|
Latvian Air Force
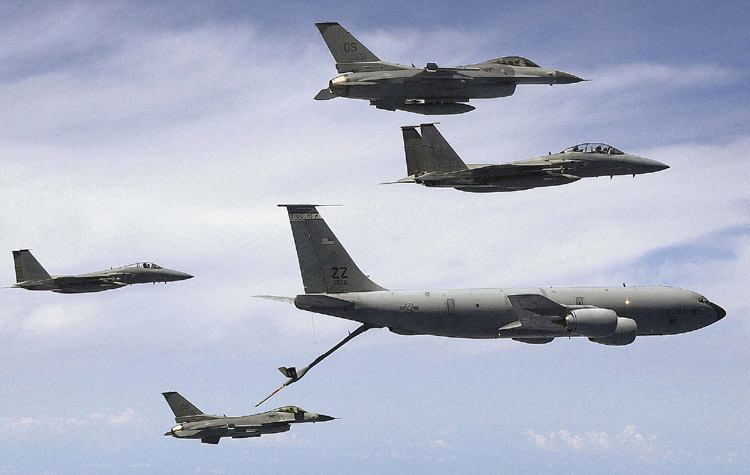
Latvian Air Force ( lv, Latvijas Gaisa spēki) is the aviation branch of the National Armed Forces. The first air force (AF) units were established 1992. It has no air combat capability, thus the defense of Latvian air space is maintained by NATO, with rotating detachments of four aircraft to Lithuania at four-monthly intervals (see Baltic Air Policing). History 1919–1940 The Latvian Air Force was first founded during the Latvian War of Independence. On 7 June 1919 an Air Group was formed, commanded by Lt. Alfrēds Valleika. The first aircraft were former Bolshevik Nieuport 24bis and Sopwith 1½ Strutter, both seized from German forces. They first flew on 5 August 1919, and accomplished the first bombing mission on 26 August 1919. From September the air force had three aircraft, and took part in fighting against the Germans and White Russians. Another 7–8 aircraft were seized and repaired after defeating of Russo-German forces, and 7 Sopwith Camels and 3 Sopwith 1½ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army or navy. Typically, air forces are responsible for gaining control of the air, carrying out strategic and tactical bombing missions, and providing support to land and naval forces often in the form of aerial reconnaissance and close air support. The term air force may also refer to a tactical air force or numbered air force, which is an operational formation either within a national air force or comprising several air components from allied nations. Air forces typically consist of a combination of fighters, bombers, helicopters, transport planes and other aircraft. Many air forces may command and control other air defence forces assets such as anti-aircraft artillery, surface-to-air missiles, or anti-ballistic missile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lettonie Identification Ancienne Et Variante
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the Baltic states; and is bordered by Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of , with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts; and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population. After centuries of Teutonic, Swedish, Polish-Lithuanian and Russian rule, which was mainly executed by the local Baltic German aristocracy, the independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aizsargi
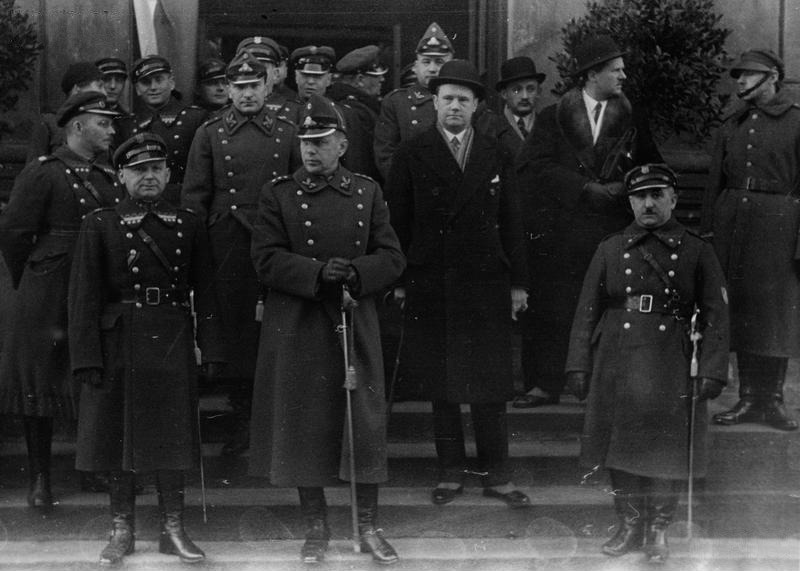
Aizsargi (literally: "Defenders", "Guards") was a volunteer paramilitary organization or militia ( lv, Aizsargu organizācija, "Guards Organization", AO) in Latvia during the interbellum period (1918–1939). The Aizsargi was created on March 30, 1919, by the Latvian Provisional Government as a self-defense force, a kind of National Guard, during the Latvian War of Independence. In 1921 it was reorganized to follow the example of the Finnish '' Suojeluskunta'' (known as the "White Guard"). The Aizsargi published a newspaper, entitled ("Defender"/"Guard"), and the movement had subsidiary sections for women ("") and youth (""). The organization was among those which militarily supported the 1934 coup d'état of Kārlis Ulmanis. By 1 January 1940 the organization had a membership of 60,684: 31,874 guards (aizsargi), 14,810 women members (aizsardzes), and 14,000 youth members (jaunsargu). The organization consisted of 19 infantry regiments and the separate Railroad and Aviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
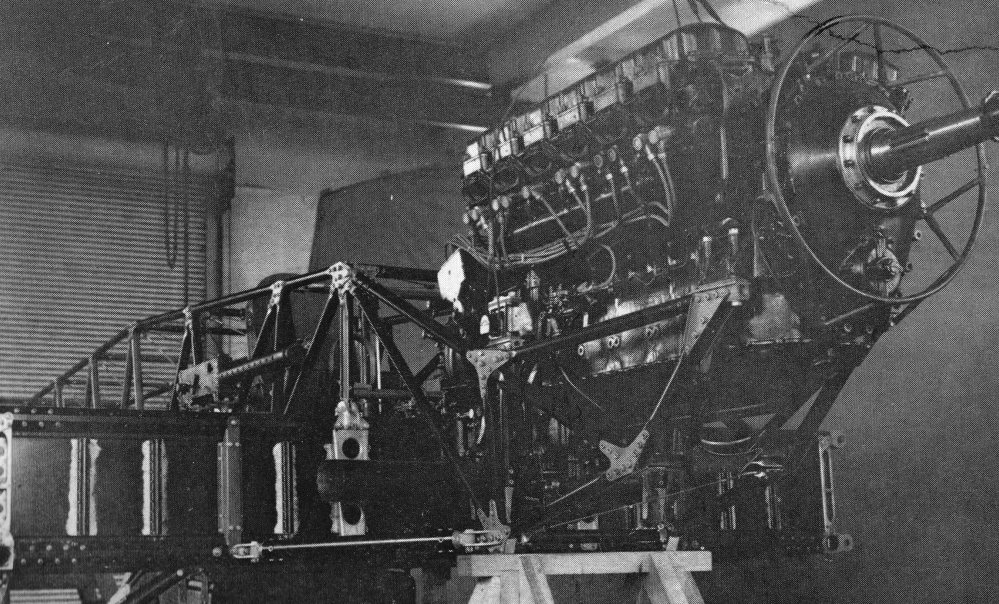
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stampe Et Vertongen SV (1957–2012), Danish football player and coach
* Rigmor Stampe (1850–1923), Danish baroness, writer and philanthropist
* Veronika Stampe East German retired slalom canoeist
Stampe is a surname of German origin. Notable people with the surname include: *John Stampe John Stampe Møller (16 February 1957 – 29 July 2012) was a Danish football player and coach. He played 444 games (and scored 12 goals) for AGF Aarhus and 1 game for the Danish national football team. He later managed his former club AGF. See also * Stampe et Vertongen, a Belgian aircraft manufacturer * Stampee als ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
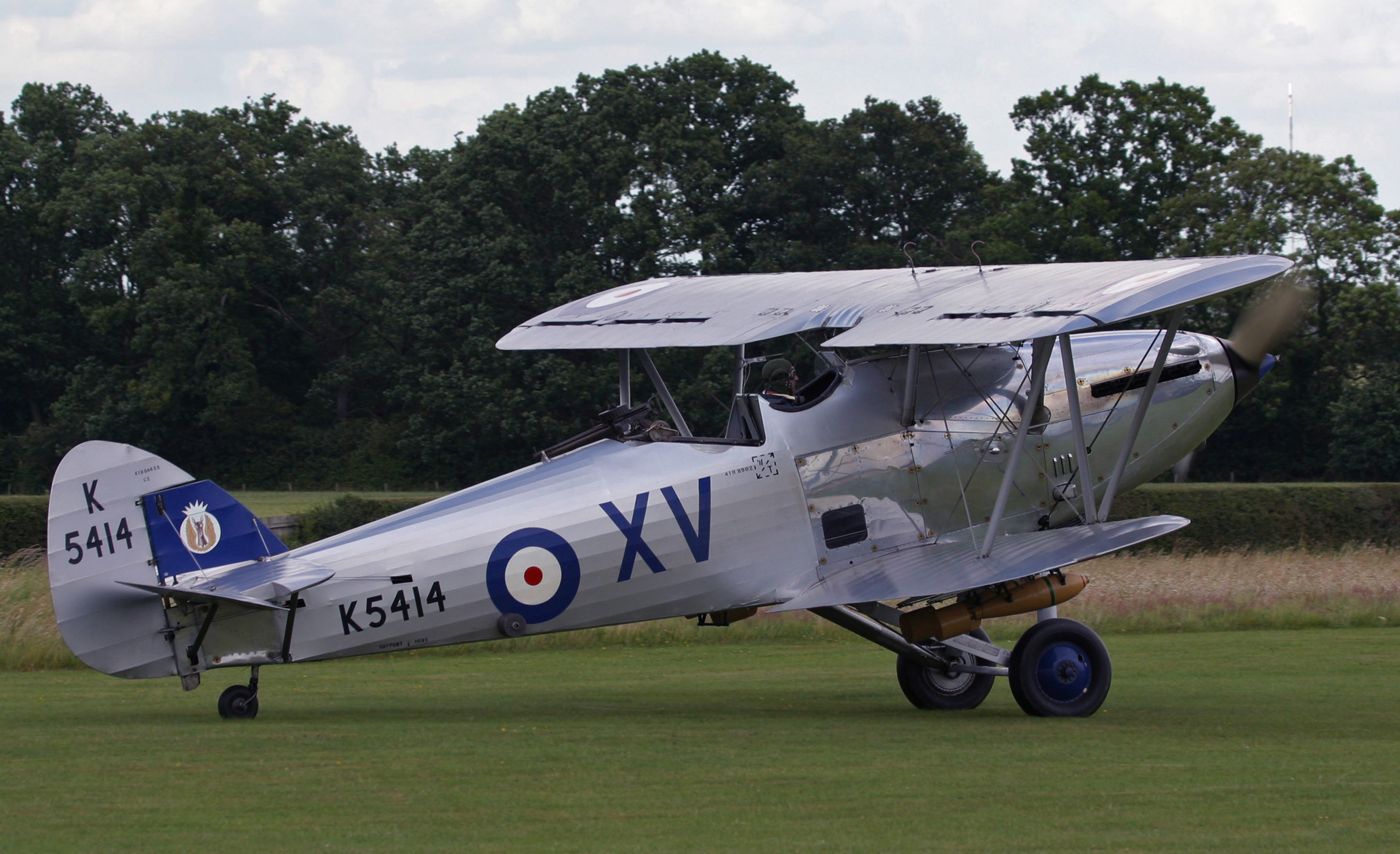
Hawker Hind
The Hawker Hind was a British light bomber of the inter-war years produced by Hawker Aircraft for the Royal Air Force. It was developed from the Hawker Hart day bomber introduced in 1931. Design and development An improved Hawker Hart bomber defined by Specification G.7/34, was purchased by the RAF as an interim aircraft, while more modern monoplane bombers such as the Fairey Battle were still in development. Structural elements were a mixture of steel and duralumin with the wings being fabric covered; the main differences compared to the earlier Hart was a new powerplant, (the Rolls-Royce Kestrel V) and the inclusion of refinements from the earlier derivatives such as the cut-down rear cockpit developed for the Demon. The prototype (Serial number ''K2915'') was constructed very rapidly due to Hawker's development work for other proposals and made its first flight on 12 September 1934. A variety of changes were subsequently incorporated ("ram's horn" exhaust manifolds, Fairey-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letov Š-16
The Letov Š-16 was a Czechoslovak single-engined, two-seat biplane bomber. It was designed by Alois Šmolík at Letov Kbely. The Š-16 first flew in 1926. Variants ;Š-16:Two-seat bomber, reconnaissance biplane. ;Š-16J:Seaplane version for Yugoslavia. One built. ;Š-16L:Export version for Latvia. ;Š-16T:Export version for Turkey. ;Š-116:version with Skoda L engine ;Š-216:version with Walter-built Bristol Jupiter engine ;Š-316:version with Hispano-Suiza 12N engine ;Š-416:version with Breitfeld-Danek BD-500 engine ;Š-516:version with Isotta-Fraschini Asso 750 engine ;Š-616:version with Hispano-Suiza 12Nbr engine ;Š-716:version with Skoda L engine ;Š-816:version with Praga ESV engine ;Š-916:version with Lorraine-Dietrich engine ;Š-17:third prototype Š-16 with a V-12 Breitfeld-Danek (Praga) BD-500 engine Operators ; * Czechoslovakian Air Force (115 aircraft) ; * Aviation Regiment (21 aircraft) ; *Turkish Air Force (16 aircraft) ; *Yugoslav Royal Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
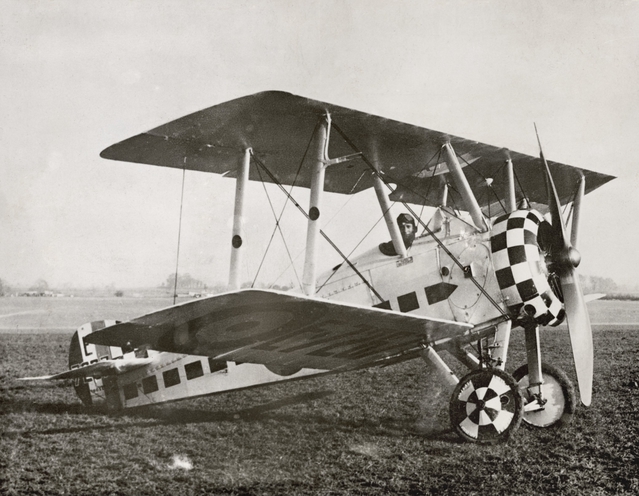
Bristol Bulldog
The Bristol Bulldog is a British Royal Air Force single-seat biplane fighter designed during the 1920s by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. More than 400 Bulldogs were produced for the RAF and overseas customers, and it was one of the most famous aircraft used by the RAF during the inter-war period. Background The design of the Bulldog was the outcome of a series of design studies for fighters undertaken by Frank Barnwell during the 1920s. In 1924 Barnwell had started work on a fighter powered by the Rolls-Royce Falcon to meet the requirements of specification F.17/24. The project was shelved since Bristol preferred to use its own engine designs, but was revived in 1926 when Barnwell started work on a design, designated the Bristol 102, to meet either F.9/26 for a day-and-night fighter or N.21/26 for a shipborne fighter. The Type 105 designation was first applied to a subsequent proposal for another aircraft to meet F.9/26 powered by the Mercury engine then under develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloster Gladiator
The Gloster Gladiator is a British biplane fighter. It was used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) (as the Sea Gladiator variant) and was exported to a number of other air forces during the late 1930s. Developed privately as the Gloster SS.37, it was the RAF's last biplane fighter aircraft, and was rendered obsolete by newer monoplane designs even as it was being introduced. Though often pitted against more formidable foes during the early days of the Second World War, it acquitted itself reasonably well in combat. The Gladiator saw action in almost all theatres during the Second World War, with a large number of air forces, some of them on the Axis side. The RAF used it in France, Norway, Greece, the defence of Malta, the Middle East, and the brief Anglo-Iraqi War (during which the Royal Iraqi Air Force was similarly equipped). Other countries deploying the Gladiator included China against Japan, beginning in 1938; Finland (along with Swedish volunte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Seal
The Fairey Seal was a British carrier-borne spotter-reconnaissance aircraft, operated in the 1930s. The Seal was derived – like the Gordon – from the IIIF. To enable the Fairey Seal to be launched by catapult from warships, it could be fitted with floats. Service life and operations The Seal was designed and built by Fairey Aviation. It first flew in 1930 and entered squadron service with the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) in 1933. Ninety-one aircraft were produced. The FAA started to replace it with the Swordfish Mk1 from 1936. By 1938 all FAA torpedo squadrons had been entirely re-equipped with the Swordfish. The Seal was removed from front-line service by 1938, but remained in secondary and support roles. By the outbreak of the Second World War, only four remained in service. The type was retired fully by 1943. The type was last used in India as an instructional airframe from the Royal Navy Photographic Unit. The RAF also operated the Seal as a target tug. Twelve aircraft we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Camel
The Sopwith Camel is a British First World War single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that was introduced on the Western Front in 1917. It was developed by the Sopwith Aviation Company as a successor to the Sopwith Pup and became one of the best known fighter aircraft of the Great War. The Camel was powered by a single rotary engine and was armed with twin synchronized Vickers machine guns. Though difficult to handle, it was highly manoeuvrable in the hands of an experienced pilot, a vital attribute in the relatively low-speed, low-altitude dogfights of the era. In total, Camel pilots have been credited with downing 1,294 enemy aircraft, more than any other Allied fighter of the conflict. Towards the end of the First World War, the type also saw use as a ground-attack aircraft, partly because the capabilities of fighter aircraft on both sides had advanced rapidly and left the Camel somewhat outclassed. The main variant of the Camel was designated as the F.1. Other variant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |