|
Laser Cooling
Laser cooling includes a number of techniques in which atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled, often approaching temperatures near absolute zero. Laser cooling techniques rely on the fact that when an object (usually an atom) absorbs and re-emits a photon (a particle of light) its momentum changes. For an ensemble of particles, their thermodynamic temperature is proportional to the variance in their velocity. That is, more homogeneous velocities among particles corresponds to a lower temperature. Laser cooling techniques combine atomic spectroscopy with the aforementioned mechanical effect of light to compress the velocity distribution of an ensemble of particles, thereby cooling the particles. The 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Claude Cohen-Tannoudji, Steven Chu, and William Daniel Phillips "for development of methods to cool and trap atoms with laser light". Methods The first example of laser cooling, and also still the most common method (so mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Laser Cooling
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer (physics), observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch (music), pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave Crest (physics), crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeeman Slower
A Zeeman slower is a scientific apparatus that is commonly used in atomic physics to slow and cool a beam of hot atoms to speeds of several meters per second and temperatures below a kelvin. The Gas-phase atoms used in atomic physics are often generated in an oven by heating a solid or liquid atomic sample to temperatures where the vapor pressure is high enough that there are a substantial number of atoms in the gas phase. These atoms effuse out of a hole in the oven with average speeds on the order of hundreds of m/s and large velocity distributions (due to their high temperature). The Zeeman slower is attached close to where the hot atoms exit the oven and is used to slow them to less than 10 m/s (slowing) with a very small velocity spread (cooling). A Zeeman slower consists of a cylinder, through which an atomic beam travels, a pump laser that counterpropagates with respect to the beam's direction , and a magnetic field (commonly produced by a solenoid-like coil) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Leonard Schawlow
Arthur Leonard Schawlow (May 5, 1921 – April 28, 1999) was an American physicist and co-inventor of the laser with Charles Townes. His central insight, which Townes overlooked, was the use of two mirrors as the resonant cavity to take maser action from microwaves to visible wavelengths. He shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics with Nicolaas Bloembergen and Kai Siegbahn for his work using lasers to determine atomic energy levels with great precision. Biography Schawlow was born in Mount Vernon, New York. His mother, Helen (Mason), was from Canada, and his father, Arthur Schawlow, was a Jewish immigrant from Riga (then in the Russian Empire, now in Latvia). Schawlow was raised in his mother's Protestant religion. When Arthur was three years old, they moved to Toronto, Ontario, Canada. At the age of 16, he completed high school at Vaughan Road Academy (then Vaughan Collegiate Institute), and received a scholarship in science at the University of Toronto (Victoria College). After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor W
Theodor is a masculine given name. It is a German form of Theodore. It is also a variant of Teodor. List of people with the given name Theodor * Theodor Adorno, (1903–1969), German philosopher * Theodor Aman, Romanian painter * Theodor Blueger, Latvian professional ice hockey forward for the Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League (NHL) * Theodor Burghele, Romanian surgeon, President of the Romanian Academy * Theodor Busse, German general during World War I and World War II * Theodor Cazaban, Romanian writer * Theodor Fischer (fencer), German Olympic épée and foil fencer * Theodor Fontane, (1819–1898), German writer * Theodor Geisel, American writer and cartoonist, known by the pseudonym Dr. Seuss * Theodor W. Hänsch (born 1940), German physicist * Theodor Herzl, (1860–1904), Austrian-Hungary Jewish journalist and the founder of modern political Zionism * Theodor Heuss, (1884–1963), German politician and publicist * Theodor Innitzer, Austrian Catholic car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Frisch
Otto Robert Frisch FRS (1 October 1904 – 22 September 1979) was an Austrian-born British physicist who worked on nuclear physics. With Lise Meitner he advanced the first theoretical explanation of nuclear fission (coining the term) and first experimentally detected the fission by-products. Later, with his collaborator Rudolf Peierls he designed the first theoretical mechanism for the detonation of an atomic bomb in 1940. Early life Frisch was born in Vienna in 1904 to a Jewish family, the son of Justinian Frisch, a painter, and Auguste Meitner Frisch, a concert pianist. He himself was talented at both but also shared his aunt Lise Meitner's love of physics and commenced a period of study at the University of Vienna, graduating in 1926 with some work on the effect of the newly discovered electron on salts. Nuclear physics After some years working in relatively obscure laboratories in Germany, Frisch obtained a position in Hamburg under the Nobel Prize-winning scientist Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Ferrie Hull
Gordon Ferrie Hull (October 7, 1870 in Garnet, Ontario, Canada – October 7, 1956) was a Canadian-American mathematician, teacher and physicist, especially known for the experimental detection of the radiation pressure exerted by light which he achieved in 1903. Life Hull began his career in 1890-1891 as a teacher of mathematics and science at Hamilton Collegiate Institute, Ontario. He attended Toronto University where he obtained his bachelor's degree in 1892 and became a Fellow in physics, University of Toronto 1892-1895 . Hull earned his 1897 doctorate of physics at the University of Chicago and was later a professor of physics there at Colby College. Thereafter (1899–1940), he taught physics at Dartmouth College. In addition, he had a research position at Cambridge University (1905–1906) and taught physics at Columbia University (1909–1915). As well as his academic career he was conscripted into the army in both World War I (1918–1919) and World War II (1941–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Fox Nichols
Ernest Fox Nichols (June 1, 1869 – April 29, 1924) was an American educator and physicist. He served as the 10th President of Dartmouth College. Early life Nichols was born in Leavenworth County, Kansas, and received his undergraduate degree from Kansas State University in 1888. After working for a year in the Chemistry Department at Kansas State, he matriculated to graduate school at Cornell University, where he received degrees in 1893 and 1897. He also studied at the University of Berlin and Cambridge University. Nichols served as a professor of physics at Colgate University from 1892 to 1898, at Dartmouth College from 1898 to 1903, and Columbia University from 1903 to 1909. He served as the President of Dartmouth College from 1909 to 1916 and as the president of MIT from 1921 until 1922. However, he was too ill from heart disease during his brief tenure to enter actively into his responsibilities. Nichols was awarded the Rumford Prize by the American Academy of Arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annalen Der Physik
''Annalen der Physik'' (English: ''Annals of Physics'') is one of the oldest scientific journals on physics; it has been published since 1799. The journal publishes original, peer-reviewed papers on experimental, theoretical, applied, and mathematical physics and related areas. The editor-in-chief is Stefan Hildebrandt. Prior to 2008, its ISO 4 abbreviation was ''Ann. Phys. (Leipzig)'', after 2008 it became ''Ann. Phys. (Berl.)''. The journal is the successor to , published from 1790 until 1794, and ', published from 1795 until 1797. The journal has been published under a variety of names (', ', ', ''Wiedemann's Annalen der Physik und Chemie'') during its history. History Originally, was published in German, then a leading scientific language. From the 1950s to the 1980s, the journal published in both German and English. Initially, only foreign authors contributed articles in English but from the 1970s German-speaking authors increasingly wrote in English in order to reach an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Lebedev
Pyotr Nikolaevich Lebedev (; 24 February 1866 – 1 March 1912) was a Russian physicist. His name was also transliterated as Peter Lebedew and Peter Lebedev. Lebedev was a creator of first scientific school in Russia. Career Lebedev made his doctoral degree in Strasbourg under the supervision of August Kundt in 1887–1891. In 1891, he started working in Moscow State University in the group of Alexander Stoletov. There he made his famous experimental studies of electromagnetic waves. Along with Indian physicist Jagadish Chandra Bose he was one of the first to investigate millimeter waves, generating 50 GHz (6 mm) microwaves beginning in 1895 with a spark oscillator made of two platinum cylinders 1.5 cm long and 0.5 diameter immersed in kerosene at the focus of a parabolic reflector, and detecting the waves with an iron-constantan thermocouple detector.A. A. Kostenko, A. I. Nosich, P. F. Goldsmith, "Historical background and development of Soviet quasiop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
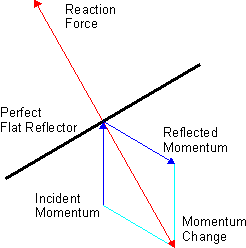
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electricity and magnetism, two distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. In essence, electric forces occur between any two charged particles, causing an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs exclusively between ''moving'' charged particles. These two effects combine to create electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of charge particles, which can exert influence on other particles via the Lorentz force. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. The electromagnetic force is responsible for many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |