor vehicles, but the principles of a disc brake are applicable to almost any rotating shaft. The components include the disc, master cylinder, and caliper (which contains a cylinder and two brake pads) on both sides of the disc. Design The development of disc-type brakes began in England in the 1890s. In 1902, the Lanchester Motor Company designed brakes that looked and operated in a similar way to a modern disc-brake system even though the disc was thin and a cable activated the brake pad. Other designs were not practical or widely available in cars for another 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brembo
Brembo S.p.A. is an Italian manufacturer of automotive brake systems, especially for high-performance cars and motorcycles. Its head office is in Curno, Bergamo, Italy. History Brembo was established in Paladina, Italy on January 11, 1961 by Emilio Bombassei and Italo Breda (father and uncle, respectively, to the current Chairman Alberto Bombassei). The company was named after the Brembo river, as Bombassei lived in a village on the coast of the river before moving to Milan. Soon after Brembo was formed, it specialized in disc brakes, which were imported from the UK at the time. The company entered into a supply contract with Alfa Romeo in 1964 and became Moto Guzzi's brake component supplier in 1966. In the 1980s, Brembo also began supplying brakes to BMW, Chrysler, Ferrari, Mercedes-Benz, Nissan, and Porsche. Brembo went public on the Milan Stock Exchange in 1995. In 2000, Brembo purchased the UK-based racing brake and clutch manufacturer AP Racing (a former division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic Fork
A telescopic fork is a form of motorcycle front suspension whose use is so common that it is virtually universal. The telescopic fork uses fork tubes and sliders which contain the springs and dampers. The main advantages of the telescopic fork are that (i) it is simple in design and relatively cheap to manufacture and assemble; (ii) it is lighter than older designs using external components and linkage systems; and (iii) it has a clean and simple appearance that bikers find attractive. Telescopic forks sometimes have gaiters to protect the fork tubes from abrasion and corrosion. A more modern (and more expensive) version of the conventional telescopic fork is the inverted or "USD" (upside-down) fork. BMW's patented telelever front suspension appears at first glance to be conventional telescopic fork, but the fork tubes contain neither springs nor damping. Instead, a wishbone and an inboard monoshock perform suspension duties, and the forks serve to locate the front wheel an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriani
Ceriani, formerly Arces, was an Italian company that designed and fabricated motorcycle frames and suspensions. The company was founded by Arturo Ceriani in 1951. Arces is an acronym derived from Arturo Ceriani S.r.l. In the European motorcycle industry, it was common for many smaller parts companies to exist, each responsible for creating individual parts to later be assembled into a complete motorcycle. Within a few years of its creation, Ceriani's company was able to successfully make a name for itself by manufacturing components noted for their quality and vision. In 1964, under the leadership of Arturo's son Enrico Ceriani, the companies operations were expanded. Enrico accelerated the expansion by moving the company to a new and more modern plant in Samarate. From 1964 the company was known within the industry as ARCES (an acronym of ARturo CEriani Samarate) but the brand identity was maintained and the company continued to be known as Ceriani by consumers. A central de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |