|
Latrunculin
The latrunculins are a family of natural products and toxins produced by certain sponges, including genus '' Latrunculia'' and '' Negombata'', whence the name is derived. It binds actin monomers near the nucleotide binding cleft with 1:1 stoichiometry and prevents them from polymerizing. Administered ''in vivo'', this effect results in disruption of the actin filaments of the cytoskeleton, and allows visualization of the corresponding changes made to the cellular processes. This property is similar to that of cytochalasin, but has a narrow effective concentration range. Latrunculin has been used to great effect in the discovery of cadherin distribution regulation and has potential medical applications. Latrunculin A, a type of the toxin, was found to be able to make reversible morphological changes to mammalian cells by disrupting the actin network. Latrunculin A: Target and functions Gelsolin - Latrunculin A causes end- blocking; this protein binds to the barbed sides of the act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latrunculin
The latrunculins are a family of natural products and toxins produced by certain sponges, including genus '' Latrunculia'' and '' Negombata'', whence the name is derived. It binds actin monomers near the nucleotide binding cleft with 1:1 stoichiometry and prevents them from polymerizing. Administered ''in vivo'', this effect results in disruption of the actin filaments of the cytoskeleton, and allows visualization of the corresponding changes made to the cellular processes. This property is similar to that of cytochalasin, but has a narrow effective concentration range. Latrunculin has been used to great effect in the discovery of cadherin distribution regulation and has potential medical applications. Latrunculin A, a type of the toxin, was found to be able to make reversible morphological changes to mammalian cells by disrupting the actin network. Latrunculin A: Target and functions Gelsolin - Latrunculin A causes end- blocking; this protein binds to the barbed sides of the act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen Tube
A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of seed plants when it germinates. Pollen tube elongation is an integral stage in the plant life cycle. The pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells from the pollen grain—either from the stigma (in flowering plants) to the ovules at the base of the pistil or directly through ovule tissue in some gymnosperms. In maize, this single cell can grow longer than to traverse the length of the pistil. Pollen tubes were first discovered by Giovanni Battista Amici in the 19th century. They are used as a model for understanding plant cell behavior. Research is ongoing to comprehend how the pollen tube responds to extracellular guidance signals to achieve fertilization. Description Pollen tubes are produced by the male gametophytes of seed plants. Pollen tubes act as conduits to transport the male gamete cells from the pollen grain—either from the stigma (in flowering plants) to the ovule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfilament
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other proteins in the cell. Microfilaments are usually about 7 nm in diameter and made up of two strands of actin. Microfilament functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement, cell motility, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility, and mechanical stability. Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton tensile forces. In inducing cell motility, one end of the actin filament elongates while the other end contracts, presumably by myosin II molecular motors. Additionally, they function as part of actomyosin-driven contractile molecular motors, wherein the thin filaments serve as tensile platforms for myosin's ATP-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabecular Meshwork
The trabecular meshwork is an area of tissue in the eye located around the base of the cornea, near the ciliary body, and is responsible for draining the aqueous humor from the eye via the anterior chamber (the chamber on the front of the eye covered by the cornea). The tissue is spongy and lined by trabeculocytes; it allows fluid to drain into a set of tubes called Schlemm's canal which is lined by endothelium with blood and lymphatic properties that allow aqueous humor to flow into the blood system. Structure The meshwork is divided up into three parts, with characteristically different ultrastructures: #''Inner uveal meshwork'' - Closest to the anterior chamber angle, contains thin cord-like trabeculae, orientated predominantly in a radial fashion, enclosing trabeculae spaces larger than the corneoscleral meshwork. #''Corneoscleral meshwork'' - Contains a large amount of elastin, arranged as a series of thin, flat, perforated sheets arranged in a laminar pattern; cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
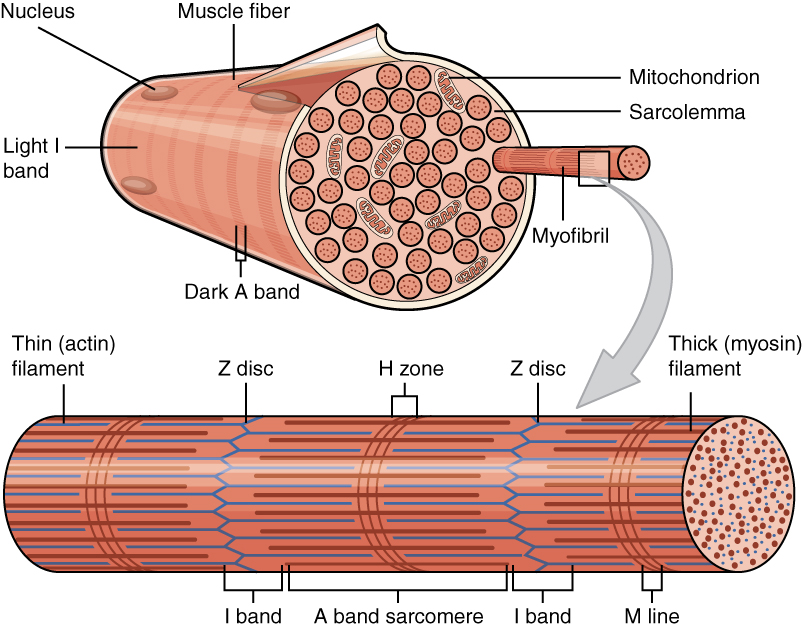
Myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2 micrometres. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis. Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilaments, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomeres. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other. Structure Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometres (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilaments, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments. *Thin filaments consist primarily of the protein acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotransformation
Biotransformation is the biochemical modification of one chemical compound or a mixture of chemical compounds. Biotransformations can be conducted with whole cells, their lysates, or purified enzymes. Increasingly, biotransformations are effected with purified enzymes. Major industries and life-saving technologies depend on biotransformations. Advantages and disadvantages Compared to the conventional production of chemicals, biotransformations are often attractive because their selectivities can be high, limiting the coproduction of undesirable coproducts. Generally operating under mild temperatures and pressures in aqueous solutions, many biotransformations are "green". The catalysts, i.e. the enzymes, are amenable to improvement by genetic manipulation. Biotechnology usually is restrained by substrate scope. Petrochemicals for example are often not amenable to biotransformations, especially on the scale required for some applications, e.g. fuels. Biotransformations can be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicokinetics
Toxicokinetics (often abbreviated as 'TK') is the description of both what rate a chemical will enter the body and what occurs to excrete and metabolize the compound once it is in the body. Relation to Pharmacokinetics It is an application of pharmacokinetics to determine the relationship between the systemic exposure of a compound and its toxicity. It is used primarily for establishing relationships between exposures in toxicology experiments in animals and the corresponding exposures in humans. However, it can also be used in environmental risk assessments in order to determine the potential effects of releasing chemicals into the environment. In order to quantify toxic effects, toxicokinetics can be combined with toxicodynamics. Such toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic (TKTD) models are used in ecotoxicology (seecotoxmodelsa website on mathematical models in ecotoxicology). Similarly, physiological toxicokinetic models are physiological pharmacokinetic models developed to describe an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSBP
Oxysterol-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OSBP'' gene. Function Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) is an intracellular protein that was identified as a cytosolic 25-hydroxycholesterol-binding protein. OSBP is a lipid transfer protein that controls cholesterol/PI4P exchange at ER-Golgi membrane contact sites. 25-hydroxycholesterol acts as a natural inhibitor of this exchange. OSBP regulates ER-Golgi membrane contact sites formation by bridging ER and Golgi membranes together. OSBP plays also a role as a sterol-regulated scaffolding protein for several cytosolic reactions including the phosphorylation of ERK 1/2. It has been shown that expression and maturation of SREBP-1c is controlled by OSBP. SREBP-1c is a major transcription factor for hepatic lipogenesis (fatty acids and triglycerides biosynthesis). OSBP expression levels in transgenic mice affect liver and serum TG levels. OSBP is thought to be an essential scaffolding compound of the prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Epithelium
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelial cells, it serves two main functions: absorbing useful substances into the body and restricting the entry of harmful substances. As part of its protective role, the intestinal epithelium forms an important component of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Certain diseases and conditions are caused by functional defects in the intestinal epithelium. On the other hand, various diseases and conditions can lead to its dysfunction which, in turn, can lead to further complications. Structure The intestinal epithelium is part of the intestinal mucosa. The epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells, while the other two layers of the mucosa, the lamina propria and the muscularis mucosae, support and articulate the epithelial layer. To securely contain the contents of the intes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |