|
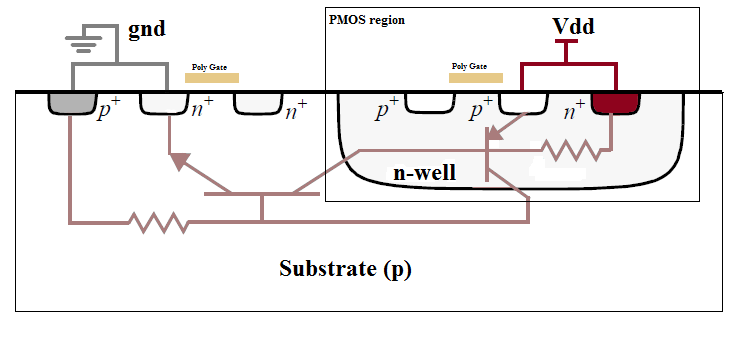
Latch-up
A latch-up is a type of short circuit which can occur in an integrated circuit (IC). More specifically it is the inadvertent creation of a low- impedance path between the power supply rails of a MOSFET circuit, triggering a parasitic structure which disrupts proper functioning of the part, possibly even leading to its destruction due to overcurrent. A power cycle is required to correct this situation. The parasitic structure is usually equivalent to a thyristor (or SCR), a PNPN structure which acts as a PNP and an NPN transistor stacked next to each other. During a latch-up when one of the transistors is conducting, the other one begins conducting too. They both keep each other in saturation for as long as the structure is forward-biased and some current flows through it - which usually means until a power-down. The SCR parasitic structure is formed as a part of the totem-pole PMOS and NMOS transistor pair on the output drivers of the gates. The latch-up does not have to happe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latchup
A latch-up is a type of short circuit which can occur in an integrated circuit (IC). More specifically it is the inadvertent creation of a low- impedance path between the power supply rails of a MOSFET circuit, triggering a parasitic structure which disrupts proper functioning of the part, possibly even leading to its destruction due to overcurrent. A power cycle is required to correct this situation. The parasitic structure is usually equivalent to a thyristor (or SCR), a PNPN structure which acts as a PNP and an NPN transistor stacked next to each other. During a latch-up when one of the transistors is conducting, the other one begins conducting too. They both keep each other in saturation for as long as the structure is forward-biased and some current flows through it - which usually means until a power-down. The SCR parasitic structure is formed as a part of the totem-pole PMOS and NMOS transistor pair on the output drivers of the gates. The latch-up does not have to happen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
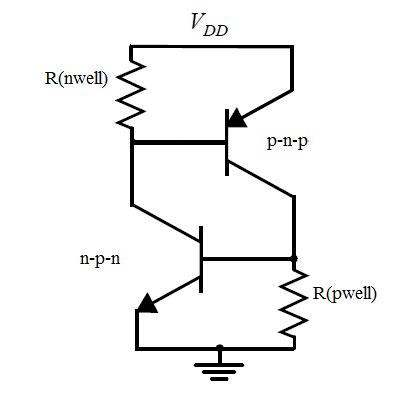
Latchup Ckt
A latch-up is a type of short circuit which can occur in an integrated circuit (IC). More specifically it is the inadvertent creation of a low- impedance path between the power supply rails of a MOSFET circuit, triggering a parasitic structure which disrupts proper functioning of the part, possibly even leading to its destruction due to overcurrent. A power cycle is required to correct this situation. The parasitic structure is usually equivalent to a thyristor (or SCR), a PNPN structure which acts as a PNP and an NPN transistor stacked next to each other. During a latch-up when one of the transistors is conducting, the other one begins conducting too. They both keep each other in saturation for as long as the structure is forward-biased and some current flows through it - which usually means until a power-down. The SCR parasitic structure is formed as a part of the totem-pole PMOS and NMOS transistor pair on the output drivers of the gates. The latch-up does not have to happen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Event Upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element (e.g. memory "bit"). The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error. The SEU itself is not considered permanently damaging to the transistor's or circuits' functionality unlike the case of single-event latch-up (SEL), single-event gate rupture (SEGR), or single-event burnout (SEB). These are all examples of a general class of radiation effects in electronic devices called ''single-event effects'' (SEEs). History Single-event upsets were first described during above-ground nuclear testing, from 1954 to 1957, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Hardening
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation (particle radiation and high-energy electromagnetic radiation), especially for environments in outer space (especially beyond the low Earth orbit), around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare. Most semiconductor electronic components are susceptible to radiation damage, and radiation-hardened (rad-hard) components are based on their non-hardened equivalents, with some design and manufacturing variations that reduce the susceptibility to radiation damage. Due to the extensive development and testing required to produce a radiation-tolerant design of a microelectronic chip, the technology of radiation-hardened chips tends to lag behind the most recent developments. Radiation-hardened products are typically tested to one or more resultant-effects tests, including total i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an "open circuit", which is an infinite resistance between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same voltage. In an 'ideal' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualification
Qualification is either the process of qualifying for an achievement, or a credential attesting to that achievement, and may refer to: * Professional qualification, attributes developed by obtaining academic degrees or through professional experience * Qualification badge, a decoration of People's Liberation Army Type 07 indicating military rank or length of service * Qualifications-Based Selection (QBS), a competitive contract procurement process established by the United States Congress * Qualifications for professional social work, professional degrees in social work in various nations * Qualification problem, the impossibility of listing all the preconditions required for an action to have its intended effect * Qualification principle, in programming language theory, the statement that syntactic classes may admit local definitions * Qualification types in the United Kingdom, different levels of academic, vocational or skills-related education achievements * International Quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JEDEC
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States. JEDEC has over 300 members, including some of the world's largest computer companies. Its scope and past activities includes standardization of part numbers, defining an electrostatic discharge (ESD) standard, and leadership in the lead-free manufacturing transition. The origin of JEDEC traces back to 1944, when RMA (subsequently renamed EIA) and NEMA established the Joint Electron Tube Engineering Council (JETEC) to coordinate vacuum tube type numberings. In 1958, with the advent of semiconductor technology, the joint JETEC-activity of EIA and NEMA was renamed into Joint Electron Device Engineering Council. NEMA discontinued its involvement in 1979. In the fall of 1999, JEDEC became a separate trade association under the current name, but maintained an EIA alliance, until EIA ceased o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Industries Alliance
The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA; until 1997 Electronic Industries Association) was an American standards and trade organization composed as an alliance of trade associations for electronics manufacturers in the United States. They developed standards to ensure the equipment of different manufacturers was compatible and interchangeable. The EIA ceased operations on February 11, 2011, but the former sectors continue to serve the constituencies of EIA. History In 1924, 50 radio manufacturers in Chicago formed a trade group called the ''Associated Radio Manufacturers''. This organization was designed to control the licensing of the large number of radio patents so that each member could have access to all the relevant patents necessary to build radio transmitters, antennas and receivers. Over time, new electronic technologies brought new members, non-manufacturer members, and name changes. Names in chronological order: * 1924 – ''Associated Radio Manufacturers'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon On Insulator
In semiconductor manufacturing, silicon on insulator (SOI) technology is fabrication of silicon semiconductor devices in a layered silicon–insulator–silicon substrate, to reduce parasitic capacitance within the device, thereby improving performance. SOI-based devices differ from conventional silicon-built devices in that the silicon junction is above an electrical insulator, typically silicon dioxide or sapphire (these types of devices are called silicon on sapphire, or SOS). The choice of insulator depends largely on intended application, with sapphire being used for high-performance radio frequency (RF) and radiation-sensitive applications, and silicon dioxide for diminished short-channel effects in other microelectronics devices. The insulating layer and topmost silicon layer also vary widely with application. Industry need SOI technology is one of several manufacturing strategies to allow the continued miniaturization of microelectronic devices, colloquially referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Swap
Hot swapping is the replacement or addition of components to a computer system without stopping, shutting down, or rebooting the system; hot plugging describes the addition of components only. Components which have such functionality are said to be ''hot-swappable'' or ''hot-pluggable''; likewise, components which do not are ''cold-swappable'' or ''cold-pluggable''. Most desktop computer hardware, such as CPUs and memory, are only cold-pluggable. However, it is common for mid to high-end servers and mainframes to feature hot-swappable capability for hardware components, such as CPU, memory, PCIe, SATA and SAS drives. An example of hot swapping is the express ability to pull a Universal Serial Bus (USB) peripheral device, such as a thumb drive, external hard disk drive (HDD), mouse, keyboard, or printer out of a computer's USB slot or peripheral hub without ejecting it first. Most smartphones and tablets with tray-loading holders can interchange SIM cards without powering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Research Institute
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, is an independent and nonprofit applied research and development (R&D) organization. Founded in 1947 by oil businessman Tom Slick, it provides contract research and development services to government and industrial clients. Description The institute consists of eleven technical divisions, The Center for Nuclear Waste Regulatory Analyses, a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, also operates on the SwRI grounds. More than 4,000 projects are active at the institute at any given time. These projects are funded between the government and commercial sectors. At the close of fiscal year 2021, the staff numbered approximately 3,000 employees and research volume was nearly $726 million. The institute provided more than $8 million to fund research through its internally sponsored R&D program. A partial listing of research areas includes space science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation, whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, nearly all types of laser light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area is not sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts between 10 electronvolts (eV) and 33 eV. Typical ionizing subatomic particles include alpha particles, beta particles, and neutrons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |