|
Larende
Karaman, historically known as Laranda (Greek: Λάρανδα), is a city in south central Turkey, located in Central Anatolia, north of the Taurus Mountains, about south of Konya. It is the capital district of the Karaman Province. According to the 2000 census, the population of the province is 231,872 of which 132,064 live in the town of Karaman. The district covers an area of , and the town lies at an average elevation of . The Karaman Museum is one of the major sights. Etymology The town owes its name to Karaman Bey, who was one of the rulers of the Karamanid dynasty. The former name ''Laranda'' which in turn comes from the Luwian language ''Larawanda'', literally means "sandy, a sandy place". History In ancient times, Karaman was known as Laranda ( el, Λάρανδα). In the 6th century BC it came under Achaemenid rule until 322 BC, when it was destroyed by Perdiccas, a former general of Alexander the Great, after he had defeated Ariarathes I, king of Cappadocia. It lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
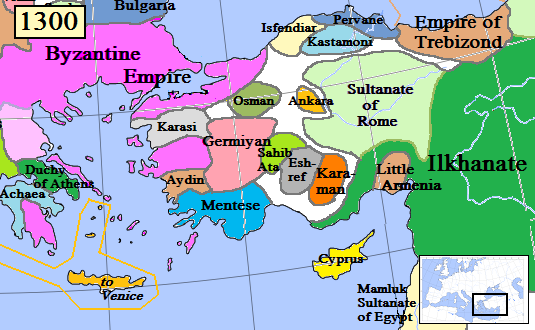
Karamanid
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the middle 1300s until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu and others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jones-Williams (New York: Taplinger, 1968), pp. 281–2. which participated in the revolt led by Baba Ishak and afterwards m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolian Beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A second more extensive period of foundations took place as a result of the decline of the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm in the second half of the 13th century. One of the beyliks, that of the Osmanoğlu from the Kayi tribe of the Oghuz Turks, from its capital in Bursa completed its conquest of other beyliks by the late 15th century, becoming the Ottoman Empire. The word "beylik" denotes a territory under the jurisdiction of a bey, equivalent in other European societies to a lord. History Following the 1071 Seljuq victory over the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert and the subsequent conquest of Anatolia, Oghuz clans began settling in present-day Turkey. The Seljuq Sultanate's central power established in Konya was largely the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilge Umar
Bilge Umar (born 1936) is a Turkish writer, researcher and jurist born in Karşıyaka, İzmir, Turkey. He did his studies in Istanbul University Law School, where he also worked, after graduation in 1958, as an assistant and received his doctorate degree in 1962, with a thesis entitled ''Annulment Suit under Turkish Enforcement-Bankruptcy Law'' becoming an Associate Professor in 1967. Then he moved back to İzmir and held various managerial posts in İzmir's Ege University, as aside a career as an academician. He became one of the founders of the university's Law School, where he became the deputy to the dean, and a full professor in 1970. Prof. Dr. Bilge Umar is currently the Head of the Department of Public Law of Yeditepe University (İstanbul) Faculty of Law and is teaching "Civil Procedure Law" and "Appeal Procedure and Arbitration". As much as his studies in various legal matters, he came to be known in Turkey for his popular books on ancient history (particularly on an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Kingdom Of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, Կիլիկիայի հայկական իշխանութիւն), was an Armenians, Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian refugees fleeing the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk invasion of Armenia., pp. 630–631. Located outside the Armenian Highlands and distinct from the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia of classical antiquity, antiquity, it was centered in the Cilicia region northwest of the Gulf of Alexandretta. The kingdom had its origins in the principality founded c. 1080 by the Rubenid dynasty, an alleged offshoot of the larger Bagratuni dynasty, which at various times had held the throne of Armenia. Their capital was originally at Tarsus (city), Tarsus, and later became Sis (ancient city), Sis. Cilicia wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 1152. He was crowned King of Italy on 24 April 1155 in Pavia and emperor by Pope Adrian IV on 18 June 1155 in Rome. Two years later, the term ' ("holy") first appeared in a document in connection with his empire. He was later formally crowned King of Burgundy, at Arles on 30 June 1178. He was named by the northern Italian cities which he attempted to rule: Barbarossa means "red beard" in Italian; in German, he was known as ', which means "Emperor Redbeard" in English. The prevalence of the Italian nickname, even in later German usage, reflects the centrality of the Italian campaigns to his career. Frederick was by inheritance Duke of Swabia (1147–1152, as Frederick III) before his i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes by the Turkomans at the battle of Malazgirt (Manzikert) is taken as a turning point in the history of Anatolia and the Byzantine Empire. or the Saljuqids, was an Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate and contributed to the Turco-Persian tradition in the medieval Middle East and Central Asia. The Seljuks established the Seljuk Empire (1037-1194), the Sultanate of Kermân (1041-1186) and the Sultanate of Rum (1074-1308), which at their heights stretched from Iran to Anatolia, and were the prime targets of the First Crusade. Early history The Seljuks originated from the Kinik branch of the Oghuz Turks, who in the 8th century lived on the periphery of the Muslim world, north of the Caspian Sea and Aral Sea in their Ogh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipater Of Derbe
Antipater of Derbe ( grc, Ἀντίπατρος) was a tyrant or prince of Derbe. He was a friend of Cicero's, one of whose letters, of uncertain date, is addressed on Antipater's behalf to Quintus Philippus, proconsul of the province of Asia, who was offended with Antipater and therefore held his sons hostage.Strabo xii. p. 392 ; Cic. ''Epistulae ad Familiares'' xiii. 73. Amyntas, the Lycaonia Lycaonia (; el, Λυκαονία, ''Lykaonia''; tr, Likaonya) was a large region in the interior of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), north of the Taurus Mountains. It was bounded on the east by Cappadocia, on the north by Galatia, on the west by ...n chieftain, murdered him and seized his principality. References * 1st-century BC rulers in Asia Correspondents of Cicero People from Roman Anatolia {{AncientRome-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revolt (499 BC), the Cappadocians were reported as occupying a region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine (Black Sea). Cappadocia, in this sense, was bounded in the south by the chain of the Taurus Mountains that separate it from Cilicia, to the east by the upper Euphrates, to the north by Pontus, and to the west by Lycaonia and eastern Galatia. Van Dam, R. ''Kingdom of Snow: Roman rule and Greek culture in Cappadocia.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002, p.13 The name, traditionally used in Christian sources throughout history, continues in use as an international Tourism in Turkey, tourism concept to define a region of exceptional natural wonders, in particular characterized by fairy chimneys and a unique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariarathes I Of Cappadocia
Ariarathes I (Old Iranian: ''Aryaraθa'', Aramaic: ''Ariorath'' or ''Ariourat''; grc, Ἀριαράθης, Ariaráthēs; 405/4 BC – 322 BC) was the last Achaemenid Persian governor (satrap) of the province (satrapy) of Northern Cappadocia, serving from the 340s BC to 331 BC. He led defensive efforts against the Macedonian invasion, commanded by Alexander the Great, and later fought at the Battle of Gaugamela under Darius III, the last King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire. After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, Ariarathes continued his resistance against the Macedonians, ruling concomitantly as an Achaemenid remnant and a precursor to the Kingdom of Cappadocia. He is regarded as the founder of the Iranian Ariarathid dynasty. Ariarathes was eventually captured and executed in 322 BC by the Macedonian Perdiccas. His territory was seized, whereafter it was contested between several of Alexander's successors and former generals. However, Ariarathes's dynastic successors reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)